|
Andromeda (mythology)
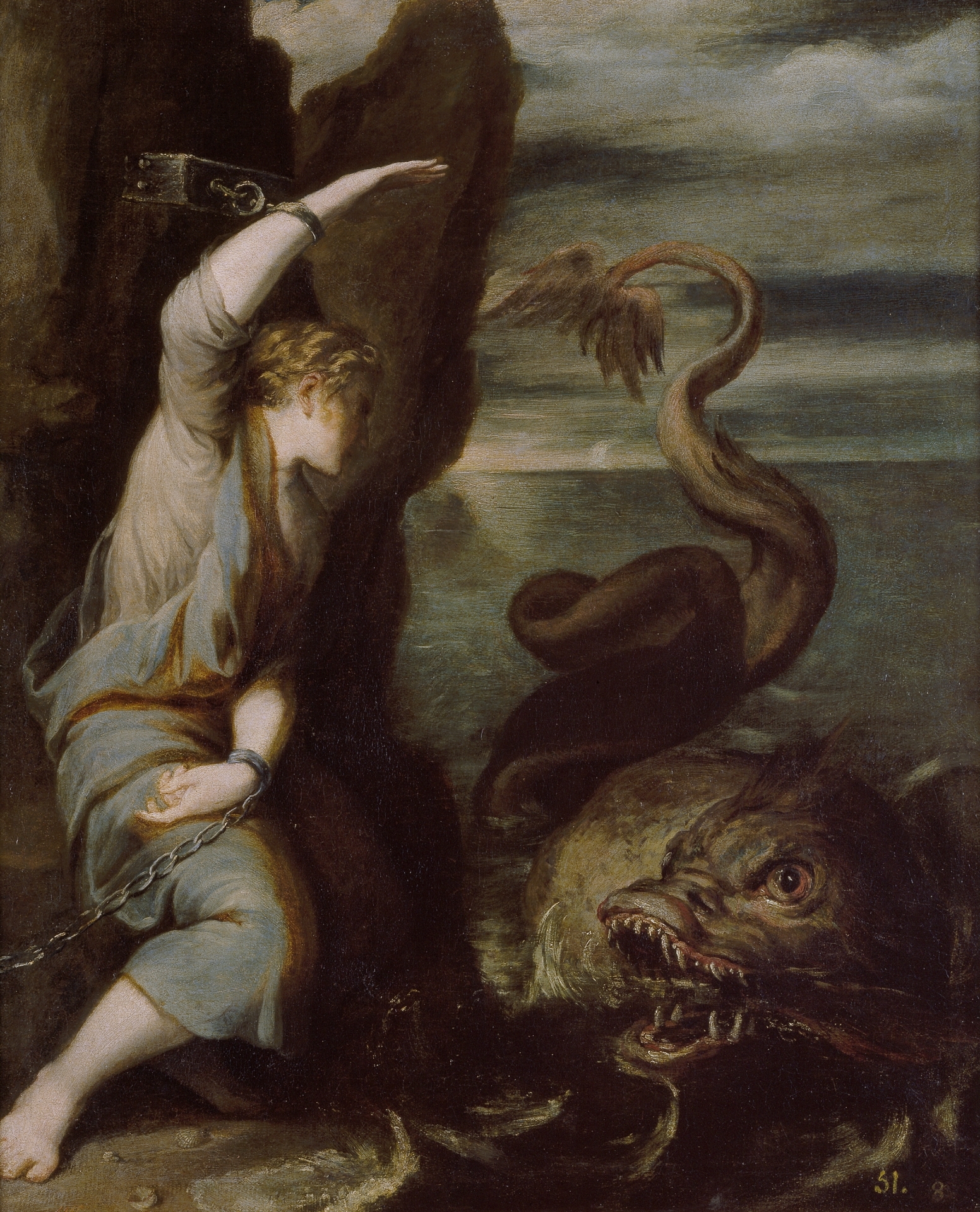
In Greek mythology, Andromeda (; or ) is the daughter of Cepheus (father of Andromeda), Cepheus, the king of Aethiopia, and his wife, Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia. When Cassiopeia boasts that she (or Andromeda) is more beautiful than the Nereids, Poseidon sends the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus to ravage the coast of Aethiopia as divine punishment. Queen Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia understands that chaining Andromeda to a rock as a human sacrifice is what will appease Poseidon. Perseus finds her as he is coming back from his quest to decapitate Medusa, and brings her back to Greece to marry her and let her reign as his queen. With the head of Medusa, Perseus Petrifaction in mythology and fiction, petrifies Cetus to stop it from terrorizing the coast any longer. As a subject, Andromeda has been popular in art since classical antiquity; rescued by a Greek hero cult, Greek hero, Andromeda's narration is considered the forerunner to the "pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
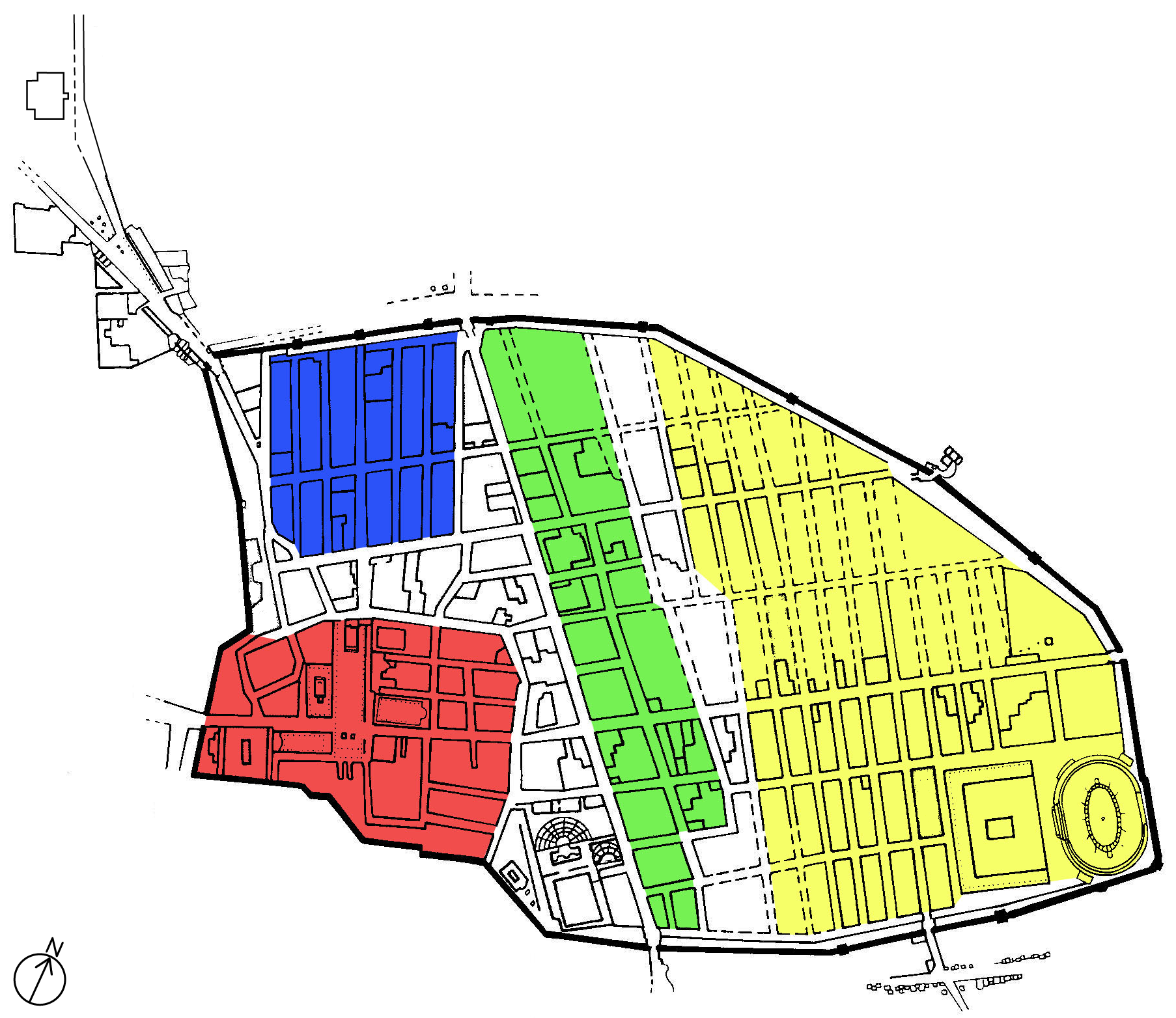
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cities and colonies. In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, Poseidon was venerated as a chief deity at Pylos and Thebes, with the cult title "earth shaker"; in the myths of isolated Arcadia, he is related to Demeter and Persephone and was venerated as a horse, and as a god of the waters.Seneca quaest. Nat. VI 6 :Nilsson Vol I p.450 Poseidon maintained both associations among most Greeks: he was regarded as the tamer or father of horses, who, with a strike of his trident, created springs (the terms for horses and springs are related in the Greek language).Nilsson Vol I p.450 His Roman equivalent is Neptune. Homer and Hesiod suggest that Poseidon became lord of the sea when, following the overthrow of his father Cronus, the world was divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphoses
The ''Metamorphoses'' (, , ) is a Latin Narrative poetry, narrative poem from 8 Common Era, CE by the Ancient Rome, Roman poet Ovid. It is considered his ''Masterpiece, magnum opus''. The poem chronicles the history of the world from its Creation myth, creation to the deification of Julius Caesar in a mythico-historical framework comprising over 250 myths, 15 books, and 11,995 lines. Although it meets some of the criteria for an epic poem, epic, the poem defies simple genre classification because of its varying themes and tones. Ovid took inspiration from the genre of metamorphosis poetry. Although some of the ''Metamorphoses'' derives from earlier treatment of the same myths, Ovid diverged significantly from all of his models. The ''Metamorphoses'' is one of the most influential works in Western culture. It has inspired such authors as Dante Alighieri, Giovanni Boccaccio, Geoffrey Chaucer, and William Shakespeare. Numerous episodes from the poem have been depicted in works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovid
Publius Ovidius Naso (; 20 March 43 BC – AD 17/18), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a younger contemporary of Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the three Western canon, canonical poets of Latin literature. The Roman Empire, Imperial scholar Quintilian considered him the last of the Latin love elegy, elegists.Quint. ''Inst.'' 10.1.93 Although Ovid enjoyed enormous popularity during his lifetime, the emperor Augustus Exile of Ovid, exiled him to Constanța, Tomis, the capital of the newly-organised province of Moesia, on the Black Sea, where he remained for the last nine or ten years of his life. Ovid himself attributed his banishment to a "poem and a mistake", but his reluctance to disclose specifics has resulted in much speculation among scholars. Ovid is most famous for the ''Metamorphoses'', a continuous mythological narrative in fifteen books written in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motif (narrative)
A motif ( ) is any distinctive feature or idea that recurs across a story; often, it helps develop other narrative elements such as theme or mood. A narrative motif can be created through the use of imagery, structural components, language, and other elements throughout literature. The flute in Arthur Miller's play '' Death of a Salesman'' is a recurrent sound motif that conveys rural and idyllic notions. Another example from modern American literature is the green light found in the novel '' The Great Gatsby'' by F. Scott Fitzgerald. Narratives may include multiple motifs of varying types. In Shakespeare's play ''Macbeth'', he uses a variety of narrative elements to create many different motifs. Imagistic references to blood and water are continually repeated. The phrase "fair is foul, and foul is fair" is echoed at many points in the play, a combination that mixes the concepts of good and evil. The play also features the central motif of the washing of hands, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess And Dragon
Princess and dragon is an Archetype, archetypical premise common to many legends, fairy tales, and chivalric romances. Northrop Frye identified it as a central form of the quest romance. The story involves an upper-class woman, generally a princess or similar high-ranking nobility, saved from a dragon, either a literal dragon or a similar danger, by the virtuous hero (see damsel in distress). She may be the first woman endangered by the peril, or may be the end of a long succession of women who were not of as high birth as she is, nor as fortunate. Normally the princess ends up married to the dragonslayer. The motifs of the hero who finds the princess about to be sacrificed to the dragon and saves her, the false hero who takes his place, and the final revelation of the true hero, are the identifying marks of the Aarne–Thompson folktale type 300, the Dragon-Slayer. They also appear in type 303, the Two Brothers. These two tales have been found, in different variants, in countrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Hero Cult
Hero cults were one of the most distinctive features of ancient Greek religion. In Homeric Greek, "hero" (, ) refers to the mortal offspring of a human and a god. By the historical period, the word came to mean specifically a ''dead'' man, venerated and propitiated at his tomb or at a designated shrine, because his fame during life or his unusual manner of death gave him power to support and protect the living. A hero was more than human but less than a Greek god, god, and various kinds of minor supernatural figures came to be assimilated to the class of heroes; the distinction between a hero and a god was less than certain, especially in the case of Heracles, the most prominent, but atypical hero. The grand ruins and Tumulus, tumuli (large burial mounds) remaining from the Bronze Age gave the pre-literate Greeks of the 10th century BC a sense of a once grand and now vanished age; they reflected this in the oral epic tradition, which would become famous by way of works such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrifaction In Mythology And Fiction
Petrifaction, or petrification, defined as turning people into solid stone, is a common theme in folklore and mythology, as well as in some works of modern literature. Amos Brown noted that "Fossils are to be found all over the world, a clear evidence to human beings from earliest times that living beings can indeed turn into stone (...) Previous to the modern scientific accounts of how fossils are formed, the idea of magicians or gods turning living creatures into stone seemed completely plausible in terms of these cultures". Historical Petrification is associated with the legends of Medusa (mythology), Medusa and the Svartálfar among others. In fairy tales, characters who fail in a quest may be turned to stone until they are rescued by the successful hero, as in the tales such as The Giant Who Had No Heart in His Body, The Water of Life (Spanish fairy tale), The Water of Life and The Dancing Water, the Singing Apple, and the Speaking Bird, as well as many troll tales. In Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medusa
In Greek mythology, Medusa (; ), also called Gorgo () or the Gorgon, was one of the three Gorgons. Medusa is generally described as a woman with living snakes in place of hair; her appearance was so hideous that anyone who looked upon her was Petrifaction in mythology and fiction, turned to stone. Medusa and her Gorgon sisters Euryale and Stheno were usually described as daughters of Phorcys and Ceto; of the three, only Medusa was mortal. Medusa was beheaded by the Greek hero Perseus, who then used her head, which retained its ability to turn onlookers to stone, as a weapon until he gave it to the goddess Athena to place on her Aegis, shield. In classical antiquity, the image of the head of Medusa appeared in the apotropaic magic, evil-averting device known as the ''Gorgoneion''. According to Hesiod and Aeschylus, she lived and died on Sarpedon, somewhere near Cisthene (Mysia), Cisthene. The 2nd-century BC novelist Dionysios Skytobrachion puts her somewhere in Ancient Libya, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
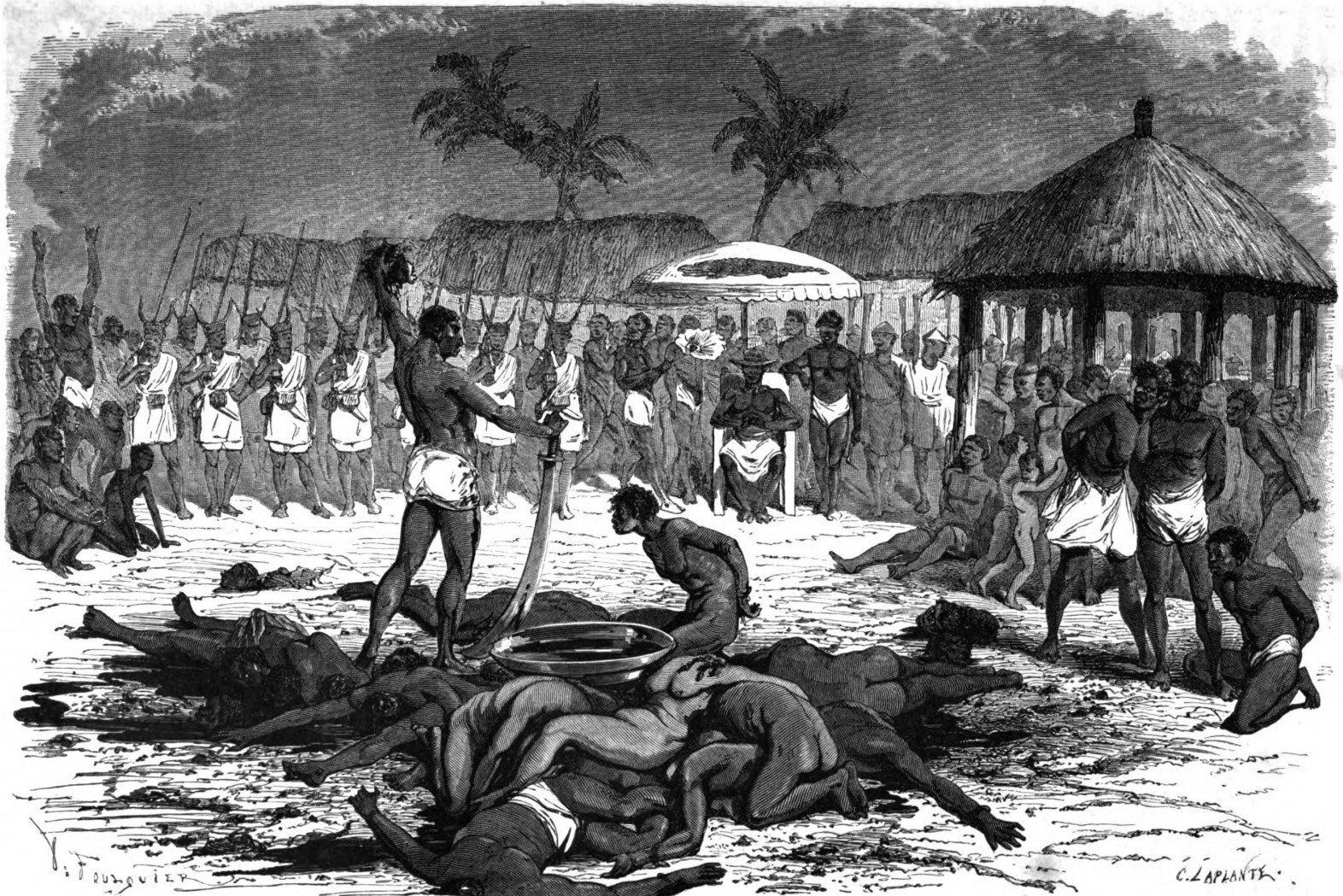
Human Sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/priestly figure, spirits of veneration of the dead, dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein a monarch's servants are killed in order for them to continue to serve their master in the next life. Closely related practices found in some tribe, tribal societies are human cannibalism, cannibalism and headhunting. Human sacrifice is also known as ritual murder. Human sacrifice was practiced in many human societies beginning in prehistoric times. By the Iron Age with the associated developments in religion (the Axial Age), human sacrifice was becoming less common throughout Africa, Europe, and Asia, and came to be looked down upon as barbarian, barbaric during classical antiquity. In the New World, Americas, however, human sacrifice cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |