|
Antoniotto Usodimare
Antoniotto Usodimare or Usus di Mare (1416–1462) was a Genoese trader and explorer in the service of the Portuguese Prince Henry the Navigator. Jointly with Alvise Cadamosto, Usodimare discovered a great stretch of the West African coast in two known voyages in 1455 and 1456. They notably discovered the Cape Verde islands, and the Guinea coast from the Gambia River to the Geba River (in Guinea-Bissau). Background Antoniotto Usodimare was a prominent merchant and citizen of the Republic of Genoa, a director of the Genoese mint and a shareholder in the Banco di S. Giorgio. However, his fortunes soon took a turn for the worse. Around 1450, Usodimare fled Genoa to escape his creditors, making his way first to Seville, and then Lisbon.Russell, 2000: p.298, n.18 He eventually entered into the service of Portuguese Prince Henry the Navigator, hoping that by engaging in the profitable Portuguese trade on the West African coast, he might quickly recover his fortunes and pay back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Republic Of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in both the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Black Sea. Between the 16th and 17th centuries, it was one of the major financial centres of Europe. Throughout its history, the Genoese Republic established Genoese colonies, numerous colonies throughout the Mediterranean and the Black Sea, including Corsica from 1347 to 1768, Monaco, Gazaria (Genoese colonies), Southern Crimea from 1266 to 1475, and the islands of Lesbos and Chios from the 14th century to 1462 and 1566, respectively. With the arrival of the early modern period, the Republic had lost many of its colonies, and shifted its focus to banking. This was successful for Genoa, which remained a hub of capitalism, with highly developed banks and trading companies. Genoa was known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caravel
The caravel (Portuguese language, Portuguese: , ) is a small sailing ship developed by the Portuguese that may be rigged with just lateen sails, or with a combination of lateen and Square rig, square sails. It was known for its agility and speed and its capacity for Windward and leeward, sailing windward (Tacking (sailing)#Beating, beating). Caravels were used by the Portuguese and Spanish for the voyages of exploration during the 15th and 16th centuries, in the Age of Exploration. The caravel is a poorly understood type of vessel. Though there are now some archaeologically investigated wrecks that are most likely caravels, information on this type is limited. We have a better understanding of the ships of the Greeks and Romans of classical antiquity than we do of the caravel. History The long development of the caravel was probably influenced by various Mediterranean tending or coastal craft. Among these influences might have been the boats known as , that were introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Navigatori Class Destroyer
The Navigatori class were a group of Italian destroyers built in 1928–1929 for the (Royal Italian Navy), named after Italian explorers. They fought in World War II. Just one vessel, ''Nicoloso Da Recco'', survived the conflict. Design These ships were built for the Regia Marina as a reply to the large ''contre-torpilleurs'' of the ''Jaguar'' and classes built for the French Navy. These ships were significantly larger than other contemporary Italian destroyers and were initially classed as ''esploratori'' or scouts. They were re-rated as destroyers in 1938. The main armament was a new model /50 gunCampbell, pp. 335–338 in three twin turrets which allowed for 45° elevation. The torpedo launchers consisted of two triple banks, each unusually comprising two separated by one . Two rangefinder positions were provided; one above the bridge and one in the after superstructure. Unit machinery was used comprising four boilers in two widely spaced boiler rooms and two turbine roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Regia Marina
The , ) (RM) or Royal Italian Navy was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy () from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the changed its name to '' Marina Militare'' ("Military Navy"). Origins The was established on 17 March 1861 following the proclamation of the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. Just as the Kingdom was a unification of various states in the Italian peninsula, so the was formed from the navies of those states, though the main constituents were the navies of the former kingdoms of Sardinia and Naples. The new Navy inherited a substantial number of ships, both sail- and steam-powered, and the long naval traditions of its constituents, especially those of Sardinia and Naples, but also suffered from some major handicaps. Firstly, it suffered from a lack of uniformity and cohesion; the was a heterogeneous mix of equipment, standards and practice, and even saw hostility between the officers from the various f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia (country), Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is Inflow (hydrology), supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Dniester. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea, not including the Sea of Azov, covers , has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caffa
Feodosia (, ''Feodosiia, Teodosiia''; , ''Feodosiya''), also called in English Theodosia (from ), is a city on the Crimean coast of the Black Sea. Feodosia serves as the administrative center of Feodosia Municipality, one of the regions into which Crimea is divided. During much of its history, the city was a significant settlement known as Caffa () or Kaffa ( Old Crimean Tatar/Ottoman Turkish: ; Crimean Tatar/). According to the 2014 census, its population was 69,145. History Theodosia (Greek colony) The city was founded as ''Theodosia'' (Θεοδοσία) by Greek colonists from Miletos in the 6th century BC. Noted for its rich agricultural lands, on which its trade depended, the city was destroyed by the Huns in the 4th century AD. Theodosia remained a minor village for much of the next nine hundred years. It was at times part of the sphere of influence of the Khazars (excavations have revealed Khazar artifacts dating back to the 9th century) and of the Byzantine Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wolof People
The Wolof people () are a Niger-Congo peoples, Niger-Congo ethnic group native to the Senegambia, Senegambia region of West Africa. Senegambia is today split between western Senegal, northwestern the Gambia, Gambia and coastal Mauritania; the Wolof form the largest ethnic group within Senegambia. In Senegal as a whole, the Wolof are the largest ethnic group (~39.7%), while elsewhere they are a minority. They Endonym and exonym, refer to themselves as ''Wolof'' and speak the Wolof language, in the West Atlantic languages, West Atlantic branch of the Niger–Congo family of languages; English inherited ''Wolof'' as both the adjectival ethnonym and the name of the language. Their early history is unclear. The earliest documented mention of the Wolof is found in the records of 15th-century, Portuguese-financed Italian traveller Alvise Cadamosto, who mentioned well-established Islamic Wolof chiefs advised by Muslim counselors. The Wolof belonged to the medieval-era Wolof Empire of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cacheu River
The Cacheu ( Portuguese: ''Rio Cacheu'') is a river of Guinea-Bissau also known as the Farim along its upper course. Its total length is about 257 km. One of its major tributaries is the Canjambari River. Course Its headwaters are near the northern border of the country, north of Contuboel and close to a bend of the Geba River. It runs west, by the town of Farim and close to Bigenè, and broadens into an estuary on whose south shore the town of Cacheu may be found. Elia Island is a fairly large island located on the right bank of the river close to its mouth. The island's western end lies east of the confluence with the Elia River with Ongueringao Island on the other bank. The Cacheu is navigable to large (2,000-ton) ships for about 97 km, and to smaller vessels much further; it was formerly an important route for commerce. History During the Portuguese Colonial War, the Guinea-Bissau War of Independence The Guinea-Bissau War of Independence (), also known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cape Roxo
Cape Roxo (, ) is a headland in West Africa, marking the westernmost frontier of Guinea-Bissau with Senegal. On the lower side is the São Domingos district of the Cacheu Region of the Republic of Guinea-Bissau; above it is the Oussouye Department of the Ziguinchor Region of the Republic of Senegal. Cape Roxo marks a significant angle shift in the outline of the African coast, with the coast running north–south above it, and turning southeast below it. It was originally called ''Capo Rosso'' by Venetian explorer Alvise Cadamosto in 1456 on account of its reddish appearance ( = red in Italian). Although it is sometimes found translated as ''Cabo Vermelho'' in some old Portuguese maps, Cadamosto's Italian term was largely adopted as ''Cabo Roxo'' by most Portuguese cartographers (in Portuguese, means 'purple', so it did not sound foreign.)e.g. A.M. de Castilho (1866)'' Descripção e roteiro da costa occidental de Africa, desde o cabo de Espartel até o das Agulhas''. Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Casamance River
The Casamance River ( French: ''Fleuve Casamance'') in Senegal flows westward for the most part into the Atlantic Ocean along a path about in length. However, only are navigable. The Casamance is the principal river of the Kolda, Sédhiou, and Ziguinchor Regions in the southern portion of Senegal. It is located between the Gambia River to the north and the Cacheu and Geba rivers to the south. There is a bridge at Ziguinchor Ziguinchor (; ; ) is the capital of the Ziguinchor Region, and the chief town of the Casamance area of Senegal, lying at the mouth of the Casamance River. It has a population of 214,874 (2023 census). It is the eighth largest city of Senegal ..., one of the most important towns on the river, that connects it to Bignona on the north bank. Other important settlements on its banks include Goudomp, Sedhiou, Diattakounda, Tanaff, and Kolda. The river is named after the ''Kasa Mansa'', or king of the precolonial Kasa kingdom. References *Much of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
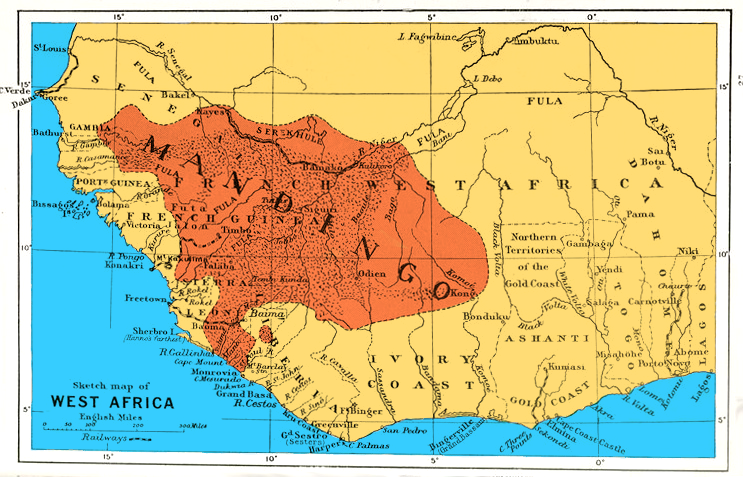
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |