|
Amphiregulin
Amphiregulin, also known as AREG, is a protein synthesized as a transmembrane glycoprotein with 252 aminoacids and it is encoded by the ''AREG'' gene. in humans. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family. It is a critical autocrine growth factor as well as a mitogen for astrocytes, Schwann cells, and fibroblasts. It is a ligand for epidermal growth factor (EGF) and it is related to transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha). This protein interacts with the Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to promote the growth of normal epithelial cells. Biological role AREG is a critical factor in estrogen action and ductal development of the mammary glands. Amphiregulin has been found to be essential for mammary ductal development, as evidenced by absence of ductal growth in amphiregulin knockout mice. This is similar to the phenotypes of EGFR and ERα knockout mice, which also show absence of ductal growth. Amphiregulin i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor (biochemistry), receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF family) of extracellular protein ligand (biochemistry), ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB, ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/neu (ErbB-2), ERBB3, Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). In many cancer types, mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor was discovered by Stanley Cohen (biochemist), Stanley Cohen of Vanderbilt University. Cohen shared the 1986 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Rita Levi-Montalcini for their discovery of growth factors. Deficient signaling of the EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases in humans is associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, while over-expression is associated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Lymphoid Cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of Innate immune system, innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of Cytokine, signalling molecules, and the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune cells. ILCs are primarily tissue resident cells, found in both Lymphatic system, lymphoid (immune associated), and non- lymphoid tissues, and rarely in the blood. They are particularly abundant at mucosal surfaces, playing a key role in mucosal immunity and homeostasis. Characteristics allowing their differentiation from other immune cells include the regular Lymphocyte, lymphoid morphology, absence of rearranged antigen receptors found on T cell receptor, T cells and B cell receptor, B cells (due to the lack of the recombination-activating gene, RAG gene), and phenotypic markers usually present on Myelocyte, myeloid or dendritic cells. Based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
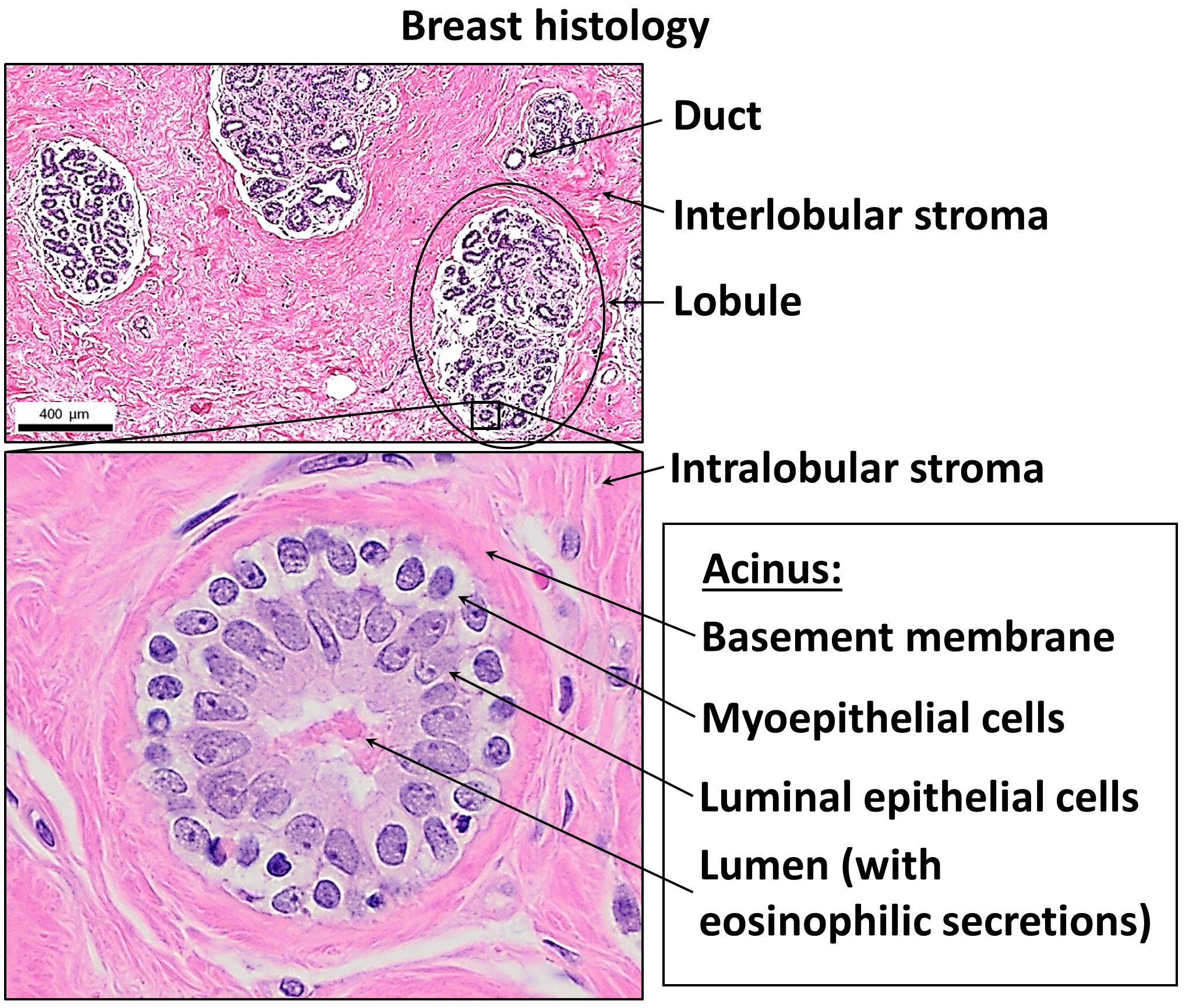
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats) to feed young offspring. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: monotremes, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of monotremes, their mammary glands are modified seba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KLRG1
Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KLRG1'' gene. Function Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without previous activation. They can also regulate specific humoral and cell-mediated immunity. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the killer cell lectin-like receptor (KLR) family, which is a group of transmembrane proteins preferentially expressed in NK cells. Studies in mice suggested that the expression of this gene may be regulated by MHC class I molecules. KLRG1 is a lymphocyte co-inhibitory, or immune checkpoint, receptor expressed predominantly on late-differentiated effector and effector memory CD8+ T and NK cells. Its ligands are E-cadherin and N-cadherin Cadherin-2 also known as Neural cadherin (N-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH2'' gene. CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 (cluster of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death Protein 1
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), (CD279 cluster of differentiation 279). PD-1 is a protein encoded in humans by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor on T cells and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint and guards against autoimmunity through two mechanisms. First, it promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nodes. Second, it reduces apoptosis in regulatory T cells (anti-inflammatory, suppressive T cells). PD-1 inhibitors, a new class of drugs that block PD-1, activate the immune system to attack tumors and are used to treat certain types of cancer. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobulin sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD103
Integrin, alpha E (ITGAE) also known as CD103 (cluster of differentiation 103) is an integrin protein that in human is encoded by the ''ITGAE'' gene. CD103 binds integrin beta 7 (β7– ITGB7) to form the complete heterodimeric integrin molecule αEβ7, which has no distinct name. The αEβ7 complex is often referred to as "CD103" though this strictly refers only to the αE chain. Note that the β7 subunit can bind with other integrin α chains, such as α4 (CD49d). Tissue distribution CD103 is expressed widely on intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) T cells (both αβ T cells and γδ T cells) and on some peripheral regulatory T cells (Tregs). It has also been reported on lamina propria T cells. A subset of dendritic cells in the gut mucosa and mesenteric lymph nodes, known as CD103 dendritic cells, also expresses this marker. It is useful in identifying hairy cell leukemia which is positive for this marker in contrast to most other hematologic malignancies which are negative fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD62L
L-selectin, also known as CD62L, is a cell adhesion molecule found on the cell surface of leukocytes, and the blastocyst. It is coded for in the human by the ''SELL'' gene. L-selectin belongs to the selectin family of proteins, which recognize sialylated carbohydrate groups containing a Sialyl LewisX (sLeX) determinant. L-selectin plays an important role in both the innate and adaptive immune responses by facilitating leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion events. These tethering interactions are essential for the trafficking of monocytes and neutrophils into inflamed tissue as well as the homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. L-selectin is also expressed by lymphoid primed hematopoietic stem cells and may participate in the migration of these stem cells to the primary lymphoid organs. In addition to its function in the immune response, L-selectin is expressed on embryonic cells and facilitates the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrial endothelium during human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD44
The CD44 antigen is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell–cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. In humans, the CD44 antigen is encoded by the ''CD44'' gene on chromosome 11. CD44 has been referred to as HCAM (homing cell adhesion molecule), Pgp-1 (phagocytic glycoprotein-1), Hermes antigen, lymphocyte homing receptor, ECM-III, and HUTCH-1. Tissue distribution and isoforms CD44 is expressed in a large number of mammalian cell types. The standard isoform, designated CD44s, comprising exons 1–5 and 16–20 is expressed in most cell types. CD44 splice variants containing variable exons are designated CD44v. Some epithelial cells also express a larger isoform (CD44E), which includes exons v8–10. Function CD44 participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. CD44 is a receptor for hyaluronic acid and internalizes metals bound to hyaluronic acid and can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocrine Signaling
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with paracrine signaling, intracrine signaling, or classical endocrine signaling. Examples An example of an autocrine agent is the cytokine interleukin-1 in monocytes. When interleukin-1 is produced in response to external stimuli, it can bind to cell-surface receptors on the same cell that produced it. Another example occurs in activated T cell lymphocytes, i.e., when a T cell is induced to mature by binding to a peptide: MHC complex on a professional antigen-presenting cell and by the B7:CD28 costimulatory signal. Upon activation, "low-affinity" IL-2 receptors are replaced by "high-affinity" IL-2 receptors consisting of α, β, and γ chains. The cell then releases IL-2, which binds to its own new IL-2 receptors, causing self-stimulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-18 Receptor
The interleukin-18 receptor (IL-18R) is an interleukin receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Endometrial IL-18 receptor mRNA and the ratio of IL-18 binding protein to interleukin 18 are significantly increased in adenomyosis Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterized by the growth of cells that proliferate on the inside of the uterus (endometrium) atypically located among the cells of the uterine wall (myometrium), as a result, thickening of the uterus occurs. ... patients in comparison to normal people, indicating a role in its pathogenesis. References External links * Clusters of differentiation Immunoglobulin superfamily cytokine receptors {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-cell Receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex, located on the surface of T cells (also called T lymphocytes). They are responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is biologically degenerate (that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide, and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR). The TCR is composed of two different protein chains (that is, it is a hetero dimer). In humans, in 95% of T cells the TCR consists of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by '' TRA'' and ''TRB'', respectively), whereas in 5% of T cells the TCR consists of gamma and delta (γ/δ) chains (encoded by '' TRG'' and '' TRD'', respectively). This ratio changes during ontogeny and in diseased states (such as leukemia). It also differs between species. Orthologues of the 4 loci have been mapped in various speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain immune tolerance, tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppression, immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulation and upregulation, downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same cell lineage, lineage as naïve T helper cell, CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine Transforming growth factor beta, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |