|
Antheia (Argolis)
Antheia or Anthea () was a town in the Troezene in ancient Argolis, said to have been founded by the mythological figure Anthes. In mythology, King Pittheus transferred the town's population (synoecism) to Troezen Troezen (; ancient Greek: Τροιζήν, modern Greek: Τροιζήνα ) is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the munic .... The site is near modern Damala. References Populated places in ancient Argolis Former populated places in Greece Places in Greek mythology {{ancientArgolis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troezene
Troezen (; ancient Greek: Τροιζήν, modern Greek: Τροιζήνα ) is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia-Methana, of which it is a municipal unit. It is part of the Islands regional unit. In the 2021 cencus it had a population of 4,668. Troezen is located southwest of Athens, across the Saronic Gulf, and a few miles south of Methana. The seat of the former municipality was in Galatas. Before 2011, Troizina was part of the Argolis and Korinthos prefecture from 1833 to 1925, Attica prefecture from 1925 to 1964, Piraeus Prefecture from 1964 to 1972 and then back in Attica prefecture (in antiquity it was part of Argolis). The municipality had a land area of 190.697 km2. Its largest towns and villages were Galatás, Kalloní, Troizína, Taktikoúpoli, Karatzás, Dryópi, Ágios Geórgios, and Agía Eléni. It included num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
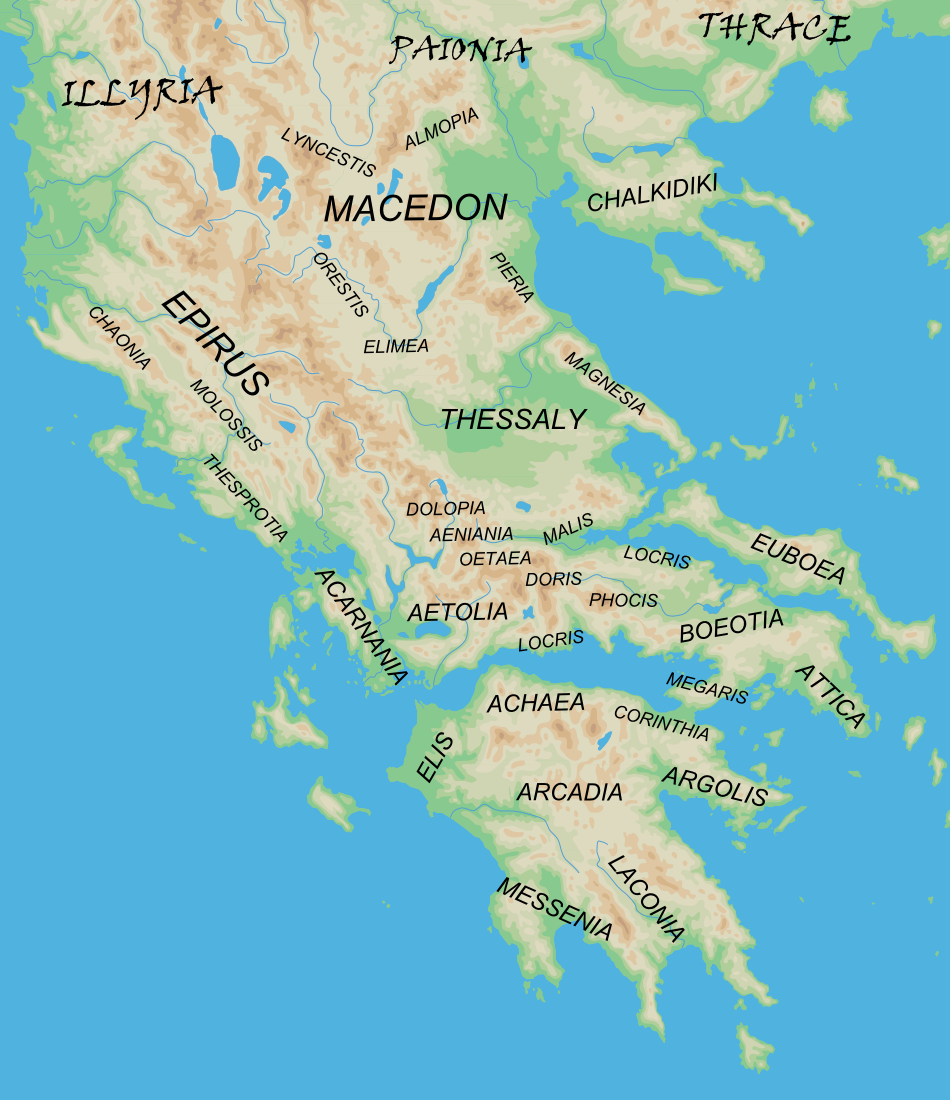
Ancient Argolis
The regions of ancient Greece were sub-divisions of the Hellenic world as conceived by the ancient Greeks, shown by their presence in the works of ancient historians and geographers or in surviving legends and myths. Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the #Peloponnese, Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. Conversely, the division of #Central Greece, central Greece between #Boeotia, Boeotia, #Phocis, Phocis, #Doris, Doris and the three parts of #Locris, Locris, seems to be attributable to ancient tribal divisions and not major geographical features. Both types of regions retained their identity throughout the Greek Dark Ages and its tumultuous changes in the local population and culture, giving them a less political and more symbolic presence. Other geographical divisions not identified with the aforementioned areas did, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthes
In Greek mythology, Anthas or Anthes () was a son of Poseidon and Alcyone, and brother of Hyperes. The brothers were eponymous founders and first kings of the cities Hyperea and Anthea in a region they reigned over; later on these two cities were merged into the historical Troezen.Pausanias2.30.8/ref> Anthas was father of at least two sons, Aëtius and Dius, of whom Aëtius was the successor to both his father and uncle, and further co-ruled with Pittheus and Troezen. The descendants of Anthas through Aëtius reputedly founded colonies in Caria: Halicarnassus and Myndus, and accordingly the people of Halicarnassus were referred to by the poetic epithet ''Antheades'' 'descendants of Anthas'. Alternately, Halicarnassus was founded by Anthas himself. Anthas also was the presumed eponym of Anthedon, over which he was said to have reigned,Pausanias9.22.5/ref> and of Anthana in Laconia.Stephanus of Byzantium, s.v. Anthana': he is further said to have been killed and flayed by Cleomenes I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittheus
In Greek mythology, Pittheus (; ) was the king of Troezen, city in Argolis, which he had named after his brother Troezen. Biography Pittheus was a son of Pelops and Dia (maybe another name for Hippodamia), father of AethraDiodorus Siculus. ''Bibliotheca Historica, Book 4.59.1'' and Henioche, and grandfather and instructor of Theseus. He was described by Euripides as the most pious son of Pelops, a wise man, and well versed on understanding the oracle thus sought by Aegeus.Euripides''. Medea683'' Plutarch. ''Life of Theseus, 3.4'' Pittheus is said to have taught the art of speaking, and even to have written a book upon it. Plutarch spoke of Pittheus' account in the following verses: ittheushad the highest repute as a man versed in the lore of his times and of the greatest wisdom. Now the wisdom of that day had some such form and force as that for which Hesiod was famous, especially in the sententious maxims of his 'Works and Days' .One of these maxims is ascribed to Pitthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoecism
Synoecism or synecism ( ; , ''sunoikismos'', ), also spelled synoikism ( ), was originally the amalgamation of villages in Ancient Greece into ''poleis'', or city-states. Etymologically, the word means "dwelling together (''syn'') in the same house (''oikos'')." Subsequently, any act of civic union between polities of any size was described by the word ''synoikismos'', in addition to the Latinized synoecism. Synoecism is opposed to Greek dioecism (διοικισμóς, ''dioikismos''), the creation of independent communities within the territory of a polis. Synoecism is the result of a few major factors, mainly an increase in population density of adjacent settlements, with an incorporation proposed for economic, political or ideological advantages, such as the synoecism of the communities of Attica into Athens, or by imposition of a ruling power, such as the synoecism of Messenia into the newly built city of Messene. Additionally, synoecism may be the result of less active forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troezen
Troezen (; ancient Greek: Τροιζήν, modern Greek: Τροιζήνα ) is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia-Methana, of which it is a municipal unit. It is part of the Islands regional unit. In the 2021 cencus it had a population of 4,668. Troezen is located southwest of Athens, across the Saronic Gulf, and a few miles south of Methana. The seat of the former municipality was in Galatas. Before 2011, Troizina was part of the Argolis and Korinthos prefecture from 1833 to 1925, Attica prefecture from 1925 to 1964, Piraeus Prefecture from 1964 to 1972 and then back in Attica prefecture (in antiquity it was part of Argolis). The municipality had a land area of 190.697 km2. Its largest towns and villages were Galatás, Kalloní, Troizína, Taktikoúpoli, Karatzás, Dryópi, Ágios Geórgios, and Agía Eléni. It included n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Hirschfeld
Gustav Hirschfeld (4 November 1847, Pyritz – 10 April 1895, Wiesbaden) was a German classical archaeologist. He was the great-uncle of Walter Benjamin. Life Born into a Jewish merchant family,Jonathan M. Hess, ''Middlebrow Literature and the Making of German-Jewish Identity'', Stanford University Press (2010), p. 201 he studied in Tübingen, Leipzig and Berlin and from 1870 stayed in Greece, Italy and Asia Minor as a stipendary of the German Archaeological Institute. From 1875 to 1877 he led the German excavations at Olympia, for which he was appointed extraordinary professor (1878) then ordinary professor (1880) at the University of Königsberg The University of Königsberg () was the university of Königsberg in Duchy of Prussia, which was a fief of Poland. It was founded in 1544 as the world's second Protestant Reformation, Protestant academy (after the University of Marburg) by Duke A .... Works * ''Tituli statuarum sculptorumque graecorum'' (Berlin 1871) * ''Athena und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damala
Troezen (; ancient Greek: Τροιζήν, modern Greek: Τροιζήνα ) is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia-Methana, of which it is a municipal unit. It is part of the Islands regional unit. In the 2021 cencus it had a population of 4,668. Troezen is located southwest of Athens, across the Saronic Gulf, and a few miles south of Methana. The seat of the former municipality was in Galatas. Before 2011, Troizina was part of the Argolis and Korinthos prefecture from 1833 to 1925, Attica prefecture from 1925 to 1964, Piraeus Prefecture from 1964 to 1972 and then back in Attica prefecture (in antiquity it was part of Argolis). The municipality had a land area of 190.697 km2. Its largest towns and villages were Galatás, Kalloní, Troizína, Taktikoúpoli, Karatzás, Dryópi, Ágios Geórgios, and Agía Eléni. It included num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Argolis
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |