|
Antares
Antares is the brightest star in the constellation of Scorpius. It has the Bayer designation α Scorpii, which is Latinisation of names, Latinised to Alpha Scorpii. Often referred to as "the heart of the scorpion", Antares is flanked by Sigma Scorpii, σ Scorpii and Tau Scorpii, τ Scorpii near the center of the constellation. Distinctly reddish when viewed with the naked eye, Antares is a slow irregular variable star that ranges in brightness from an apparent visual magnitude of +0.6 down to +1.6. It is on average list of brightest stars, the fifteenth-brightest star in the night sky. Antares is the brightest and most evolved stellar member of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, the nearest Stellar association#OB associations, OB association to the Sun. It is located about from Earth at the rim of the Upper Scorpius subgroup, and is illuminating the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex in its foreground. Classified as stellar classification#Spectral types, spectral type Stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition predates Greek culture; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Notable features Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco ( Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco ( Sargas, of Sumerian origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale). Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco ( Shaula) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes. The constellation's bright stars form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tau Scorpii
Tau Scorpii, Latinized from τ Scorpii, formally known as Paikauhale , is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. The apparent visual magnitude of Tau Scorpii is +2.8, which make it among the brightest stars of the Scorpius constellation. Parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of roughly 470 light-years (150 parsecs) from Earth. Description Tau Scorpii is a B-type star with an early spectral classification of B0.2V. It has 15 times the Sun's mass and 6.4 times the radius of the Sun. It is radiating about 25,000 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 28,860 K. This gives it the blue-white hue characteristic of B-type stars. As yet there is no evidence of a companion in orbit around τ Sco. It is a magnetic star whose surface magnetic field was mapped by means of Zeeman–Doppler imaging. Tau Scorpii is rotating relatively slowly with a period of 41 days. This star is 5.22 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sigma Scorpii
Sigma Scorpii (or σ Scorpii, abbreviated Sigma Sco or σ Sco), is a multiple star system in the constellation of Scorpius, located near the red supergiant Antares, which outshines it. This system has a combined apparent visual magnitude of +2.88, making it one of the List of stars in Scorpius, brighter members of the constellation. Based upon stellar parallax, parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to Sigma Scorpii is roughly 696 light-years (214 parsecs). North ''et al.'' (2007) computed a more accurate estimate of light years ( parsecs). The system consists of a spectroscopic binary with components designated Sigma Scorpii Aa1 (officially named Alniyat , the traditional name for the entire star system) and a Beta Cephei variable) and Aa2; a third component (designated Sigma Scorpii Ab) at 0.4 arcseconds from the spectroscopic pair, and a fourth component (Sigma Scorpii B) at about 20 arcseconds. Nomenclature ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Red Supergiant
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) and a stellar classification K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelgeuse and Antares A are the brightest and best known red supergiants (RSGs), indeed the only first magnitude red supergiant stars. Classification Stars are classified as supergiants on the basis of their spectral luminosity class. This system uses certain diagnostic spectral lines to estimate the surface gravity of a star, hence determining its size relative to its mass. Larger stars are more luminous at a given temperature and can now be grouped into bands of differing luminosity. The luminosity differences between stars are most apparent at low temperatures, where giant stars are much brighter than main-sequence stars. Supergiants have the lowest surface gravities and hence are the largest and brightest at a particular temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Binary Star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars using a telescope, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort each other's outer stellar atmospheres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rho Ophiuchi Cloud Complex
The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is a complex of interstellar clouds with different nebulae, particularly a dark nebula which is centered 1° south of the star ρ Ophiuchi, which it among others extends to, of the constellation Ophiuchus. At an estimated distance of about , or 460 light years, it is one of the closest Star formation, star-forming regions to the Solar System. Cloud complex This cloud covers an angular area of on the celestial sphere. It consists of two major regions of dense gas and dust. The first contains a star-forming cloud (L1688) and two filaments (L1709 and L1755), while the second has a star-forming region (L1689) and a filament (L1712–L1729). These filaments extend up to 10–17.5 parsecs in length and can be as narrow as 0.24 parsecs in width. The large extensions of the complex are also called ''Dark River'' clouds (or ''Rho Ophiuchi Streamers'') and are identified as Barnard Catalogue, Barnard 44 and 45. Some of the structures within the complex appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
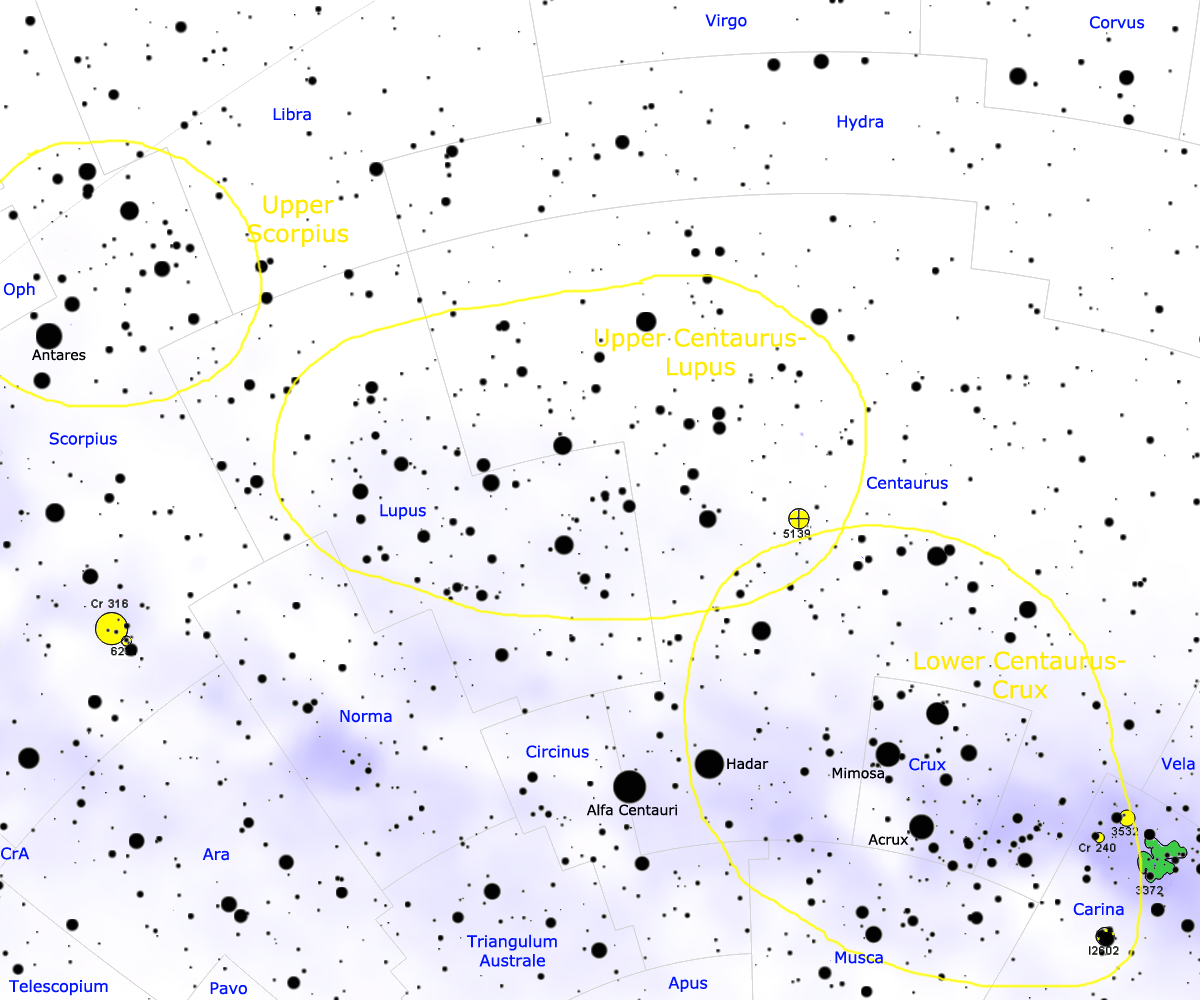
Scorpius–Centaurus Association
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 parsecs or 420 light-years. Analysis using improved Hipparcos data has brought the number of known members to 436. The cluster shows a continuous spread of stars with no apparent need for subclassification. The Sco–Cen subgroups range in age from 11 million years (Upper Scorpius) to roughly 15 million years (Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux). Many of the bright stars in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus, and Crux are members of the Sco–Cen association, including Antares (the most massive member of Upper Scorpius), and most of the stars in the Southern Cross. Hundreds of stars have been identified as members of Sco-Cen, with masses ranging from roughly 15 solar masses (Antares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Brightest Stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude – their brightness as observed from Earth. It includes all stars brighter than magnitude +2.50 in visible light, measured using a ''V''-band filter in the UBV photometric system. Stars in binary systems (or other multiples) are listed by their ''total'' or ''combined'' brightness if they appear as a single star to the naked eye, or listed separately if they do not. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the scale is logarithmic and inverted i.e. lower/more negative numbers are brighter. Most stars on this list appear bright from Earth because they are nearby, not because they are intrinsically luminous. For a list which compensates for the distances, converting the ''apparent'' magnitude to the ''absolute'' magnitude, see the list of most luminous stars. Measurement The Sun is the brightest star as viewed from Earth, at −26.78 mag. The second brightest is Sirius at −1.46 mag. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the cool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Projected Separation
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth. The field of astronomy features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon. A B C D E F G H I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |