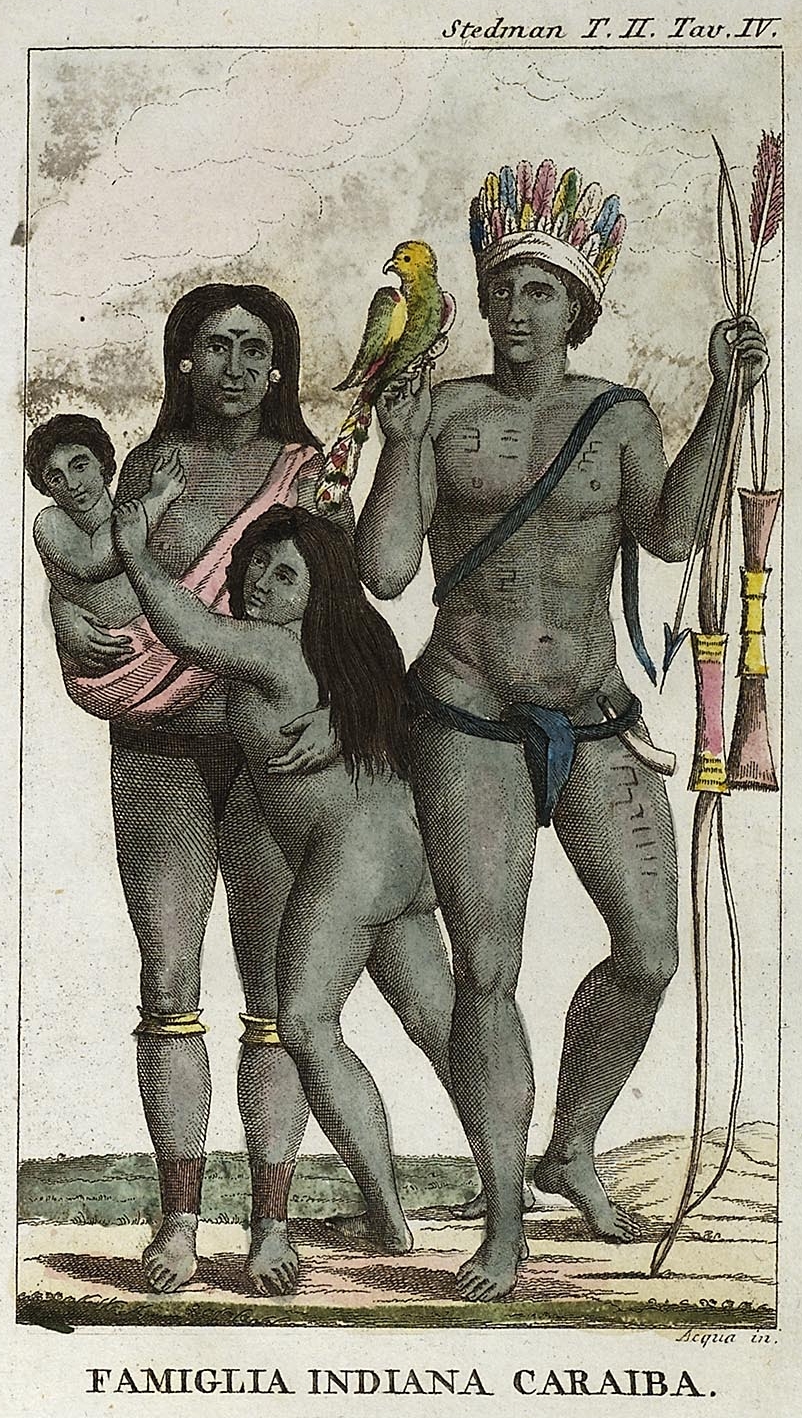|
Antiguans And Barbudans
Antiguans and Barbudans () are the people associated with the country of Antigua and Barbuda. They primarily speak Antiguan and Barbudan Creole and share the same culture. Antiguans and Barbudans are found worldwide, most notably in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. There are about 147,000 Antiguans and Barbudans in total, including about 42,000 in the diaspora. Antigua and Barbuda has been primarily inhabited by African descendants, multiracial people, Europeans since the 17th century, with significant influxes of Hispanic people and other groups during the 20th and 21st centuries. Following associated statehood in 1967, the first major Antiguan and Barbudan migrations outside of the Caribbean took place. The culture of Antiguans and Barbudans encompasses various forms of music, art, cuisine, oral history, and clothing, many of which have since spread throughout the Caribbean. Internationally, many Antiguans and Barbudans such as writer Jamaica Kincaid and spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flag Of Antigua And Barbuda
The national flag of Antigua and Barbuda was adopted on 27 February 1967 to mark the achievement of self-government. A competition to design the flag was held in which more than 600 local people entered. The winning design was put forth by nationally well-known artist and sculptor Sir Reginald Samuel. Design and symbolism The design is a red field with an inverted isosceles triangle based on the top edge of the field pointed toward the bottom edge of the field bearing the horizontal tricolour of black, light blue (half width) and white with the rising sun centred on top of the black band. The rising sun symbolises the dawning of a new era. The colours have different meanings: the black is for the African ancestry of the people; the blue for hope; and the red for energy or life of the people. The successive colouring of black, yellow, blue, and white (from the sun down) also stands for the soil, sun, sea, and sand. The blue also represents the Caribbean Sea, and the V-shape is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Art In Antigua And Barbuda
Art is a diverse range of cultural activity centered around ''works'' utilizing creative or imaginative talents, which are expected to evoke a worthwhile experience, generally through an expression of emotional power, conceptual ideas, technical proficiency, or beauty. There is no generally agreed definition of what constitutes ''art'', and its interpretation has varied greatly throughout history and across cultures. In the Western tradition, the three classical branches of visual art are painting, sculpture, and architecture. Theatre, dance, and other performing arts, as well as literature, music, film and other media such as interactive media, are included in a broader definition of "the arts". Until the 17th century, ''art'' referred to any skill or mastery and was not differentiated from crafts or sciences. In modern usage after the 17th century, where aesthetic considerations are paramount, the fine arts are separated and distinguished from acquired skills in general, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British Leeward Islands
The British Leeward Islands was a British colony from 1671 to 1958, consisting of the English overseas possessions, English (later British) overseas possessions in the Leeward Islands. It ceased to exist from 1816 to 1833, during which time it was split into two separate colonies (Antigua–Barbuda–Montserrat and Saint Kitts, Saint Christopher–Nevis–Anguilla–British Virgin Islands, Virgin Islands). It was dissolved in 1958 after the separation of the British Virgin Islands, and the remaining islands became parts of the West Indies Federation. History The Leeward Islands was established as an English colony in 1671. In 1816, the islands were divided in two regions: Antigua, Barbuda, and Montserrat in one colony, and Saint Kitts, Saint Christopher, Nevis, Anguilla, and the British Virgin Islands, Virgin Islands in the other. The Leeward Islands were united again as a semi-federal entity in 1833, coming together until 1872 under the administration of the Governor of Antigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barbudans
The Barbudans are an ethnic group native to the island of Barbuda in the eastern Caribbean, primarily of Fante and other Coromantee ancestry. The Barbudans speak Barbudan Creole and the Barbudan dialect of English. The Barbudans make up the majority of the African descendant population in Barbuda, and are also located in various other English-speaking developed countries. History and origins The Barbudan people originate from the coasts of Ghana, west of the city of Accra. The Barbudans had been shipped from the port of Cormantin, part of the Fante people inland from the port. Upon arrival in Barbuda, these slaves established a community in the island. The population grew naturally, with only eight new slaves arriving after the initial shipment. During slavery, the Barbudans enjoyed relatively good conditions according to Michael Wood. Except for a brief period in the 1780s, families were rarely broken apart, and were never involved in sugar production due to the island's dry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prince Klaas
Prince Klaas, also known as King Court, Tackey, or by his African name, Kwaku, was an enslaved Antiguan who was a posthumous recipient of the Most Exalted Order of the National Hero. In order to establish an independent African-ruled Kingdom of Antigua and destroy the colonial white administration, Klaas launched a slave uprising that was put down. Background In 1736, on the island of Antigua, an enslaved African known as Prince Klaas (whose real name was thought to be Court or Kwaku Takyi) planned an uprising in which whites would be massacred. Court was crowned "King of the Coromantees" in a pasture outside the capital of St. John's, in what white observers thought was a colourful spectacle, but was for the Africans a ritual declaration of war on the white enslavers. Due to information obtained from other enslaved people, colonists discovered and suppressed the plot. Prince Klaas and four accomplices were caught and executed by the breaking wheel. They hung and starved six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Varieties Of Antiguan And Barbudan Creole
There are several varieties of Antiguan and Barbudan Creole forming a branch of the Eastern Caribbean Creole, many of which are only partially mutually intelligible. Variation is strongest in the mountainous regions of southwestern Antigua. The varieties are classified into seven main groups: North Antiguan, South Antiguan, Barbudan, Saint Kitts, Anguillan, Montserratian, and Kokoy. Classification Antiguan and Barbudan Creole forms a dialect continuum, with varieties tending to become less mutually intelligible by distance. ;North Antiguan Creole :This variety has the most speakers and is considered the standard variety of Antiguan and Barbudan Creole. It originated in the city of St. John's and has spread throughout northern Antigua due to the amount of people who commute to the city. The variety has about 48,000 native speakers in Antigua and Barbuda. It is most similar to Montserrat Creole. ;South Antiguan Creole :This variety is the most distant from the other creoles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kwa Languages
The Kwa languages, often specified as New Kwa, are a proposed but as-yet-undemonstrated family of languages spoken in the south-eastern part of Ivory Coast, across southern Ghana, and in central Togo. The Kwa family belongs to the Niger-Congo phylum. The name was introduced in 1895 by Gottlob Krause and derives from the word for 'people' (''Kwa'') in many of these languages, as illustrated by Akan names. This branch consists of around 50 different languages spoken by about 25 million people. Some of the largest Kwa languages are Ewe, Akan and Baule. Languages See the box at right for a current classification. The various clusters of languages included in Kwa are at best distantly related, and it has not been demonstrated that they are closer to each other than to neighboring Niger–Congo languages. Stewart distinguished the following major branches, which historical-comparative analysis supports as valid groups: * Potou–Tano (including Akan) * Ga–Dangme * Na-Togo * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British People
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, which can be acquired, for instance, by descent from British nationals. When used in a historical context, "British" or "Britons" can refer to the Ancient Britons, the Celtic languages, Celtic-speaking inhabitants of Great Britain during the British Iron Age, Iron Age, whose descendants formed the major part of the modern Welsh people, Cornish people, Bretons and considerable proportions of English people. It also refers to those British subjects born in parts of the former British Empire that are now independent countries who settled in the United Kingdom prior to 1973. Though early assertions of being British date from the Late Middle Ages, the Union of the Crowns in 1603 and the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707 triggered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kalinago
The Kalinago, also called Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an Indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Kalinago or Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean (the name of which is derived from "Carib", as the Kalinago were once called). They lived throughout north-eastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of Indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. The term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to different Indigenous groups, from the Lokono of South America to the Taíno (Island Arawaks), who lived in the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. All these groups spoke related Arawakan languages. Name Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and '' Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for Indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. In 1871, ethnologist Daniel Garrison Brinton proposed calling the Caribbean populace "Island Arawak" because of their cultural and linguistic similarities with the mainland Arawak. Subsequent scholars shortened this convention to "Arawak", creating confusion between the island and mainland groups. In the 20th century, scholars such as Irving Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protestant Christians
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divine grace, the priesthood of all believers, and the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. The five solae, five ''solae'' summarize the basic theological beliefs of mainstream Protestantism. Protestants follow the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began in the 16th century with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church from perceived Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies. The Reformation began in the Holy Roman Empire in 1517, when Martin Luther published his ''Ninety-five Theses'' as a reaction against abuses in the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church, which purported to offer the remission of the Purgatory, temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |