|
Apple Lossless Audio Codec
The Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC, ), also known as Apple Lossless, or Apple Lossless Encoder (ALE), is an audio coding format, and its reference audio codec implementation, developed by Apple for lossless data compression of digital music. After initially keeping it proprietary from its inception in 2004, in late 2011 Apple made the codec available open source and royalty-free. Traditionally, Apple has referred to the codec as ''Apple Lossless'', though more recently it has begun to use the abbreviated term ''ALAC'' when referring to the codec. ALAC data is frequently stored within an MP4 container with the filename extension '' .m4a''. This extension is also used by Apple for AAC (which is a lossy format) in an MP4 container (same container, different audio encoding). ALAC can also be used by the .CAF file type container, though this is much less common. Codec ALAC supports up to 8 channels of audio at 16, 20, 24 and 32 bit depth with a maximum sample rate of 384&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Inc
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Company by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne, the company was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. the following year. It was renamed Apple Inc. in 2007 as the company had expanded its focus from computers to consumer electronics. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue, with billion in the 2024 fiscal year. The company was founded to produce and market Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Its second computer, the Apple II, became a best seller as one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple introduced the Lisa in 1983 and the Macintosh in 1984, as some of the first computers to use a graphical user interface and a mouse. By 1985, internal company problems led to Jobs leavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossy Compression
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size for storing, handling, and transmitting content. Higher degrees of approximation create coarser images as more details are removed. This is opposed to lossless data compression (reversible data compression) which does not degrade the data. The amount of data reduction possible using lossy compression is much higher than using lossless techniques. Well-designed lossy compression technology often reduces file sizes significantly before degradation is noticed by the end-user. Even when noticeable by the user, further data reduction may be desirable (e.g., for real-time communication or to reduce transmission times or storage needs). The most widely used lossy compression algorithm is the discrete cosine transform (DCT), first published by N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: information extraction, modeling, and review. Information extraction is the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling is the practice of combining the gathered information into an abstract model, which can be used as a guide for designing the new object or syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serafina Brocious
Serafina Brocious is an American software engineer best known for her work on PyMusique and her demonstration of Onity HT lock system vulnerabilities in 2012. Notable projects PyMusique Brocious first saw recognition as founder of the PyMusique project, where she worked with Jon Lech Johansen of DeCSS fame. PyMusique allowed Linux users to purchase music from the iTunes music store without the standard FairPlay DRM implementation in place. Falling Leaf Systems During her employment with MP3Tunes, Brocious also joined forces with Brian Thomason, then an employee of another Michael Robertson company, Linspire Inc., to form Falling Leaf Systems LLC. Falling Leaf Systems attempted to commercialize the Alky Project, which was started by Brocious to enable Microsoft Windows games to run on other platforms. Falling Leaf Systems sold access to a membership site dubbed the Sapling Program, whereby users could access a build of Alky allowing them to demo the game Prey on either Linu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AirPlay
Airplay is how frequently a song is being played through broadcasting on radio stations. A song which is being played several times every day (spins) would have a significant amount of airplay. Music which became very popular on jukeboxes, in nightclubs and at discotheques between the 1940s and 1960s would also have airplay. Background For commercial broadcasting, airplay is usually the result of being placed into rotation, also called adding it to the station's playlist by the music director, possibly as the result of a Pay for Play sponsored by the record label. For student radio and other community radio or indie radio stations, it is often the selection by each disc jockey, usually at the suggestion of a music director. Geography Most countries have at least one radio airplay chart in existence, although larger countries such as Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, Japan, and Brazil have several, to cover different genres and areas of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
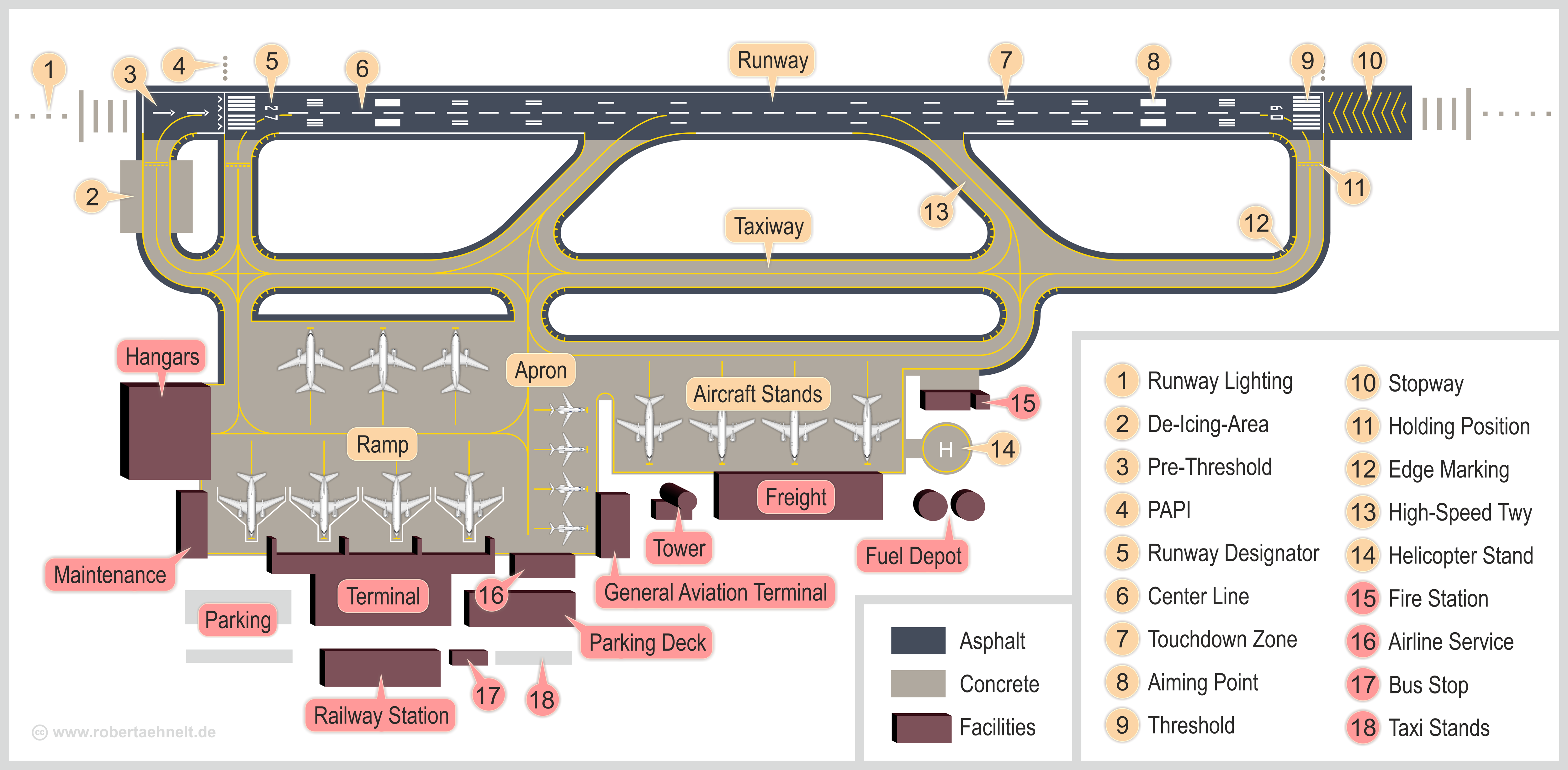
AirPort
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a airplane, plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as Air traffic control, control towers, hangars and airport terminal, terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and Airport lounge, lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Airport operations are extremely complex, with a complicated system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macworld
''Macworld'' is a digital magazine and website dedicated to products and software of Apple Inc., published by Foundry, a subsidiary of IDG. History ''Macworld'' was founded by David Bunnell and Cheryl Woodard (publishers) and Andrew Fluegelman (editor). It began as a print magazine in 1984, with its first issue distributed at the launch of the Macintosh computer. As a print magazine, it had the largest audited circulation (both total and newsstand) of Macintosh-focused magazines in North America, more than double its nearest competitor, '' MacLife''. In 1997, the Ziff-Davis-owned '' MacUser'' magazine was consolidated into ''Macworld'' within the new Mac Publishing joint venture between IDG and Ziff-Davis. In 1999, the combined company also purchased the online publication MacCentral Online, because ''Macworld'' did not have a powerful online news component at the time. In late 2001 IDG bought out Ziff-Davis' share of Mac Publishing, making it a wholly-owned subsidiary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITunes
iTunes is a media player, media library, and mobile device management (MDM) utility developed by Apple. It is used to purchase, play, download and organize digital multimedia on personal computers running the macOS and Windows operating systems, and can be used to rip songs from CDs as well as playing content from dynamic, smart playlists. It includes options for sound optimization and wirelessly sharing iTunes libraries. iTunes was announced by Apple CEO Steve Jobs on January 9, 2001. Its original and main focus was music, with a library offering organization and storage of Mac users' music collections. With the 2003 addition of the iTunes Store for purchasing and downloading digital music, and a Windows version of the program, it became an ubiquitous tool for managing music and configuring other features on Apple's line of iPod media players, which extended to the iPhone and iPad upon their introduction. From 2005 on, Apple expanded its core music features with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime
QuickTime (or QuickTime Player) is an extensible multimedia architecture created by Apple, which supports playing, streaming, encoding, and transcoding a variety of digital media formats. The term ''QuickTime'' also refers to the QuickTime Player front-end media player application, which is built-into macOS, and was formerly available for Windows. QuickTime was created in 1991, when the concept of playing digital video directly on computers was "groundbreaking." QuickTime could embed a number of advanced media types, including panoramic images (called QuickTime VR) and Adobe Flash. Over the 1990s, QuickTime became a dominant standard for digital multimedia, as it was integrated into many websites, applications, and video games, and adopted by professional filmmakers. The QuickTime File Format became the basis for the MPEG-4 standard. During its heyday, QuickTime was notably used to create the innovative ''Myst'' and '' Xplora1'' video games, and to exclusively distribute mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Audio
Core Audio is a low-level API for dealing with sound in Apple's macOS and iOS operating systems. It includes an implementation of the cross-platform OpenAL. Apple's Core Audio documentation states that "in creating this new architecture on Mac OS X, Apple's objective in the audio space has been twofold. The primary goal is to deliver a high-quality, superior audio experience for Macintosh users. The second objective reflects a shift in emphasis from developers having to establish their own audio and MIDI protocols in their applications to Apple moving ahead to assume responsibility for these services on the Macintosh platform." History It was introduced in Mac OS X 10.0 (Cheetah). Architecture Core Audio supports plugins, which can generate, receive, or process audio streams; these plugins are packaged as a bundle with the extension . See also * Audio Units Audio Units (AU) are a system-level Plug-in (computing), plug-in architecture provided by Core Audio in Ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding: encoding is done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Prediction
Linear prediction is a mathematical operation where future values of a discrete-time signal are estimated as a linear function of previous samples. In digital signal processing, linear prediction is often called linear predictive coding (LPC) and can thus be viewed as a subset of filter theory. In system analysis, a subfield of mathematics, linear prediction can be viewed as a part of mathematical modelling or optimization. The prediction model The most common representation is :\widehat(n) = \sum_^p a_i x(n-i)\, where \widehat(n) is the predicted signal value, x(n-i) the previous observed values, with p \leq n , and a_i the predictor coefficients. The error generated by this estimate is :e(n) = x(n) - \widehat(n)\, where x(n) is the true signal value. These equations are valid for all types of (one-dimensional) linear prediction. The differences are found in the way the predictor coefficients a_i are chosen. For multi-dimensional signals the error metric is often defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |