|
Arabic–English Lexicon
__NOTOC__ The ''Arabic–English Lexicon'' is an Arabic–English dictionary compiled by Edward William Lane (died 1876), It was published in eight volumes during the second half of the 19th century. It consists of Arabic words defined and explained in the English language. But Lane does not use his own knowledge of Arabic to give definitions to the words. Instead, the definitions are taken from older Arabic dictionaries, primarily medieval Arabic dictionaries. Lane translates these definitions into English, and he carefully notes which dictionaries are giving which definitions. History In 1842, Lane, who had already won fame as an Arabist for his ''Manners and Customs of the Modern Egyptians'' and his version of the '' One Thousand and One Nights'', received a sponsorship from Lord Prudhoe, later Duke of Northumberland, to compile an Arabic–English dictionary. Lane set to work at once, making his third voyage to Cairo to collect materials in the same year. Since the Muslim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Lane-Poole
Stanley Edward Lane-Poole (18 December 1854 – 29 December 1931) was a British orientalist and archaeologist. Biography Lane Poole was Born in London, England, the eldest of three children (two sons and a daughter) of Edward Stanley Poole (1830–1867) and his wife, Roberta Elizabeth Louisa (1828–1866), daughter of Charles Reddelien, a naturalized German. His paternal grandmother Sophia Lane Poole, uncle Reginald Stuart Poole and great-uncle Edward William Lane were famous for their work in orientalism and archaeology. His other great-uncle was Richard James Lane, a distinguished Victorian lithographer and engraver. His brother Reginald Lane Poole was an archivist and historian. Both his mother and father died during his childhood, so Poole and his siblings were raised by their grandmother Sophia Lane Poole and their great-uncle Edward William Lane. From 1874 to 1892 he worked in the British Museum, and after that in Egypt researching on Egyptian archaeology. From 1897 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASIN
Asin Thottumkal (born 26 October 1985), known mononyomusly as Asin, is an Indian former actress who appeared predominantly in Tamil cinema, Tamil, Hindi and Telugu language, Telugu films. Asin is a recipient of List of awards and nominations received by Asin, several accolades including a Filmfare Awards, Filmfare Award, two Filmfare Awards South and four South Indian International Movie Awards, SIIMA Awards. The Government of Tamil Nadu honoured her with the state's highest civilian award Kalaimamani, in 2009. Asin is considered as one of the leading South Indian actresses of the 2000s and is referred to as the "Queen of Kollywood". A trained Bharatanatyam dancer, Asin made her acting debut at 15 in Sathyan Anthikkad's Malayalam film ''Narendran Makan Jayakanthan Vaka'' (2001). Asin had her first commercial success with the Telugu language, Telugu film ''Amma Nanna O Tamila Ammayi'' in 2003, and won a Filmfare Award for Best Actress – Telugu, Filmfare Best Telugu Actress Aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
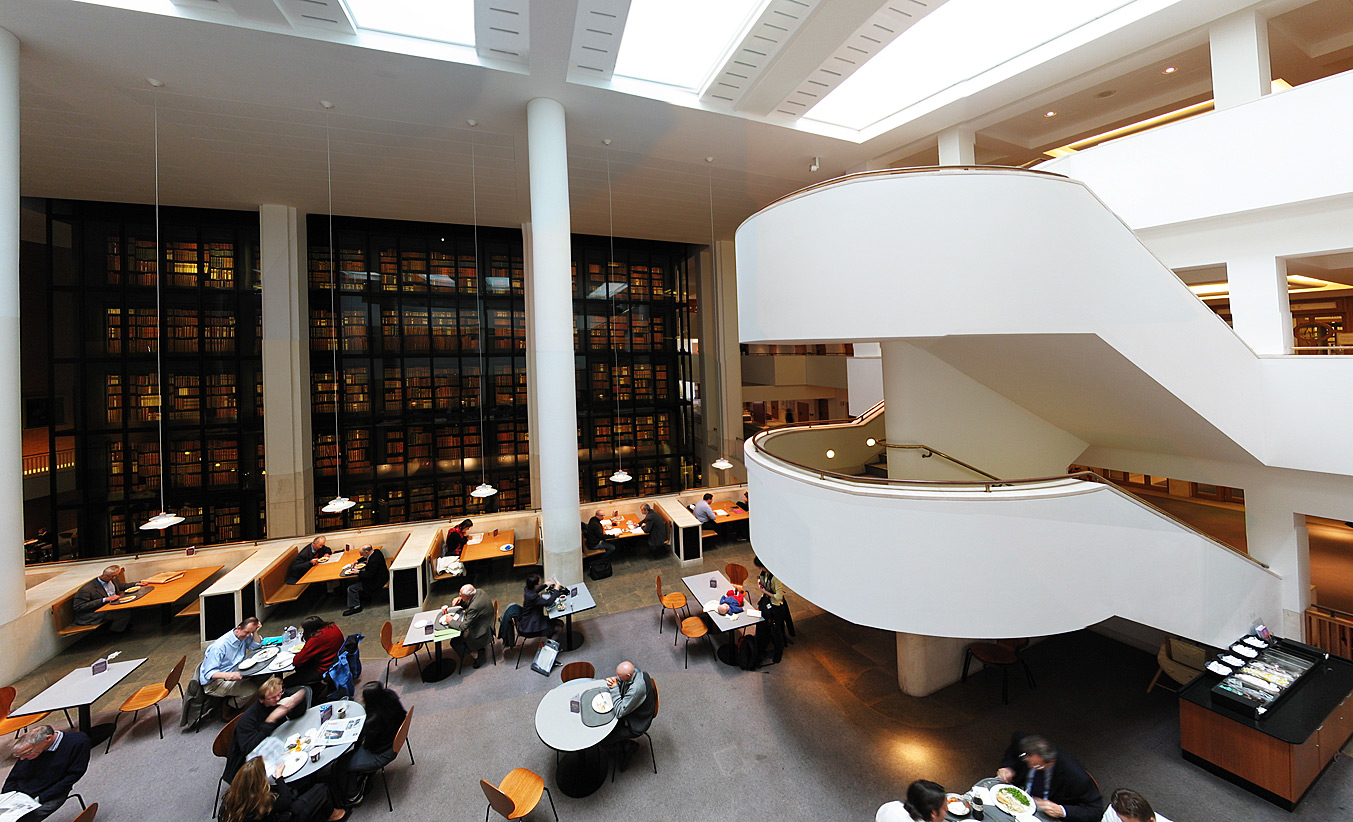
British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom. Based in London, it is one of the largest libraries in the world, with an estimated collection of between 170 and 200 million items from multiple countries. As a legal deposit library, it receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, as well as a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the United Kingdom. The library operates as a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. The British Library is a major research library, with items in many languages and in many formats, both print and digital: books, manuscripts, journals, newspapers, magazines, sound and music recordings, videos, play-scripts, patents, databases, maps, stamps, prints, drawings. The Library's collections include around 14 million books, along with substantial holdings of manuscripts and items dating as far back as 2000 BC. The library maintains a programme for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaph
Kaph (also spelled kaf) is the eleventh letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''kāp'' 𐤊, Hebrew ''kāp̄'' , Aramaic ''kāp'' 𐡊, Syriac ''kāp̄'' ܟ, and Arabic ''kāf'' (in abjadi order). It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪋, South Arabian , and Ge'ez . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek kappa (Κ), Latin K, and Cyrillic К. Origin Kaph is thought to be derived from a pictogram of a hand (in both modern Arabic and modern Hebrew, kaph means "palm" or "grip"), though in Arabic the ''a'' in the name of the letter (كاف) is pronounced longer than the ''a'' in the word meaning "palm" (كَف). The small ک above the ''kāf'' in its final and isolated forms was originally ''‘alāmatu-l-ihmāl'', but became a permanent part of the letter. Previously this sign could also appear above the medial form of ''kāf'', instead of the stroke on its ascender. D46 Arabic kāf The letter is named ''kāf'', and it is written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Morgenländische Gesellschaft
The (, ''German Oriental Society''), abbreviated DMG, is a scholarly organization dedicated to Oriental studies, that is, to the study of the languages and cultures of the Near East and the Far East, the broader Orient, Asia, Oceania, and Africa. The DMG was established on 2 October 1845 in Leipzig by leading Oriental scholars from Germany, as well as members of other Orientalist societies such as the Asiatic Societies in Paris (the Société Asiatique), London (the Royal Asiatic Society), and Calcutta (the Asiatic Society). It was founded "to promote all aspects of the knowledge of Asia and of the countries closely related to it in every aspect, and to propagate participation of this in wider circles. Hence the Society will deal not only with oriental literature (''morgenländische Literatur'') but also with the history of these countries and the research of their situation both earlier and more recent times." The DMG has traditionally concentrated on the "knowledge of lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhart Dozy
Reinhart Pieter Anne Dozy (Leiden, Netherlands, 21 February 1820 – Leiden, 29 April 1883) was a Dutch scholar of French (Huguenot) origin, who was born in Leiden. He was an Orientalist scholar of Arabic language, history and literature. Biography The Dozys, like other contemporary French families, emigrated to the Low Countries after the revocation of the edict of Nantes, but some of the former appear to have settled in the Netherlands as early as 1647. Dozy studied at the University of Leiden, obtained the degree of doctor in 1844, was appointed an extraordinary professor of history in 1850, and professor in 1857. Dozy was a correspondent of the Royal Institute between 1848 and 1851. He became a member of the successor institute, the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, in 1855. Works In 1847 Reinhart Dozy's extensive studies in Oriental literature, Arabic language and history, resulted in his first publication, ''The History of the Almohads, preceded by a Sketc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Zabidi
Al-Murtaḍá al-Husaynī al-Zabīdī (), or Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad Murtaḍá al-Zabīdī (1732–1790 / 1145–1205 AH), also known as Murtada al-Zabidi, was an Indian Sunni polymath based in Cairo. He was a Hanafi scholar, hadith specialist, philologist, linguist, lexicographer, genealogist, biographer, historian, mystic and theologian. He was considered one of the leading intellectuals of the 18th century. He was also regarded as the greatest Hadith scholar of his time and one of the foremost philologists of the Arab post-classical era. Biography Murtaḍá' was born in 1732 (1145AH) in Bilgram, Hardoi, Uttar Pradesh, India. His family originated from Wasit in Iraq, from where his parents had emigrated to the Hadramawt region in the east of Yemenwhere the Husaynī tribe is situated. Murtaḍá earned his nisba 'al-Zabīdī' from Zabīd in the south western coastal plains of Yemen, which was a centre of academic learning where he had spent time studying. He began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward William Lane
Edward William Lane (17 September 1801 – 10 August 1876) was a British orientalist, translator and lexicographer. He is known for his ''Manners and Customs of the Modern Egyptians'' and the '' Arabic-English Lexicon,'' as well as his translations of ''One Thousand and One Nights'' and ''Selections from the Kur-án''. During his lifetime, Lane also wrote a detailed account of Egypt and the country's ancient sites, but the book, titled ''Description of Egypt,'' was published posthumously. It was first published by the American University in Cairo Press in 2000 and has been republished several times since then. Early years Lane was born at Hereford, England, the third son of the Rev. Dr Theophilus Lane, and grand-nephew of Thomas Gainsborough on his mother's side. After his father died in 1814, Lane was sent to grammar school at Bath and then Hereford, where he showed a talent for mathematics. He visited Cambridge but did not enrol in any of its colleges. Instead, Lane joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qoph
Qoph is the nineteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''qōp'' 𐤒, Hebrew ''qūp̄'' , Aramaic ''qop'' 𐡒, Syriac ''qōp̄'' ܩ, and Arabic ''qāf'' . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian , South Arabian , and Ge'ez . Its original sound value was a West Semitic emphatic stop, presumably . In Hebrew numerals, it has the numerical value of 100. Origins The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' () is uncertain. It is usually suggested to have originally depicted either a sewing needle, specifically the eye of a needle (Hebrew ''quf'' and Aramaic ''qopɑʔ'' both refer to the eye of a needle), or the back of a head and neck (''qāf'' in Arabic meant " nape"). According to an older suggestion, it may also have been a picture of a monkey and its tail (the Hebrew means "monkey"). Besides Aramaic ''Qop'', which gave rise to the letter in the Semitic abjads used in classical antiquity, Phoenician ''qōp'' is also the origin of the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulaq
Boulaq ( from "guard, customs post"), is a district of Cairo, in Egypt. It neighbours Downtown Cairo, Azbakeya, and the River Nile. History The westward shift of the Nile, especially between 1050 and 1350, made land available on its eastern side. There the development of Bulaq began in the 15th century. In this century, under sultan Barsbay Bulaq became the main port of Cairo. Bulaq is a dense indigenous district filled with small-scale workshops of industries such as the old printing press, metalworking and machine shops, which supported the early stages of building Cairo. It is populated with a mixed working class from all parts of Egypt, who migrated to the city during the 19th century to work on Muhammad ‘Ali's projects. To the north of the district is located the bulk of the city's newer industrial plants. The history of Bulaq goes back to the Mamluk rule of the fourteenth century when the site was the main port of Cairo filled with several wikalas, mosques and hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |