|
Antoine Equation
The Antoine equation is a class of semi-empirical correlations describing the relation between vapor pressure and temperature for pure substances. The Antoine equation is derived from the Clausius–Clapeyron relation. The equation was presented in 1888 by the French engineer (1825–1897). Equation The Antoine equation is \log_ p = A - \frac, where is the vapor pressure, is temperature (in °C or in K according to the value of ), and , and are component-specific constants. The simplified form with set to zero, \log_ p = A - \frac, is the August equation, after the German physicist Ernst Ferdinand August (1795–1870). The August equation describes a linear relation between the logarithm of the pressure and the reciprocal temperature. This assumes a temperature-independent heat of vaporization. The Antoine equation allows an improved, but still inexact description of the change of the heat of vaporization with the temperature. The Antoine equation can also be tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which '' confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' scientific hypotheses and arbitrates between competing theories. For this role, evidence must be public and uncontroversial, like observable physical objects or events and unlike private mental states, so th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Activity
In thermodynamics, activity (symbol ) is a measure of the "effective concentration" of a species in a mixture, in the sense that the species' chemical potential depends on the activity of a real solution in the same way that it would depend on concentration for an ideal solution. The term "activity" in this sense was coined by the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis in 1907. By convention, activity is treated as a dimensionless quantity, although its value depends on customary choices of standard state for the species. The activity of pure substances in condensed phases (solids and liquids) is taken as = 1. Activity depends on temperature, pressure and composition of the mixture, among other things. For gases, the activity is the effective partial pressure, and is usually referred to as fugacity. The difference between activity and other measures of concentration arises because the interactions between different types of molecules in non-ideal gases or solutions are different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
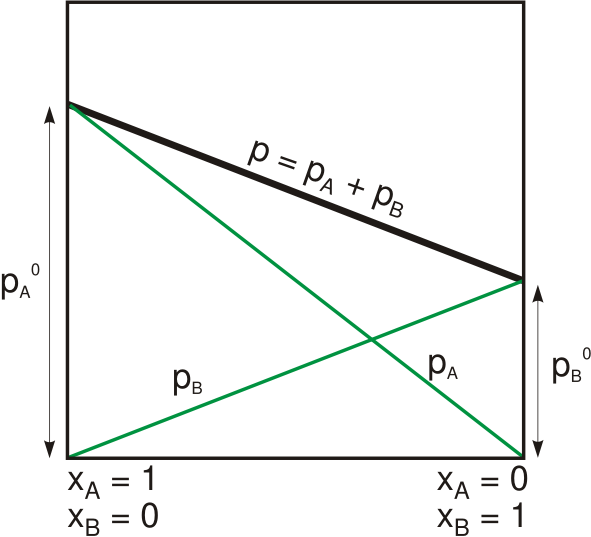
Raoult's Law
Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. In consequence, the relative lowering of vapor pressure of a dilute solution of nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution. Mathematically, Raoult's law for a single component in an ideal solution is stated as : p_i = p_i^\star x_i where p_i is the partial pressure of the component i in the gaseous mixture above the solution, p_i^\star is the equilibrium vapor pressure of the pure component i, and x_i is the mole fraction of the component i in the liquid or solid solution. Where two volatile liquids A and B are mixed with each other to form a solution, the vapor phase consists of both compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goff–Gratch Equation
The Goff–Gratch equation is one (arguably the first reliable in history) amongst many experimental correlation proposed to estimate the saturation water vapor pressure at a given temperature. Another similar equation based on more recent data is the Arden Buck equation. Historical note This equation is named after the authors of the original scientific article who described how to calculate the saturation water vapor pressure above a flat free water surface as a function of temperature (Goff and Gratch, 1946). Goff (1957) later revised his formula, and the latter was recommended for use by the World Meteorological Organization in 1988, with further corrections in 2000. The current 2015 edition of the WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49) however states in Volume 1, Part III, Section 1.2.1, that any formula or constant given in the Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation a.k.a. CIMO-Guide (WMO-No. 8) shall be used, and this document only contains the muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arden Buck Equation
The Arden Buck equations are a group of empirical correlations that relate the saturation vapor pressure to temperature for moist air. The curve fits have been optimized for more accuracy than the Goff–Gratch equation in the range .Buck 1981 A set of several equations were developed, each of which is applicable in a different situation. Formula The equations suggested by (which are modifications of the equations in ) are: : P_\left(T \right) = 6.1121 \exp \left(\left( 18.678 - \frac \right)\left( \frac \right)\right) , over liquid water, > 0 °C : P_\left(T \right) = 6.1115 \exp \left(\left( 23.036 - \frac \right)\left( \frac \right)\right) , over ice, < 0 °C where: * is the saturation vapor pressure in * is the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapour Pressure Of Water
The vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in gaseous form (whether pure or in a mixture with other gases such as air). The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. At pressures higher than saturation vapor pressure, water will condense, while at lower pressures it will evaporate or sublimate. The saturation vapor pressure of water increases with increasing temperature and can be determined with the Clausius–Clapeyron relation. The boiling point of water is the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure equals the ambient pressure. Water supercooled below its normal freezing point has a higher vapor pressure than that of ice at the same temperature and is, thus, unstable. Calculations of the (saturation) vapor pressure of water are commonly used in meteorology. The temperature-vapor pressure relation inversely describes the relation between the boilin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dortmund Data Bank
The Dortmund Data Bank (short DDB) is a factual data bank for thermodynamic and thermophysical data. Its main usage is the data supply for process simulation where experimental data are the basis for the design, analysis, synthesis, and optimization of chemical processes. The DDB is used for fitting parameters for thermodynamic models like NRTL or UNIQUAC and for many different equations describing pure component properties, e.g., the Antoine equation for vapor pressures. The DDB is also used for the development and revision of predictive methods like UNIFAC and PSRK. Contents Mixture properties * Phase equilibria data ( vapor–liquid, liquid–liquid, solid–liquid), data on azeotropy and zeotropy * Mixing enthalpies * Gas solubilities * Activity coefficients at infinite dilution * Heat capacities and excess heat capacities * Volumes, densities, and excess volumes (volume effect of mixing) * Salt solubilities * Octanol-water partition coefficients * Criti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee–Kesler Method
The Lee–Kesler method allows the estimation of the saturated vapor pressure at a given temperature for all components for which the critical pressure ''P''c, the critical temperature ''T''c, and the acentric factor ''ω'' are known. Equations : \ln P_ = f^ + \omega \cdot f^ : f^=5.92714 - \frac - 1.28862 \cdot \ln T_ + 0.169347 \cdot T_^6 : f^=15.2518 - \frac-13.4721 \cdot \ln T_ + 0.43577 \cdot T_^6 with :P_=\frac ( reduced pressure) and T_=\frac ( reduced temperature). Typical errors The prediction error can be up to 10% for polar components and small pressures and the calculated pressure is typically too low. For pressures above 1 bar, that means, above the normal boiling point, the typical errors are below 2%. Example calculation For benzene with * ''T''c = 562.12 KBrunner E., Thies M.C., Schneider G.M., ''J.Supercrit. Fluids'', 39(2), 160–173, 2006 * ''P''c = 4898 kPa * ''T''b = 353.15 K * ''ω'' = 0.2120 Dortmund Data Bank the following calculati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Chemical Physics
''The Journal of Chemical Physics'' is a scientific journal published by the American Institute of Physics that carries research papers on chemical physics."About the Journal" from the ''Journal of Chemical Physics'' website. Two volumes, each of 24 issues, are published annually. It was established in 1933 when '''' editors refused to publish theoretical works. The editors have been: *2019–present: Tim Lian *2008–2018: Marsha I. Lester *2007–2008: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Equation
The van der Waals equation is a mathematical formula that describes the behavior of real gases. It is an equation of state that relates the pressure, volume, Avogadro's law, number of molecules, and temperature in a fluid. The equation modifies the ideal gas law in two ways: first, it considers particles to have a finite diameter (whereas an ideal gas consists of point particles); second, its particles interact with each other (unlike an ideal gas, whose particles move as though alone in the volume). The equation is named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, who first derived it in 1873 as part of his doctoral thesis. Van der Waals based the equation on the idea that fluids are composed of discrete particles, which few scientists believed existed. However, the equation accurately predicted the behavior of a fluid around its Critical point (thermodynamics), critical point, which had been discovered a few years earlier. Its qualitative and quantitative agreement w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
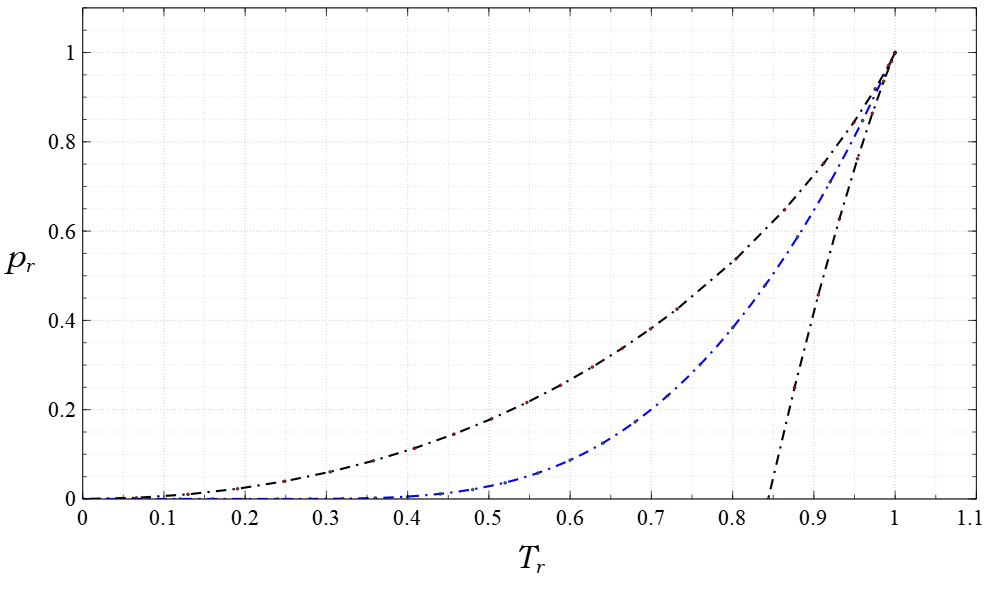
Acentric Factor
The acentric factor is a conceptual number introduced by Kenneth Pitzer in 1955, proven to be useful in the description of fluids. It has become a standard for the phase characterization of single and pure components, along with other state description parameters such as molecular weight, critical temperature, critical pressure, and critical volume (or critical compressibility). The acentric factor is also said to be a measure of the non-sphericity (centricity) of molecules. Pitzer defined from the relationship : \omega = -\log_(p^\text_\text) - 1 \text T_\text = 0.7, where p^\text_\text = p^\text / p_c is the reduced saturation vapor pressure, and T_\text = T / T_c is the reduced temperature. Pitzer developed this factor by studying the vapor-pressure curves of various pure substances. Thermodynamically, the vapor-pressure curve for pure components can be mathematically described using the Clausius–Clapeyron equation. The integrated form of equation is mainly used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |