|
Angénieux Retrofocus
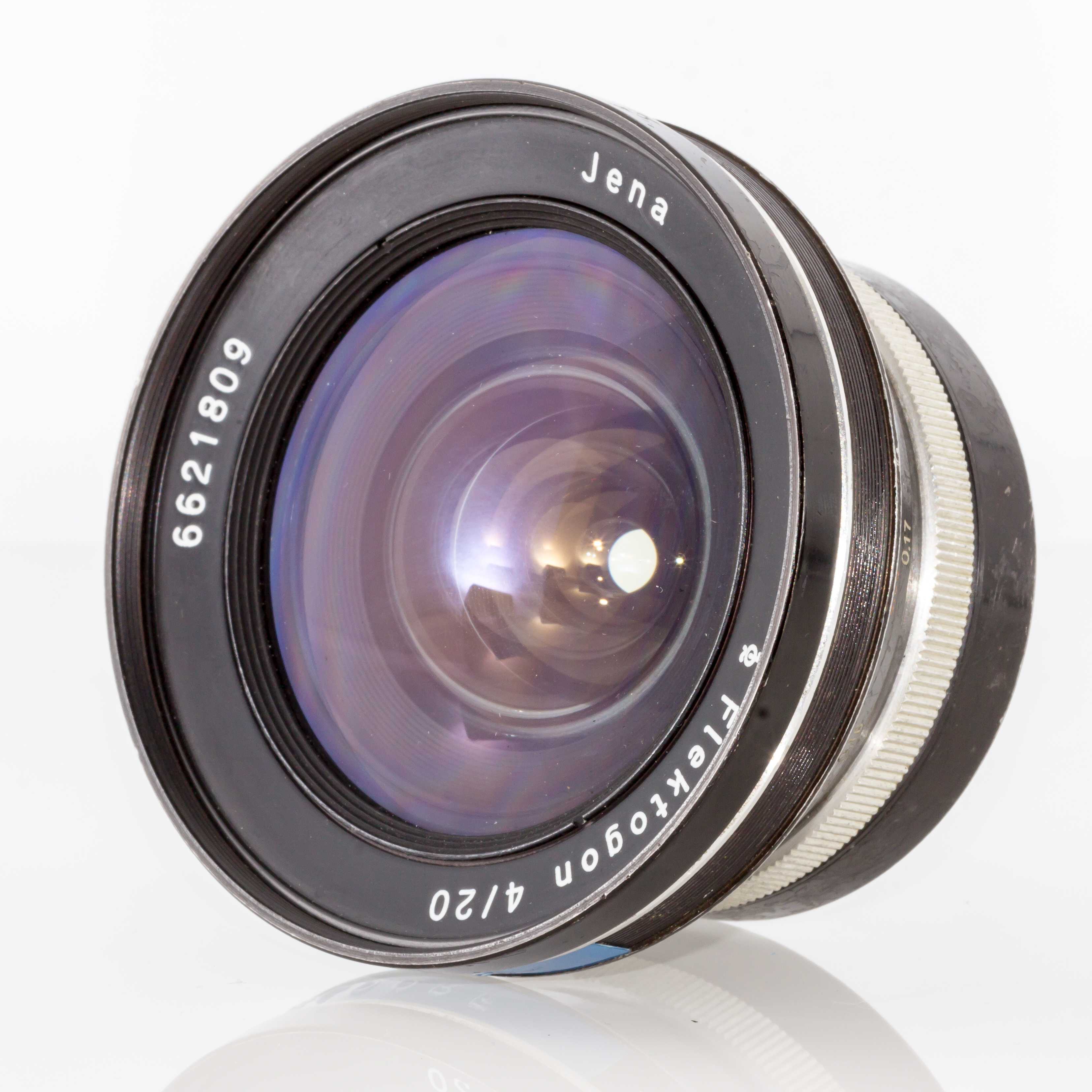
The Angénieux retrofocus photographic lens is a wide-angle lens design that uses an inverted telephoto configuration. The popularity of this lens design made the name retrofocus synonymous with this type of lens. The Angénieux retrofocus for still cameras was introduced in France in 1950 by Pierre Angénieux. Inverted telephoto concept The telephoto lens configuration combines positive and negative lens groups with the negative at the rear, serving to magnify the image, which reduces the back focal distance of the lens (the distance between the back of the lens and the image plane) to a figure shorter than the focal length. This is for practical, not optical reasons, because it allows telephoto lenses to be made shorter and less cumbersome. The first practical telephoto lens was developed by Peter Barlow in the early 1800s, with the eponymous Barlow lens referring to the negative achromat inserted between the eye and a telescope. The inverted telephoto configuration does the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Angénieux
Pierre Angénieux (; 14 July 1907 in Saint-Héand – 26 June 1998) was a French engineer and optician, one of the inventors of the modern zoom lenses, and famous for introducing the Angénieux retrofocus. Biography Angénieux graduated from the École Nationale Supérieure d'Arts et Métiers in 1928, and from the École Supérieure d'Optique the next year. He was a student of Henri Chrétien. After working for Pathé, Angénieux founded a company specialising in cinema equipment in 1935, ''Les Etablissements Pierre Angénieux''. He started using Geometric optics rather than Physical optics in the design of his lenses, as Carl Zeiss and Ernst Abbe did, and developed computing methods decreasing the time needed to design a lens by an order of magnitude. In 1950, Angénieux introduced the Angénieux retrofocus, which allowed mounting wide-angle lenses on Single-lens reflex cameras. In 1953, Angénieux designed the fastest lens of the time, reaching 0.95. The design was used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35mm Format
file:135film.jpg, 135 film. The film is wide. Each image is 24×36 mm in the most common "small film" format (sometimes called "double-frame" for its relationship to the "single-frame" 35 mm movie format or full frame after the introduction of 135 sized digital sensors; confusingly, "full frame" was also used to describe the Full frame (cinematography), full gate of the movie format half the size). file:LEI0060 186 Leica I Sn.5193 1927 Originalzustand Front-2 FS-15.jpg, Leica I, 1927, the first successful camera worldwide for 35 cine film 135 film, more popularly referred to as 35 mm film or 35 mm, is a Film format#Still photography film formats, format of photographic film with a film gauge of loaded into a standardized type of magazine (also referred to as a cassette or cartridge) for use in 135 film cameras. The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for 35 mm film specifically for still photography, perforated with Film perforation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
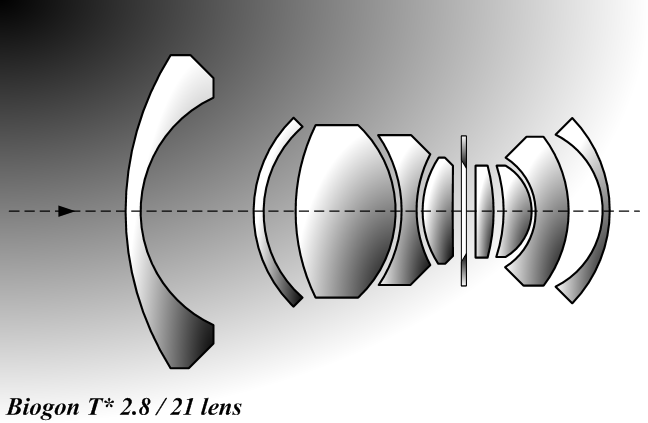
Biogon
Biogon is the brand name of Carl Zeiss for a series of photographic camera lenses, first introduced in 1934. Biogons are typically wide-angle lenses. History ''Biogon'' (I), 1934 File:Bertele-Zeiss Biogon (1934).svg, Zeiss ''Biogon'' by Bertele (1934), from US 2,084,309 File:Bertele US2549159A (Aviotar, 1947).svg, Wild ''Aviotar'' by Bertele (1947), from US 2,549,159 File:Jupiter-12 (Contax-Kiev lens mount).JPG, KMZ ''Jupiter-12'' lens The first ''Biogon'' lens (2.8 / 3.5 cm, an asymmetric design featuring seven elements in four groups) was designed in 1934 by Ludwig Bertele while he was working for Zeiss, as a modification of his earlier '' Sonnar'' design (1929). The ''Biogon'' was assigned to Zeiss Ikon Dresden and marketed with the Contax rangefinder camera. It was produced by Carl Zeiss starting in approximately 1937, first in Jena, then a redesigned version was built in Oberkochen. Bertele would go on to reuse the design for the Wild ''Aviotar''. After Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-Gauss Lens
The double Gauss lens is a compound lens used mostly in camera lenses that reduces optical aberrations over a large focal plane. Design The earliest double Gauss lens, patented by Alvan Graham Clark in 1888, consists of two symmetrically-arranged Gauss lenses. Each Gauss lens is a two-element achromatic lens with a positive meniscus lens on the object side and a negative meniscus lens on the image side. In Clark's symmetric arrangement, this makes four elements in four groups: two positive meniscus lenses on the outside with two negative meniscus lenses inside them. The symmetry of the system and the splitting of the optical power into many elements reduces the optical aberrations within the system. There are many variations of the design. Sometimes extra lens elements are added. The basic lens type is one of the most developed and used photographic lenses. The design forms the basis for many camera lenses in use today, especially the wide-aperture standard lenses used with 35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss AG
Zeiss ( ; ) is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany, in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multinational company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the small town of Oberkochen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasselblad 1000F
Victor Hasselblad AB is a Sweden, Swedish manufacturer of medium format (film), medium format cameras, photographic equipment and image scanners based in Gothenburg, Sweden. The company originally became known for its classic analog medium-format cameras that used a waist-level viewfinder. Perhaps the most famous use of the Hasselblad camera was during the Apollo program missions when the first humans Moon landing, landed on the Moon. Almost all of the still photographs taken during these missions used modified Hasselblad cameras. In 2016, Hasselblad introduced the world's first digital compact mirrorless medium-format camera, the X1D-50c, changing the portability of medium-format photography. Hasselblad produces about 10,000 cameras a year from a small three-storey building. Company history The company was established in 1841 in Gothenburg, Sweden, by Fritz Wiktor Hasselblad, as a trading company, F. W. Hasselblad and Co. The founder's son, Arvid Viktor Hasselblad, was inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss
Carl Zeiss (; 11 September 1816 – 3 December 1888) was a German scientific instrument maker, optician and businessman. In 1846 he founded his workshop, which is still in business as Zeiss (company), Zeiss. Zeiss gathered a group of gifted practical and theoretical opticians and glass makers to reshape most aspects of optical instrument production. His collaboration with Ernst Abbe revolutionized optical theory and practical design of microscopes. Their quest to extend these advances brought Otto Schott into the enterprises to revolutionize optical glass manufacture. The firm of Carl Zeiss grew to one of the largest and most respected optical firms in the world. Birth and family Carl's father, Johann Gottfried August Zeiss (1785–1849) was born in Rastenberg, where his forefathers had worked as artisans for over 100 years. August moved with his parents to Buttstädt, a small regional capital north of Weimar, where he married Johanna Antoinette Friederike Schmith (1786–18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodenstock Photo Optics
Rodenstock Photo Optics traces its origins to a mechanical workshop founded in 1877 by Josef Rodenstock and his brother Michael in Würzburg, Germany. The company relocated to Munich by 1884 and became an important manufacturer of both corrective lenses for glasses and camera lenses by the early 1900s. These two lines began to diverge in the 1960s as the center of photographic lens manufacturing shifted to Japan; the ophthalmic business continued as Rodenstock GmbH while the remaining camera lens business was repositioned to serve the large format and industrial precision optics markets, then spun off in 1996 as Rodenstock Präzisionsoptik. Since then, the precision optics brand has been acquired in succession by LINOS Photonics (Göttingen, 2000), Qioptiq Group (Luxembourg, 2006), and Excelitas Technologies (2013). Photographic lenses produced by Rodenstock during and since the 20th century include the brands ''Ysarex'', ''Heligon'', ''Eurygon'', ''Rotelar'', ''Apo-Ronar'', ''Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneider Kreuznach
Joseph Schneider Optische Werke GmbH (commonly referred to as Schneider) is a manufacturer of industrial and photographic optics. The company was founded on 18 January 1913 by Joseph Schneider as Optische Anstalt Jos. Schneider & Co. at Bad Kreuznach in Germany. The company changed its name to Jos. Schneider & Co., Optische Werke, Kreuznach in 1922, and to the current Jos. Schneider Optische Werke GmbH in 1998. In 2001, Schneider received an Academy Awards, Oscar for Technical Achievement for their Super-Cinelux motion picture lenses. It is best known as manufacturers of large format lenses for view cameras, enlarger lenses, and photographic loupes. It also makes a limited amount of 135 film, small- and Medium format (film), medium-format lenses, and has at various times manufactured eyeglasses and camera rangefinders, as well as being an OEM lens maker for Kodak and Samsung Electronics, Samsung digital cameras. It has supplied the lenses for various LG devices and the BlackBer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Bertele
Ludwig Jakob Bertele (25 December 1900 – 16 November 1985) was a German optics constructor. His developments received universal recognition and serve as a basis for considerable part of the optical designs used today. Biography Ludwig Jakob Bertele was born 25 December 1900 in Munich, to an architect's family. At Ernemann In 1916, Bertele was employed as the assistant of an optics designer at Rodenstock in Munich. In 1919, he moved to Dresden to work for Heinrich Ernemann at under the supervision of August Klughardt, as a designer of optics. In the same year, Bertele would begin the development of the ' design. Its basis was the optical scheme of the Ultrastigmat cinema lens, a modified Cooke triplet, which had been developed by Charles C. Minor in 1916 and produced by Gundlach Company. The main purpose of Bertele's developmental work was to increase the light-gathering power of a lens as well as diminishing optical aberration. In 1923, after four years of development, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |