|
Amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels. IAPP is processed from an 89-residue coding sequence. Proislet amyloid polypeptide (proIAPP, proamylin, proislet protein) is produced in the pancreatic beta cells (β-cells) as a 67 amino acid, 7404 Dalton pro-peptide and undergoes post-translational modifications including protease cleavage to produce amylin. Synthesis ProIAPP consists of 67 amino acids, which follow a 22 amino acid signal peptide which is rapidly cleaved after translation of the 89 amino acid coding sequence. The human sequence (from N-terminus to C-terminus) is: (MGILKLQVFLIVLSVALNHLKA) TPIESHQVEKR^ KCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTYG^ KR^ NAVEVLKREP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
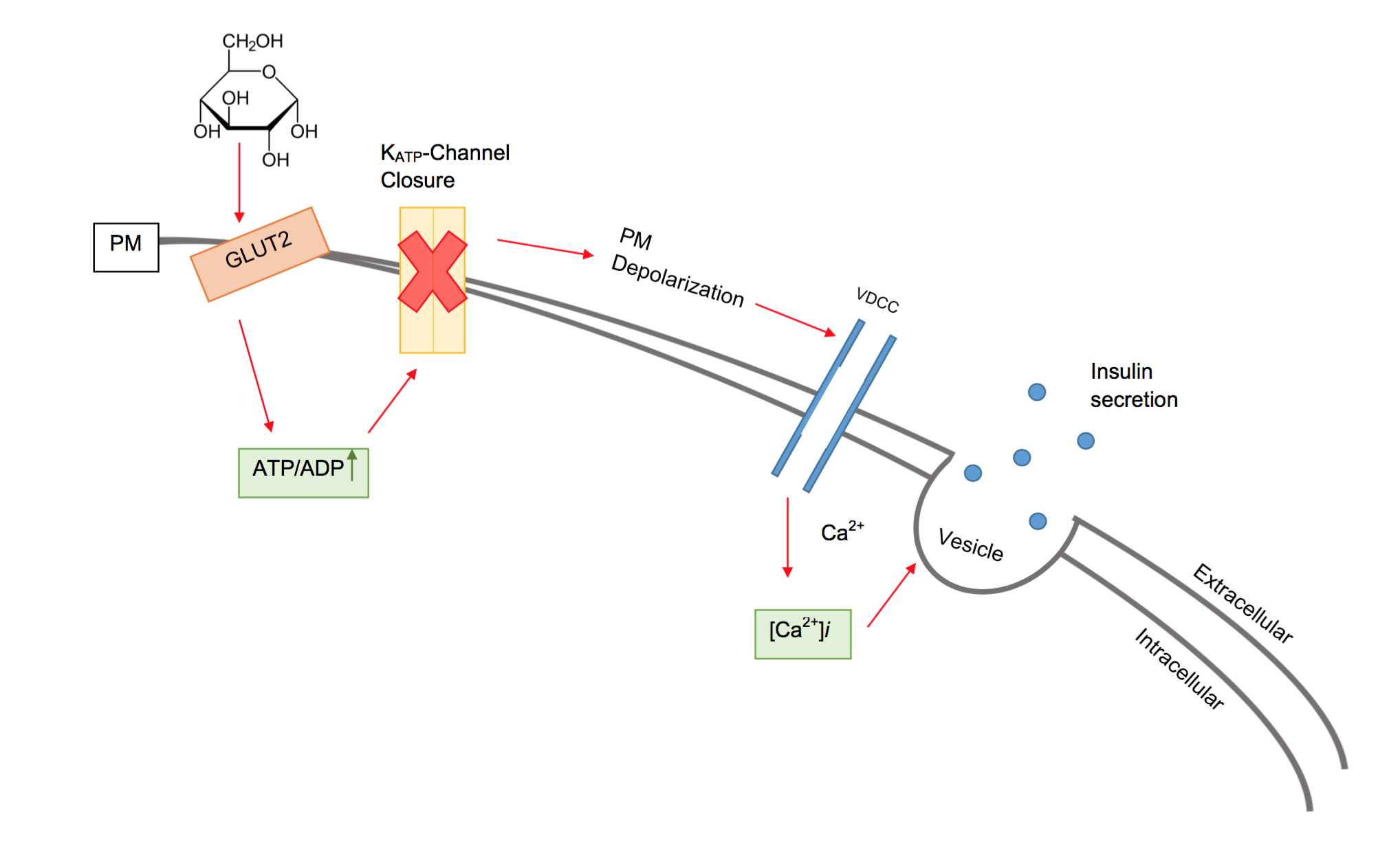
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cells
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Hormone
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid hormones. Amino-acid-based hormones are water-soluble and act on target cells via second messenger systems, whereas steroid hormones, being lipid-soluble, diffuse through plasma membranes to interact directly with intracellular receptors in the cell nucleus. Like all peptides, peptide hormones are synthesized in cell (biology), cells from amino acids based on Messenger RNA, mRNA transcripts, which are derived from DNA templates inside the cell nucleus. The initial precursors, known as preprohormones, undergo processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. This includes the removal of the N-terminal signal peptide and, in some cases, glycosylation, yielding prohormones. These prohormones are then packaged into secretory vesicle (biology), vesicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acids
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors on other cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, a family of transmembrane proteins that are cytokines, chemical messengers of the immune system. Excessive production of TNF plays a critical role in several inflammatory diseases, and TNF-blocking drugs are often employed to treat these diseases. TNF is produced primarily by macrophages but is also produced in several other cell types, such as T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and mast cells. It is produced rapidly in response to pathogens, cytokines, and environmental stressors. TNF is initially produced as a type II transmembrane protein (tmTNF), which is then cleaved by TNF alpha converting enzyme (TACE) into a soluble form (sTNF) and secreted from the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance can be improved or reversed with lifestyle approaches, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprotein Convertase 2
Proprotein convertase 2 (PC2) also known as prohormone convertase 2 or neuroendocrine convertase 2 (NEC2) is a serine protease and proprotein convertase PC2, like proprotein convertase 1 (PC1), is an enzyme responsible for the first step in the maturation of many neuroendocrine peptides from their precursors, such as the conversion of proinsulin to insulin intermediates. To generate the bioactive form of insulin (and many other peptides), a second step involving the removal of C-terminal basic residues is required; this step is mediated by carboxypeptidases E and/or D. PC2 plays only a minor role in the first step of insulin biosynthesis, but a greater role in the first step of glucagon biosynthesis compared to PC1. PC2 binds to the neuroendocrine protein named 7B2, and if this protein is not present, proPC2 cannot become enzymatically active. 7B2 accomplishes this by preventing the aggregation of proPC2 to inactivatable forms. The C-terminal domain of 7B2 also inhibits PC2 act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipotoxicity
Lipotoxicity is a metabolic syndrome that results from the accumulation of lipid intermediates in non-adipose tissue, leading to cellular dysfunction and death. The tissues normally affected include the kidneys, liver, heart and skeletal muscle. Lipotoxicity is believed to have a role in heart failure, obesity, and diabetes, and is estimated to affect approximately 25% of the adult American population. Cause In normal cellular operations, there is a balance between the production of lipids, and their oxidation or transport. In lipotoxic cells, there is an imbalance between the amount of lipids produced and the amount used. Upon entrance of the cell, fatty acids can be converted to different types of lipids for storage. Triacylglycerol consists of three fatty acids bound to a glycerol molecule and is considered the most neutral and harmless type of intracellular lipid storage. Alternatively, fatty acids can be converted to lipid intermediates like diacylglycerol, ceramides and fatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidylglycine Alpha-amidating Monooxygenase
Peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase, or PAM, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an n+1 residue long peptide with a C-terminal glycine into an n-residue peptide with a terminal amide group. In the process, one molecule of is consumed and the glycine residue is removed from the peptide and converted to glyoxylic acid. The enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of many signaling peptides and some fatty acid amides. In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the '' PAM'' gene. This transformation is achieved by conversion of a prohormone to the corresponding amide (C(=O)NH2). This enzyme is the only known pathway for generating peptide amides. Replacing the carboxylic acid group with an amide group makes the peptide more hydrophobic and more likely to be neutrally charged at physiologic pH, and it is believed that these neutrally charged peptide amides can more easily bind to receptors. Function This gene encodes a multifunctional protein. It has two enzymatical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |