|
Antoine-Augustin Préault
Antoine-Augustin Préault (6 October 1809 – 11 January 1879) was a French sculptor of the Romantic movement. Born in the Marais district of Paris, he was better known during his lifetime as Auguste Préault. Biography A student of David d'Angers, Préault first exhibited at the Paris Salon of 1833. He was not favorably looked upon by some of the artistic community's elite due to his outspokenness and because he was part of the circle of activists who participated in the French Revolution of 1830. During that period of turmoil, Préault's studio was vandalized and many of his plaster models were destroyed. As a result of these circumstances his work has been largely overshadowed by his contemporaries. Antoine-Augustin Préault died in Paris in 1879 and was interred in the Père Lachaise Cemetery. Words of a nineteenth-century critic describing Préault's work: Comments by Musée d'0rsay at time of exhibition held on Preault's work. Préault is buried in the Pere La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
église Saint-Roch
The Church of Saint-Roch (, ) is a 17th–18th-century French Baroque and classical style church in Paris, dedicated to Saint Roch. It is located at 284 rue Saint-Honoré, in the 1st arrondissement. The current church was built between 1653 and 1740. The church is particularly noted for its very exuberant 18th century chapels decorated with elaborate Baroque murals, sculpture, and architectural detail. In 1795, during the later states of the French Revolution, the front of the church was the site of the 13 Vendémiaire, when the young artillery officer Napoleon Bonaparte fired a battery of cannon to break up a force of Royalist soldiers which threatened the new revolutionary government. History Construction In 1521, the merchant Jean Dinocheau had a chapel built on the outskirts of Paris, which was dedicated to Saint Susanna. In 1577, his nephew Etienne Dinocheau had it extended into a larger church. In the early 18th century, with the beginning of the construction of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartres
Chartres () is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir Departments of France, department in the Centre-Val de Loire Regions of France, region in France. It is located about southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the Functional area (France), metropolitan area of Chartres (as defined by the Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques, INSEE), 38,534 of whom lived in the city (Communes of France, commune) of Chartres proper. Chartres is famous worldwide for its Chartres Cathedral, cathedral. Mostly constructed between 1193 and 1250, this Gothic architecture, Gothic cathedral is in an exceptional state of preservation. The majority of the original stained glass windows survive intact, while the architecture has seen only minor changes since the early 13th century. Part of the old town, including most of the library associated with the School of Chartres, was destroyed by Allies of World War II, Allied bombs i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gervasius And Protasius
Gervasius and Protasius (also Gervase and Protase, Gervasis and Prothasis and in French ''Gervais and Protais'') are venerated as Christian martyrs, probably of the 2nd century. They are the patron saints of Milan and of haymakers and are invoked for the discovery of thieves. Their feast day in the Latin Rite of the Catholic Church is 19 June, the day marking the translation of their relics. In the Eastern Orthodox Church and in the Eastern Rites of the Catholic Church, their feast takes place on 14 October ( O.S.)/24 October ( N.S.), the traditional day of their death. In Christian iconography their emblems are the scourge, the club and the sword. Legend The '' acta'' may have been expanded from a letter (''Epistle'' liii) to the bishops of Italy, falsely ascribed to Ambrose. They are written in a very simple style; it has not been possible to establish the date of their composition. According to these, Gervasius and Protasius were the twin sons of martyrs. Their father, Vita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
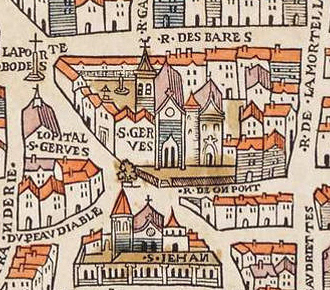
St-Gervais-et-St-Protais
Saint-Gervais-Saint-Protais () is a Roman Catholic parish church located in the 4th arrondissement of Paris, on Place Saint-Gervais in the Marais district, east of City Hall (Hôtel de Ville). The current church was built between 1494 and 1657, on the site of two earlier churches; the facade, completed last, was the first example of the French baroque style in Paris. The organists of the church included Louis Couperin and his nephew François Couperin, two of the most celebrated composers and musicians of the Baroque period; the organ they used can still be seen today. The church contains remarkable examples of medieval carved choir stalls, stained glass from the 16th century, 17th century sculpture, and modern stained glass by Sylvie Gaudin and Claude Courageux. Saint-Gervais was a parish church until 1975, when it became the headquarters of the Monastic Fraternities of Jerusalem. History A church dedicated to Saints Gervasius and Protasius, two Christian martyrs from Mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Jacques Feuchère
Jean-Jacques Feuchère (; 24 August 1807 – 26 July 1852) was a French sculptor. He was a student of Jean-Pierre Cortot, and among his students was Jacques-Léonard Maillet. Selected works * Relief panel ''Le Pont d'Arcole'', Arc de Triomphe, Paris, 1833–1834 * ''Satan'', bronze; dated 1833 (Musée du Louvre). Other examples are in the collections of the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium, Asmolean Museum, and LACMA. * Pediment sculpture, Church of St. Denys du Saint-Sacrement in Paris, 3rd arrondissement, for architect Étienne-Hippolyte Godde, 1835 * ''Portrait statue of the Marquis of Stafford'', bronze 1837. (Dunrobin Castle) * ''Amazon Taming a Horse'', bronze; dated 1843. (Musée du Louvre); an undated bronze is at the Cleveland Museum of Art The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Located in the Wade Park District of University Circle, the museum is internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan (civilization), Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaan#Canaanites, Canaanite and Aramaeans, Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Joseph Daumas
Louis-Joseph Daumas (1801–1887) was a French sculptor and medallist. Born in Toulon, Daumas was admitted into the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in 1826, and entered the ''atelier'' of David d'Angers.American architect and architecture, Volumes 33-34, No. 813, page 56 Daumas's work includes: * ''Genius of Navigation'', bronze statue of French Admiral Jules de Cuverville with four bas-reliefs on the base, port of Toulon, 1847, reconstructed after its destruction in World War II * exterior statue of François Eudes de Mézeray, Cour Napoléon in the Louvre Palace, Louvre, Paris, prior to 1853 * Roman cavalier and his horse, on the Rive Gauche, left bank of the Pont d'Iéna, Paris, 1853 * Equestrian statue of José de San Martín (Central Park), equestrian statue of José de San Martín in the Plaza San Martín (Buenos Aires), Plaza San Martín of Buenos Aires, 1862, with copies at the Parque del Oeste in Madrid, List of sculptures in Central Park, Central Park in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pont D'Iéna
Pont d'Iéna (, "Jena Bridge") is a bridge spanning the River Seine in Paris. It links the Eiffel Tower on the Left Bank to the district of Trocadéro on the Right Bank. History In 1807, by an imperial decree issued in Warsaw, Napoleon I ordered the construction of a bridge overlooking the Military School, and named it after his victory in 1806 at the Battle of Jena, disregarding other names considered previously: ''pont du Champ-de-Mars'' and ''pont de l'École militaire''. During the occupation of Paris by the Allies, Prussian General Blücher wanted to destroy the Pont d'Iéna, which was named after a French victory against Prussia. The Prefect of Paris tried everything to change the mind of Blücher, without success, and finally went to Talleyrand asking him whether he could write a letter to the General asking him not to destroy the bridge. Talleyrand instead wrote to Tsar Alexander, who was in person in Paris, asking him to grant to the people of Paris the favour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De Picardie
The Musée de Picardie is the main museum of Amiens and Picardy, in France. It is located at 48, rue de la République, Amiens. Its collections include artifacts ranging from prehistory to the 19th century, and form one of the largest regional museums in France. As an institution, the museum was founded as the ''Musée Napoléon'' in 1802 (the year of the Treaty of Amiens). However, the current building that houses the museum is more recent, being purpose-built as a regional museum between 1855 and 1867. The Second Empire architecture, Second Empire style building was designed by architects Henri Parent and Arthur-Stanislas Diet. It was built thanks to the ''Société des Antiquaires de Picardie'', keen to give the city somewhere to house the collections the society had gathered over decades. A prototype for other French regional museums, it was France's first building constructed exclusively for the purpose of conservation and exhibition of artworks. Collections Archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |