|
Archival
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials, in any medium, or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the history and function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on the grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archival Science
Archival science, or archival studies, is the study and theory of building and Curator, curating archives, which are collections of documents, Sound recording and reproduction, recordings, photographs and various other materials in physical or digital formats. To build and curate an archive, one must acquire and evaluate the materials, and be able to access them later. To this end, archival science seeks to improve methods for Archival appraisal, appraising, storing, Preservation (library and archival science), preserving, and Archival processing, processing (arranging and describing) collections of materials. An archival record preserves data that is not intended to change. In order to be of value to society, archives must be trustworthy. Therefore, an archivist has a responsibility to authenticate archival materials, such as historical documents, and to ensure their reliability, integrity, and usability. Archival records must be what they claim to be; accurately represent the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archivist
An archivist is an information professional who assesses, collects, organizes, preserves, maintains control over, and provides access to records and archives determined to have long-term value. The records maintained by an archivist can consist of a variety of forms, including letters, diaries, logs, other personal documents, government documents, sound or picture recordings, digital files, or other physical objects. Description As Richard Pearce-Moses wrote: Determining what records have enduring value can be challenging. Archivists must also select records valuable enough to justify the costs of storage and preservation, plus the labor-intensive expenses of arrangement, description, and reference service. The theory and scholarly work underpinning archives practices is called archival science. The most common related occupations are librarians, museum curators, and records managers. The occupation of archivist is distinct from that of librarian. The two occupations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respect Des Fonds
''Respect des fonds'', or ''le respect pour les fonds'', is a principle in archival theory that proposes to group collections of archival records according to their fonds In archival science, a fonds (plural also ''fonds'') is a group of documents that share the same origin and have occurred naturally as an outgrowth of the daily workings of an agency, individual, or organization. An example of a fonds could be ... (according to the entity by which they were created or from which they were received). It is one of several principles stemming from provenance that have guided archival arrangement and description from the late 19th century until the present day. It is similar to archival integrity, which dictates that "a body of records resulting from the same activity must be preserved as a group." It is also closely related to the idea of original order – the idea that archivists ought to maintain records using the creator's organizational system. However, ''respect des fon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French National Archives
The Archives nationales (; abbreviated AN; English: National Archives) are the national archives of France. They preserve the archives of the French state, apart from the archives of the Ministry of Armed Forces and Ministry of Foreign Affairs, as these two ministries have their own archive services, the Defence Historical Service (SHD) and respectively. The National Archives of France also keep the archives of local secular and religious institutions from the Paris Region seized at the time of the French Revolution (such as local royal courts of Paris, suburban abbeys and monasteries, etc), as well as the archives produced by the notaries of Paris during five centuries, and many private archives donated or placed in the custody of the National Archives by prominent aristocratic families, industrialists, and historical figures. The National Archives have one of the largest and oldest archival collections in the world. As of 2022, they held of physical records (the total l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Source
In the study of history as an academic discipline, a primary source (also called an original source) is an Artifact (archaeology), artifact, document, diary, manuscript, autobiography, recording, or any other source of information that was created at the time under study. It serves as an original source of information about the topic. Similar definitions can be used in library science and other areas of scholarship, although different fields have somewhat different definitions. In journalism, a primary source can be a person with direct knowledge of a situation, or a document written by such a person. Primary sources are distinguished from ''secondary sources'', which cite, comment on, or build upon primary sources. Generally, accounts written after the fact with the benefit of hindsight are secondary. A secondary source may also be a primary source depending on how it is used. For example, a memoir would be considered a primary source in research concerning its author or about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Hikaye
Hikaye, or Palestinian hikaye (), is a unique form of oral literature from Palestine that is performed by women, particularly those who are older. In 2005, it was listed as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO, and in 2008, it was inscribed to UNESCO's List of Intangible Cultural Heritage. However, as a result of changing social structures, broader access to school education, and the spread of mass media, the tradition is slowly dying out. Background Hikaye are a unique form of literature, taking the form of educational folk tales passed down orally by older Palestinian women to other younger women and children. Usually performed in the fallahi or madani dialects of Arabic, they are intended for entertainment and education, and are mostly performed in a domestic environment, usually in winter. Typically recited using an expressive tone, these spoken works discuss social issues and histories, particularly those that impact women. They m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
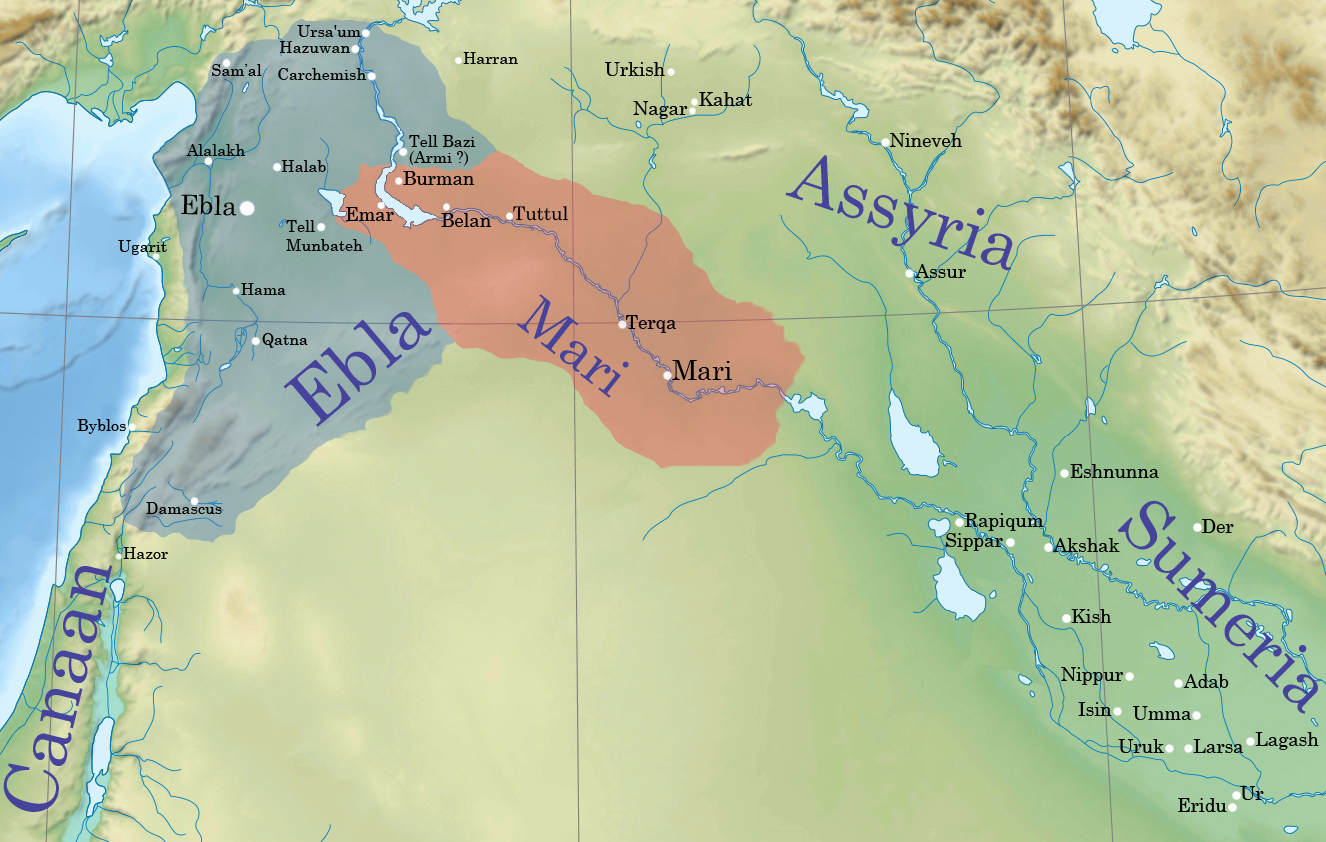
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Ancient Near East, Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electronic media, digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, Cassette tape, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer Library makerspace, creation stations for wiktionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natalis De Wailly
Natalis de Wailly (10 May 1805, Mézières, Ardennes – 4 December 1886, Paris) was a French archivist, librarian and historian. In 1841, as head of the Administrative Section of the Royal Archives, he wrote a ministerial circular, issued by Count Tanneguy Duchâtel, Minister of the Interior, stating that records should be grouped according to the nature of the institution that has accumulated them and formulating the principle of ''respect des fonds'' (up until that point, archives had often been sorted according to subject, date or place). In 1854, he was appointed head of the manuscript department of the Bibliothèque impériale. A member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres since 1841 and of several learned societies (e.g. Société de l'histoire de France, Société des anciens textes français, Comité des travaux historiques et scientifiques), he was a renowned paleographer and published scientific editions of medieval chroniclers (e.g. Villehardo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hattusas
Hattusa, also Hattuşa, Ḫattuša, Hattusas, or Hattusha, was the capital of the Hittites, Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age during two distinct periods. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey (originally Boğazköy) within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: ''Halys River, Halys''). Charles Texier brought attention to the ruins after his visit in 1834. Over the following century, sporadic exploration occurred, involving different archaeologists. The Deutsche Orient-Gesellschaft, German Oriental Society and the German Archaeological Institute began systematic excavations in the early 20th century, which continue to this day. Hattusa was added to the List of World Heritage Sites in Turkey, UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. History The earliest traces of settlement on the site are from the sixth millennium BC during the Chalcolithic period. Toward the end of the 3rd Millennium BC the Hattian people established a settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldassarre Bonifacio
Baldassarre Bonifacio (5 January 1585 – 17 November 1659) was an Italian Catholic bishop, theologian, scholar and historian, known for his work (1632), the first known treatise on the management of archives. Biography Baldassare Bonifacio was born at Crema, in the Republic of Venice, on January 5, 1586, the son of Bonifacio Bonifacio, celebrated jurist and assessor, and of Paola Corniani, the daughter of Giovanni Francesco Corniani, likewise jurist and assessor. He studied humanities at Rovigo under the supervision of Antonio Riccoboni and graduated in law at the University of Padua at the age of eighteen. About two years later he was appointed professor of law at the college of Rovigo, where he lectured on the Institutes of Justinian. Sometime within the next five years, Bonifacio accompanied Count Girolamo di Porzia, bishop of Adria and papal nuncio, to Germany as a private secretary. Upon his return to the Republic of Venice he was made archpriest of Rovigo. In 161 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |