|
Archaeological Sites
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort, although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition, such as a hoard or burial, can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined '' alluvion'' (the French term for alluvium) as new land formed by deposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmizegetusa Regia
Sarmizegetusa Regia (also known as ''Sarmisegetusa'', ''Sarmisegethusa'', ''Sarmisegethuza''; ) was the capital and the most important military, religious and political centre of the Dacians before the wars with the Roman Empire. Built on top of a 1200 m high mountain, the fortress, consisting of six citadels, was the core of a strategic and defensive system in the Orăștie Mountains (in present-day Romania). Sarmizegetusa Regia should not be confused with Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, the Roman capital of Dacia built by Roman Emperor Trajan some 40 km away, which was not the Dacian capital. Sarmizegetusa Ulpia was discovered earlier, was known already in the early 1900s, and was initially mistaken for the Dacian capital, a confusion which led to incorrect conclusions being made regarding the military history and organization of the Dacians. Etymology Several hypotheses have been advanced to explain the origin of the name ''Sarmizegetusa''. The most important of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by #Names, other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was a prominent city of the Carthaginian Empire and Roman Libya at the mouth of the Wadi Lebda in the Mediterranean. Established as a Punic people, Punic settlement prior to 500 BC, the city experienced significant expansion under Roman Emperor Septimius Severus (), who was born in the city. The Legio III Augusta, 3rd Augustan Legion was stationed here to defend the city against Berbers, Berber incursions. After the legion's dissolution under in 238, the city was increasingly open to raids in the later part of the 3rd century. Diocletian reinstated the city as provincial capital, and it grew again in prosperity until it fell to the Vandals in 439. It was reincorporated into the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Empire in 533 but continued to be plagued by Berber raids and never recovered its former importance. It fell to the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, Muslim invasion in and was subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleuron, Aetolia
Pleuron (; , ''Plevrona'' or Ασφακοβούνι, ''Asfakovouni'') was a city in ancient Aetolia, Greece. The name refers to two settlements, the older of which was at the foot of Mount Curium between the river Acheloos and the river Evenos, See ''The Geography of Strabo'', Book X, Ch. and Ch. at LacusCurtius. and was mentioned by Homer in the Catalogue of Ships in the ''Iliad''. The territory of Pleuron was called Pleuronia. The ruins of this more ancient city are 1.5 km to the southeast of the newer one. The circuit wall exhibits "the large roughly shaped stones and small stones in the interstices which are the characteristics of Cyclopean masonry." Old Pleuron Old Pleuron (ἡ παλαιὰ Πλευρών) was situated in the plain between the Achelous and the Evenus, west of Calydon, at the foot of Mount Curium, from which the Curetes are said to have derived their name. Pleuron and Calydon were the two chief towns of Aetolia in the heroic age, and are said by Strabo to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
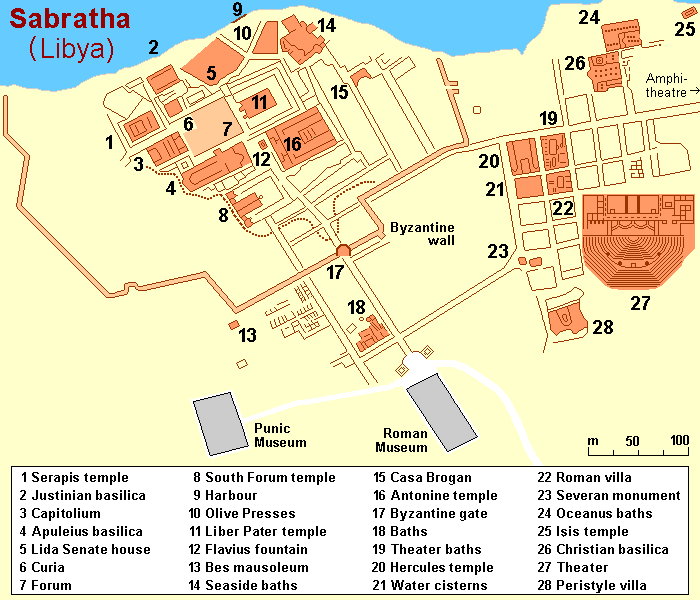
Sabratha
Sabratha (; also ''Sabratah'', ''Siburata''), in the Zawiya District''شعبيات الجماهيرية العظمى''Sha'biyat of Great Jamahiriya accessed 20 July 2009, in Arabic of Libya, was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis (region of Africa), Tripolis, alongside Oea and Leptis Magna. From 2001 to 2007 it was the capital of the former Sabratha wa Sorman District. It lies on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast about west of modern Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. The extant archaeological site was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982. Ancient Sabratha Sabratha's port was established, perhaps about 500BCE, as the Phoenician trading-post of Tsabratan (, , or , ). This seems to have been a Berber language, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. With an area of almost , it is the 4th-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya claims 32,000 square kilometres of southeastern Algeria, south of the Libyan town of Ghat, Libya, Ghat. The largest city and capital is Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, which is located in northwestern Libya and contains over a million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berber people, Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrene, Libya
Cyrene, also sometimes anglicization of names, anglicized as Kyrene, was an ancient Greeks, ancient Greek Greek colonization, colony and ancient Romans, Roman Cities of the Roman Empire, city near present-day Shahhat in northeastern Libya in North Africa. It was part of the Pentapolis (North Africa), Pentapolis, an important group of five cities in the region, and gave the area its classical and early modern name Cyrenaica. Cyrene lies on a ridge of the Jebel Akhdar (Libya), Jebel Akhdar uplands. The archaeological remains cover several hectares and include several monumental temples, stoas, theatres, bathhouses, churches, and palatial residences. The city is surrounded by the Necropolis of Cyrene. Since 1982, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city's port was Apollonia, Cyrenaica, Apollonia (Marsa Sousa), located about to the north. The city was attributed to Apollo and the legendary etymology, etymon Cyrene (mythology), Cyrene by the Greeks themselves but it was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, spanning List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands and nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions. It has a population of over 10 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilisation and the birthplace of Athenian democracy, democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major History of science in cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dion, Pieria
Dion (; ; ) is a village and municipal unit in the municipality of Dion-Olympos in the Pieria regional unit, Greece. It is located at the foot of Mount Olympus at a distance of 17 km from the capital city of Katerini. The seat of the municipal unit was in Kondariotissa. It is best known for its great ancient Macedonian sanctuary of Zeus and the ancient city, much of which is visible in the Archaeological Park of Dion and the Archaeological Museum of Dion. History The ancient city owes its name to the most important Macedonian sanctuary dedicated to Zeus (''Dios'', "of Zeus"), leader of the gods who dwelt on Mount Olympus; as recorded by Hesiod's ''Catalogue of Women'', Thyia, daughter of Deucalion, bore Zeus two sons, Magnes and Makednos, eponyms of Magnetes and Macedonians, who dwelt in Pieria at the foot of Mount Olympus. Hence from very ancient times, a large altar had been set up for the worship of Olympian Zeus and his daughters, the Muses, in a uniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Archaeology
Urban archaeology is a sub discipline of archaeology specializing in the material past of towns and cities where long-term human habitation has often left a rich record of the past. In modern times, when someone talks about living in a city, they are in an area with many surrounding people and buildings, generally quite tall ones. In archaeological terms, cities give great information because of the infrastructure they have and amounts of people that were around one another. Through the years there has been one big method used for urban archaeology along with significant historic developments. Large concentrations of humans produce large concentrations of waste. Kitchen waste, broken objects, and similar material all need to be disposed of, while small numbers of people can dispose of their waste locally without encouraging vermin or endangering their health. Once people began to live together in large numbers, around five thousand years ago, such methods began to become impracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillwash
Colluvium (also colluvial material or colluvial soil) is a general name for loose, unconsolidated sediments that have been deposited at the base of hillslopes by either rainwash, sheetwash, slow continuous downslope creep, or a variable combination of these processes. Colluvium is typically composed of a heterogeneous range of rock types and sediments ranging from silt to rock fragments of various sizes. This term is also used to specifically refer to sediment deposited at the base of a hillslope by unconcentrated surface runoff or sheet erosion. Location Colluviation refers to the buildup of colluvium at the base of a hillslope.Jackson, JA, J Mehl, and K. Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. Goodie, AS (2003) ''Colluvium'' in A. S. Goodie, ed., pp. 173, Encyclopedia of Geomorphology Volume 1, A–I. Routledge, New York, New York. 1200 pp. Colluvium is typically loosely consolidated angular material located a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |