|
Anglo-Saxon Diffusionist
The term migrationism, in the history of archaeological theory, was opposed to the term diffusionism (or "immobilism") as a means of distinguishing two approaches to explaining the spread of prehistoric archaeological cultures and innovations in artefact. Migrationism explains cultural change in terms of human migration, while diffusionism relies on explanations based on trans-cultural diffusion of ideas rather than populations (''pots, not people''). Western archaeology the first half of the 20th century relied on the assumption of migration and invasion as driving cultural change. That was criticized by the processualists in the 1960s and 1970s, leading to a new mainstream which rejected "migrationism" as outdated. Since the 1990s, there has been renewed interest in "migrationist" scenarios, as archaeologists attempted the archaeological reflexes of migrations known to have occurred historically. Since the 2000s, the developments in archaeogenetics have opened a new avenue for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Theory
Archaeological theory refers to the various intellectual frameworks through which archaeology, archaeologists interpret archaeological data. Archaeological theory functions as the application of philosophy of science to archaeology, and is occasionally referred to as philosophy of archaeology. There is no one singular theory of archaeology, but many, with different archaeologists believing that information should be interpreted in different ways. Throughout the history of the discipline, various trends of support for certain archaeological theories have emerged, peaked, and in some cases died out. Different archaeological theories differ on what the goals of the discipline are and how they can be achieved. Some archaeological theories, such as processual archaeology, holds that archaeologists are able to develop accurate, Objectivity (philosophy), objective information about past societies by applying the scientific method to their investigations, whilst others, such as post-process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Human Migrations
Early human migrations are the earliest migrations and expansions of archaic and modern humans across continents. They are believed to have begun approximately 2 million years ago with the early expansions out of Africa by ''Homo erectus''. This initial migration was followed by other archaic humans including '' H. heidelbergensis'', which lived around 500,000 years ago and was the likely ancestor of Denisovans and Neanderthals as well as modern humans. Early hominids had likely crossed land bridges that have now sunk. Within Africa, ''Homo sapiens'' dispersed around the time of its speciation, roughly 300,000 years ago. The recent African origin theory suggests that the anatomically modern humans outside of Africa descend from a population of ''Homo sapiens'' migrating from East Africa roughly 70–50,000 years ago and spreading along the southern coast of Asia and to Oceania by about 50,000 years ago. Modern humans spread across Europe about 40,000 years ago. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
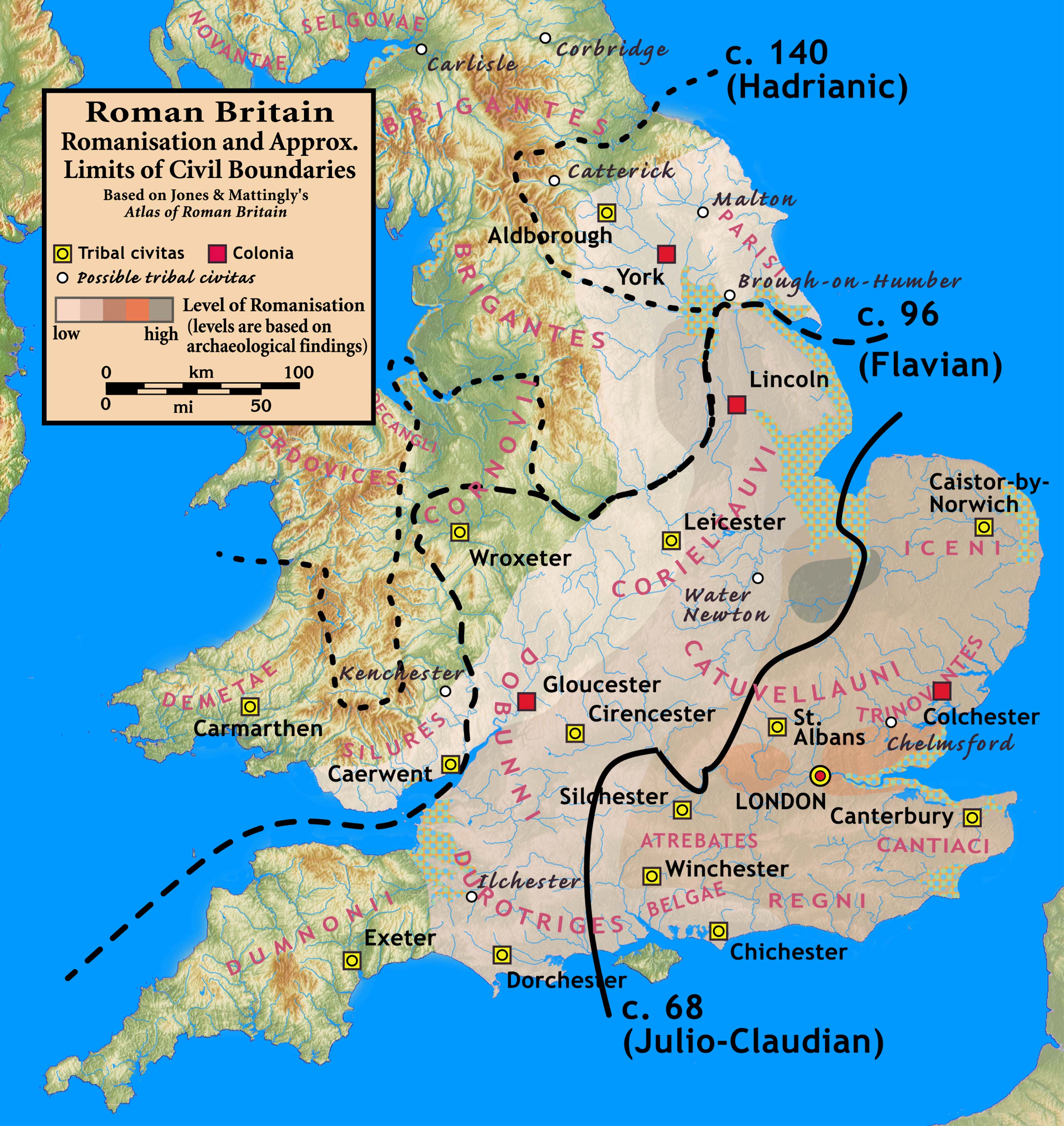
Romano-Britons
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Diffusionist
The term migrationism, in the history of archaeological theory, was opposed to the term diffusionism (or "immobilism") as a means of distinguishing two approaches to explaining the spread of prehistoric archaeological cultures and innovations in artefact. Migrationism explains cultural change in terms of human migration, while diffusionism relies on explanations based on trans-cultural diffusion of ideas rather than populations (''pots, not people''). Western archaeology the first half of the 20th century relied on the assumption of migration and invasion as driving cultural change. That was criticized by the processualists in the 1960s and 1970s, leading to a new mainstream which rejected "migrationism" as outdated. Since the 1990s, there has been renewed interest in "migrationist" scenarios, as archaeologists attempted the archaeological reflexes of migrations known to have occurred historically. Since the 2000s, the developments in archaeogenetics have opened a new avenue for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
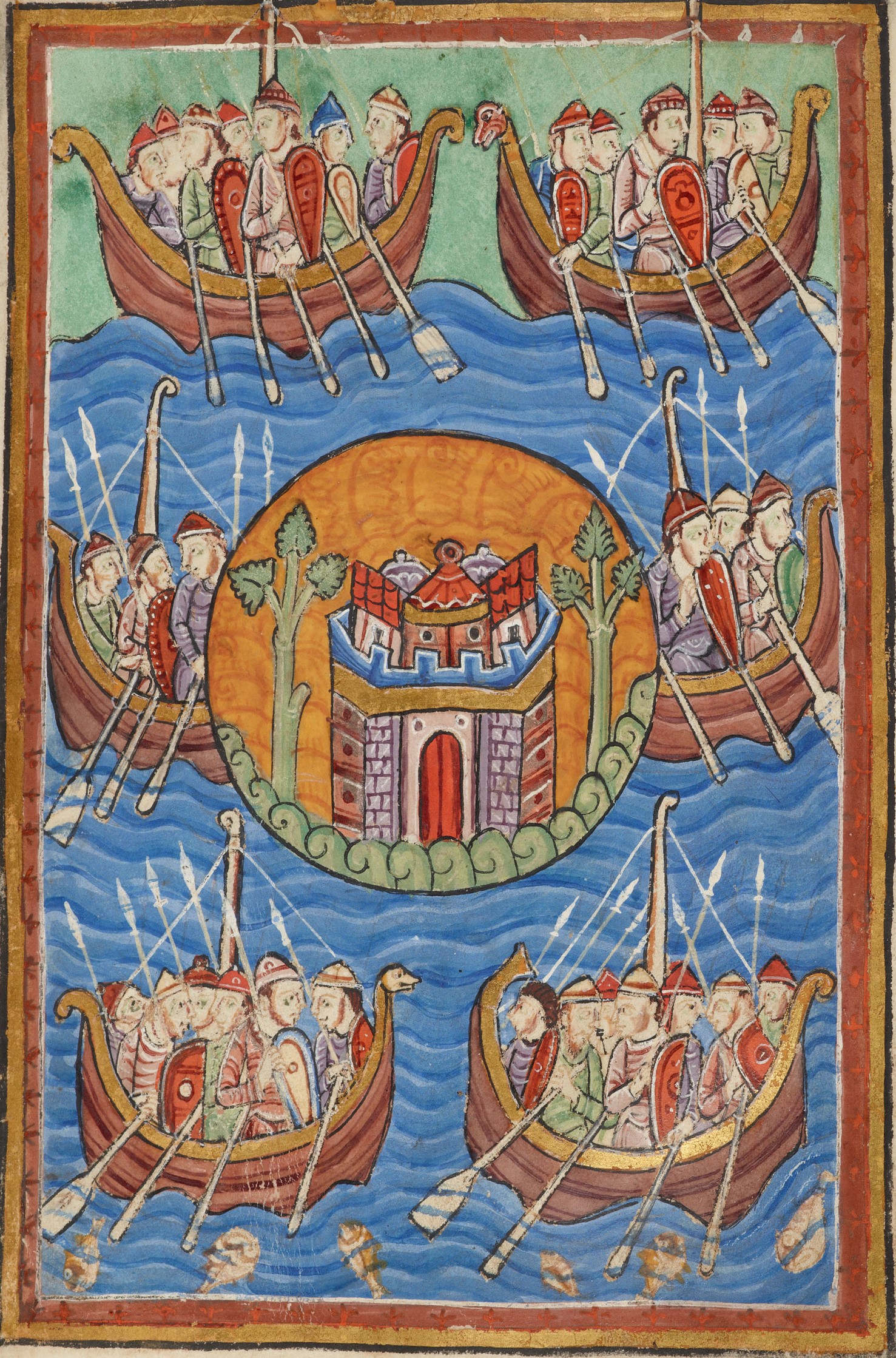
Anglo-Saxon Settlement Of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, spoken on the other side of the North Sea. The first Germanic speakers to settle Britain permanently are likely to have been soldiers recruited by the Roman administration in the 4th century AD, or even earlier. In the early 5th century, during the end of Roman rule in Britain and the breakdown of the Roman economy, larger numbers arrived, and their impact upon local culture and politics increased. There is Historiography of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, ongoing debate about the scale, timing and nature of the Anglo-Saxon settlements and also about what happened to the existing populations of the regions where the migrants settled. The available evidence includes a small number of medieval texts which emphasize Saxons, Saxon settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Migration Debate
The historiography on the Anglo-Saxon migration into Britain has tried to explain how there was a widespread change from Romano-British to Anglo-Saxon cultures in the area roughly corresponding to present-day England between the Fall of the Western Roman Empire and the eighth century, a time when there were scant historical records. From as early as the eighth century until around the 1970s, the traditional view of the settlement was a mass invasion in which "Anglo-Saxon" incomers exterminated or enslaved many of the native "Romano-British culture, Romano-British" inhabitants of Britain, driving the remainder from eastern Britain into western Britain and Brittany. This view has influenced many of the scholarly and popular perceptions of the process of anglicisation in Britain. It remains the starting point and default position from which other hypotheses are compared in modern reviews of the evidence. From the 1970s onwards there was Anglo-Saxon diffusionism, a reaction to this nar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corded Ware Culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between – 2350 BC, thus from the Late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded Ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine in the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. Autosomal genetic studies suggest that the Corded Ware culture originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures, evolving in parallel with (although under significant influence from) the Yamnaya; while the idea of direct male-line descent between them has not received significant support yet, IBD-sharing between the populations of these two cultures indicates that, at the very least, they came from a recent common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya ( ) or Yamna culture ( ), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–Caspian steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BC. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaeological excavations near the Donets River in 1901–1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: () is a Russian adjective that means (), as these people buried their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. Research in recent years has found that Mykhailivka, on the lower Dnieper River, Ukraine, formed the core Yamnaya culture (c. 3600–3400 BC). The Yamnaya culture is of particular interest to archaeologists and linguists, as the widely accepted Kurgan hypothesis posits that the people who produced the Yamnaya culture spoke a stage of the Proto-Indo-European language. The speakers of the Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Expansion
The Indo-European migrations are hypothesized migrations of peoples who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE) and the derived Indo-European languages, which took place from around 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially explaining how these related languages came to be spoken across a large area of Eurasia spanning from the Indian subcontinent and Iranian plateau to Atlantic Europe, in a process of cultural diffusion. While these early languages and their speakers are prehistoric (lacking documentary evidence), a synthesis of linguistics, archaeology, anthropology and genetics has established the existence of Proto-Indo-European and the spread of its daughter dialects through migrations of large populations of its speakers, as well as the recruitment of new speakers through emulation of conquering elites. Comparative linguistics describes the similarities between various languages governed by laws of systematic change, which allow the reconstruction of ancestral speech (see Indo-European stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiegel Online
' () is a German news website. It was established in 1994 as ''Spiegel Online'' as a content mirror of the magazine ''Der Spiegel''. In 1995, the site began producing original stories and it introduced ''Spiegel Online International'' for articles translated into English in 2004. The magazine and website were editorially aligned in 2019 and ''Spiegel Online'' was rebranded ''Der Spiegel'' in January 2020. Company and editorial staff Regular staff includes 150 people in the Hamburg headquarters, complemented by freelancers, and news bureaus both domestic and international. In the German capital, Berlin, 15 correspondents cover the German federal government, political parties, corporations and artists. The Munich and Düsseldorf offices have one correspondent each. There are journalists based in Washington, D.C., New York, London, Moscow, New Delhi and Istanbul. The online news staff also receives support from magazine's network of correspondents in Germany and abroad. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |