|
Archimedes Number
In viscous fluid dynamics, the Archimedes number (Ar), is a dimensionless number used to determine the motion of fluids due to density differences, named after the ancient Greek scientist and mathematician Archimedes. It is the ratio of gravitational forces to viscous forces and has the form: :\begin\mathrm & = \frac \\ & = \frac \\ \end where: * g is the local external field (for example gravitational acceleration), , * L is the characteristic length of body, . * \frac is the submerged specific gravity, * \rho_\ell is the density of the fluid, , * \rho is the density of the body, , * \nu = \frac is the kinematic viscosity, , * \mu is the dynamic viscosity, , Uses The Archimedes number is generally used in design of tubular chemical process reactors. The following are non-exhaustive examples of using the Archimedes number in reactor design. Packed-bed fluidization design The Archimedes number is applied often in the engineering of packed beds, which are very common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion) and (the study of water and other liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moment (physics), moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipeline transport, pipelines, weather forecasting, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space, understanding large scale Geophysical fluid dynamics, geophysical flows involving oceans/atmosphere and Nuclear weapon design, modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Fluid
For fluid power, a working fluid is a gas or liquid that primarily transfers force, motion, or mechanical energy. In hydraulics, water or hydraulic fluid transfers force between hydraulic components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, and hydraulic motors that are assembled into hydraulic machinery, hydraulic drive systems, etc. In pneumatics, the working fluid is air or another gas which transfers force between pneumatic components such as compressors, vacuum pumps, pneumatic cylinders, and pneumatic motors. In pneumatic systems, the working gas also energy storage, stores energy because it is compressible. (Gases also heat up as they are compressed and cool as they expand. Some gases also condense into liquids as they are compressed and boil as pressure is reduced.) For passive heat transfer, a working fluid is a gas or liquid, usually called a coolant or heat transfer fluid, that primarily transfers heat into or out of a region of interest by conduction (heat), conduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galilei Number
In fluid dynamics, the Galilei number (Ga), sometimes also referred to as Galileo number (see discussion), is a dimensionless number named after Italian scientist Galileo Galilei (1564-1642). It may be regarded as proportional to gravity forces divided by viscous forces. The Galilei number is used in viscous flow and thermal expansion calculations, for example to describe fluid film flow over walls. These flows apply to condensers or chemical columns. : \mathrm = \frac * ''g'': gravitational acceleration, ( SI units: m/ s2) * ''L'': characteristic length, ( SI units: m) * ''ν'': characteristic kinematic viscosity, ( SI units: m2/s) See also *Archimedes number In viscous fluid dynamics, the Archimedes number (Ar), is a dimensionless number used to determine the motion of fluids due to density differences, named after the ancient Greek scientist and mathematician Archimedes. It is the ratio of gravita ... References *VDI-Wärmeatlas; 5., extended Edition; VDI Verlag Düs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Quantity
Dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one, are quantities implicitly defined in a manner that prevents their aggregation into unit of measurement, units of measurement. ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. Typically expressed as ratios that align with another system, these quantities do not necessitate explicitly defined Unit of measurement, units. For instance, alcohol by volume (ABV) represents a volumetric ratio; its value remains independent of the specific Unit of volume, units of volume used, such as in milliliters per milliliter (mL/mL). The 1, number one is recognized as a dimensionless Base unit of measurement, base quantity. Radians serve as dimensionless units for Angle, angular measurements, derived from the universal ratio of 2π times the radius of a circle being equal to its circumference. Dimensionless quantities play a crucial role serving as parameters in differential equations in various technical disciplines. In calculus, concepts like the unitless ratios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection (heat Transfer)
Convection (or convective heat transfer) is the heat transfer, transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combined processes of Conduction (heat), conduction (heat diffusion) and advection (heat transfer by bulk fluid flow). Convection is usually the dominant form of heat transfer in liquids and gases. Note that this definition of convection is only applicable in Heat transfer and Thermodynamics, thermodynamic contexts. It should not be confused with the Fluid dynamics, dynamic fluid phenomenon of Convection#Terminology, convection, which is typically referred to as ''Natural Convection'' in thermodynamic contexts in order to distinguish the two. Overview Convection can be "forced" by movement of a fluid by means other than buoyancy forces (for example, a water pump in an automobile engine). Thermal expansion of fluids may also force convection. In o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be Transient state, transient (such as when a Multiphasic liquid, multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see convection cell). The convection may be due to Gravity, gravitational, Electromagnetism, electromagnetic or Fictitious force, fictitious body forces. Convection (heat transfer), Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its Earth's mantle, mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Flow
Stokes flow (named after George Gabriel Stokes), also named creeping flow or creeping motion,Kim, S. & Karrila, S. J. (2005) ''Microhydrodynamics: Principles and Selected Applications'', Dover. . is a type of fluid flow where advection, advective inertial forces are small compared with Viscosity, viscous forces. The Reynolds number is low, i.e. \mathrm \ll 1. This is a typical situation in flows where the fluid velocities are very slow, the viscosities are very large, or the length-scales of the flow are very small. Creeping flow was first studied to understand lubrication. In nature, this type of flow occurs in the swimming of microorganisms and sperm. In technology, it occurs in paint, Microelectromechanical systems, MEMS devices, and in the flow of viscous polymers generally. The equations of motion for Stokes flow, called the Stokes equations, are a linearization of the Navier–Stokes equations, and thus can be solved by a number of well-known methods for linear different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
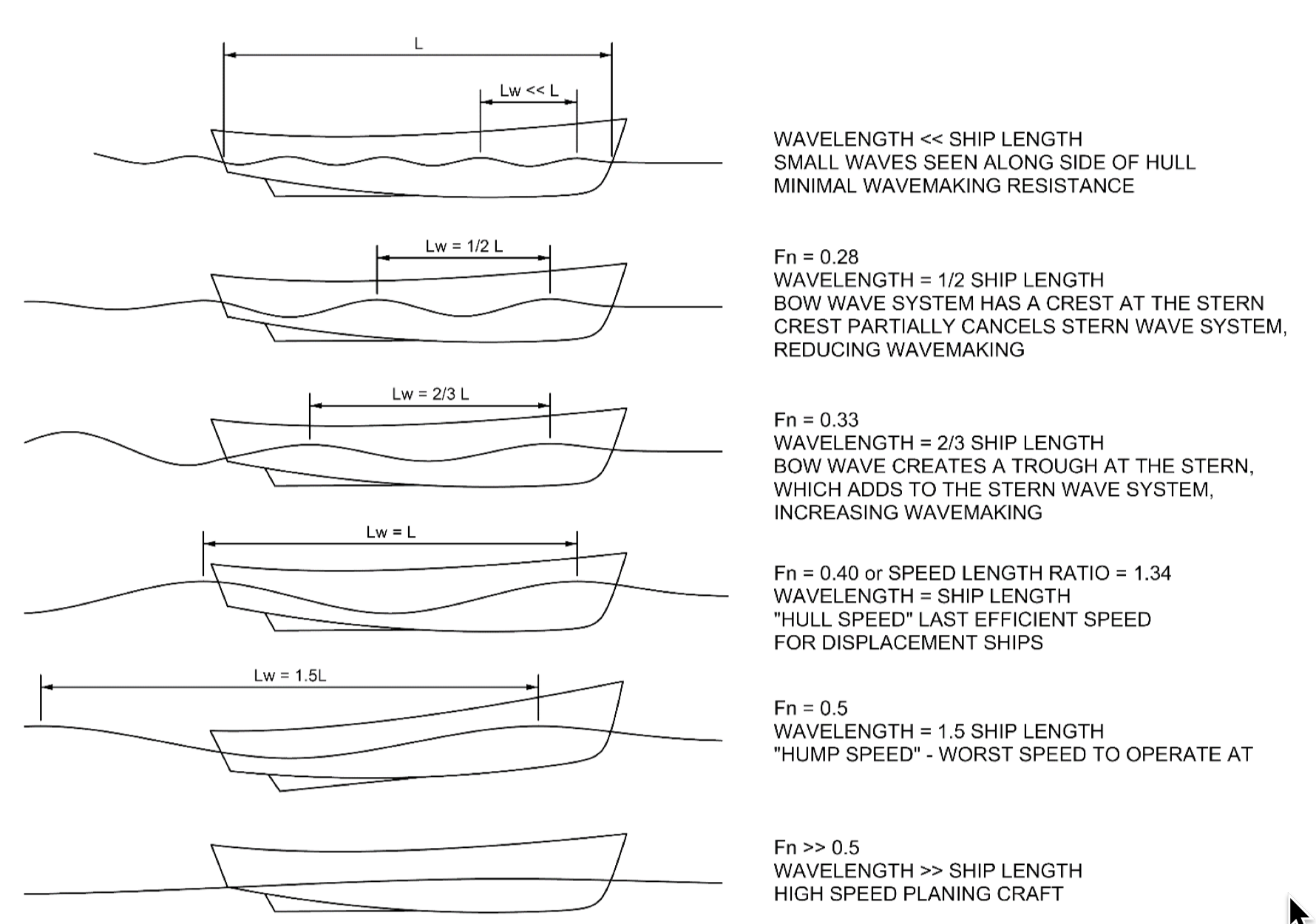
Froude Number
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external force field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity (in m/s), is the local gravity field (in m/s2), and is a characteristic length (in m). The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eötvös Number
In fluid dynamics the Eötvös number (Eo), also called the Bond number (Bo), is a dimensionless number measuring the importance of gravitational forces compared to surface tension forces for the movement of liquid front. Alongside the capillary number, commonly denoted \mathrm, which represents the contribution of viscous drag, \mathrm is useful for studying the movement of fluid in porous or granular media, such as soil.Dynamics of viscous entrapped saturated zones in partially wetted porous media Transport in Porous Media (2018), 125(2), 193-210 The Bond number (or Eötvös number) is also used (together with Morton number) to characterize the shape of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble Column Reactor
A bubble column reactor is a chemical reactor that belongs to the general class of multiphase reactors, which consists of three main categories: Trickle-bed reactor, trickle bed reactor (fixed or packed bed), fluidized bed reactor, and bubble column reactor. A bubble column reactor is a very simple device consisting of a vertical vessel filled with water with a gas distributor at the inlet. Due to the ease of design and operation, which does not involve moving parts, they are widely used in the Chemical industry, chemical, biochemical, Petrochemical industry, petrochemical, and Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical industries to generate and control gas-liquid Chemical reaction, chemical reactions. Despite the simple column arrangement, the hydrodynamics of bubble columns is very complex due to the interactions between liquid and gas phases. In recent years, Computational fluid dynamics, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has become a very popular tool to design and optimize b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |