|
Aminolysis
In chemistry, aminolysis (/am·i·nol·y·sis/) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule is Chemical decomposition, lysed (split into two parts) by reacting with ammonia () or an amine. The case where the reaction involves ammonia may be more specifically referred to as ammonolysis. Reaction Alkyl group An example of an aminolysis reaction is the replacement of a halogen in an alkyl group () by an amine () and the elimination of hydrogen halide (HX). : Synthesis of peptides Another common example is the reaction of a primary amine or secondary amine with a carboxylic acid or with a carboxylic acid derivative to form an amide. This reaction is widely used, especially in the synthesis of peptides. On the simple addition of an amine to a carboxylic acid, a salt of the organic acid and base is obtained. To overcome this, the carboxylic acid first needs to be "activated". This is usually done by converting the acid into a more reactive derivative (i.e. anhydride, acid halide) or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvolysis
In chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (S1/S2) or elimination reaction, elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of S1 reactions, solvolysis of a chirality (chemistry), chiral reactant affords the racemate. Sometimes however, the stereochemical course is complicated by intimate ion pairs, whereby the leaving anion remains close to the carbocation, effectively shielding it from an attack by the nucleophile. Particularly fast reactions can occur by neighbour group participation, with nonclassical ions as intermediates or transition states. Examples For certain nucleophiles, solvolysis reactions are classified. Solvolysis involving water (molecule), water is called hydrolysis. Related terms are alcoholysis (Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols) and specifically methanolysis (methanol), acetolysis, ammonolysis (ammonia), and aminolysis (alkyl amines). Glycolysis is however an older term for the multistep conversion of glucose to pyruvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonolysis
In chemistry, ammonolysis (/am·mo·nol·y·sis/) is the process of splitting ammonia into NH2- + H+. Ammonolysis reactions can be conducted with organic compounds to produce amines (molecules containing a nitrogen atom with a lone pair, :N), or with inorganic compounds to produce nitrides. This reaction is analogous to hydrolysis in which water molecules are split. Similar to water, liquid ammonia also undergoes auto-ionization, , where the rate constant is k = 1.9 × 10−38. Organic compounds such as alkyl halides, hydroxyls (hydroxyl nitriles and carbohydrates), carbonyl (aldehydes/ketones/esters/alcohols), and sulfur (sulfonyl derivatives) can all undergo ammonolysis in liquid ammonia. Organic synthesis Mechanism: Ammonolysis of Esters This mechanism is similar to the hydrolysis of esters, the ammonia attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The reformation of the C-O double bond ejects the ester. The alkoxide deprotonates the ammo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyl Chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, . Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides. Nomenclature Where the acyl chloride moiety takes priority, acyl chlorides are named by taking the name of the parent carboxylic acid, and substituting ''-yl chloride'' for ''-ic acid''. Thus: : : : butyr''ic acid'' (C3H7COOH) → butyr''yl chloride'' (C3H7COCl) (Idiosyncratically, for some trivial names, ''-oyl chloride'' substitutes ''-ic acid''. For example, pival''ic acid'' becomes pival''oyl chloride'' and acryl''ic acid'' becomes acryl''oyl chloride.'' The names pivalyl chloride and acrylyl chloride are less commonly used, although they are arguably more logical.) When other functional groups take priority, acyl chlorides a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well (e.g. amides), but not according to the IUPAC. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters; naturally occurring lactones are mainly 5- and 6-membered ring lactones. Lactones contribute to the aroma of fruits, butter, cheese, vegetables like celery and other foods. Esters can be formed from oxoacids (e.g. esters of acetic acid, carbonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PET Degradation With Polyamines Through Aminolysis Route
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, intelligence, and relatable personalities, but some pets may be taken in on an altruistic basis (such as a stray animal) and accepted by the owner regardless of these characteristics. Two of the most popular pets are dogs and cats. Other animals commonly kept include rabbits; ferrets; pigs; rodents such as gerbils, hamsters, chinchillas, rats, mice, and guinea pigs; birds such as parrots, passerines, and fowls; reptiles such as turtles, lizards, snakes, and iguanas; aquatic pets such as fish, freshwater snails, and saltwater snails; amphibians such as frogs and salamanders; and arthropod pets such as tarantulas and hermit crabs. Smaller pets include rodents, while the equine and bovine group include the largest companion animals. Pets provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyamine
A polyamine is an organic compound having two or more amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature. Natural polyamines Low-molecular-weight linear polyamines are found in all forms of life. The principal examples are the triamine spermidine and the tetraamine spermine. They are structurally and biosynthetically related to the diamines putrescine and cadaverine. Polyamine metabolism is regulated by the activity of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Polyamines are found in high concentrations in the mammalian brain. File:Spermidine-2D-skeletal.svg, spermidine File:Spermine.svg, spermine Synthetic polyamines Ethyleneamines are a commercially-important class of synthetic polyamines with ethylene ( linkages); global production capacity was estimated at 385,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydrate Ammonium Acetate
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild dehydration can also be caused by immersion diuresis, which may increase risk of decompression sickness in divers. Most people can tolerate a 3-4% decrease in total body water without difficulty or adverse health effects. A 5-8% decrease can cause fatigue and dizziness. Loss of over 10% of total body water can cause physical and mental deterioration, accompanied by severe thirst. Death occurs with a 15 and 25% loss of body water.Ashcroft F, Life Without Water in Life at the Extremes. Berkeley and Los Angeles, 2000, 134-138. Mild dehydration usually resolves with oral rehydration, but severe cases may need intravenous fluids. Dehydration can cause hypernatremia (high levels of sodium ions in the blood). This is distinct from hypovolemia (lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetamide
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is an amide derived from ammonia and acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound ''N'',''N''-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide. Acetamide can be considered an intermediate between acetone, which has two methyl (CH3) groups either side of the carbonyl (CO), and urea which has two amide (NH2) groups in those locations. Acetamide is also a naturally occurring mineral with the IMA symbol: Ace. Production Laboratory scale Acetamide can be produced in the laboratory from ammonium acetate by dehydration: : H4CH3CO2] → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O Alternatively acetamide can be obtained in excellent yield via ammonolysis of acetylacetone under conditions commonly used in reductive amination. It can also be made from anhydrous acetic acid, acetonitrile and very well dried hydrogen chloride gas, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
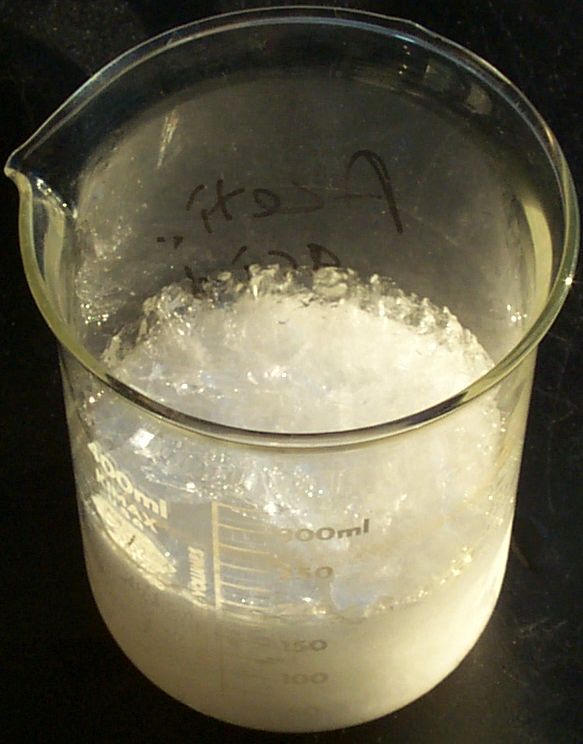
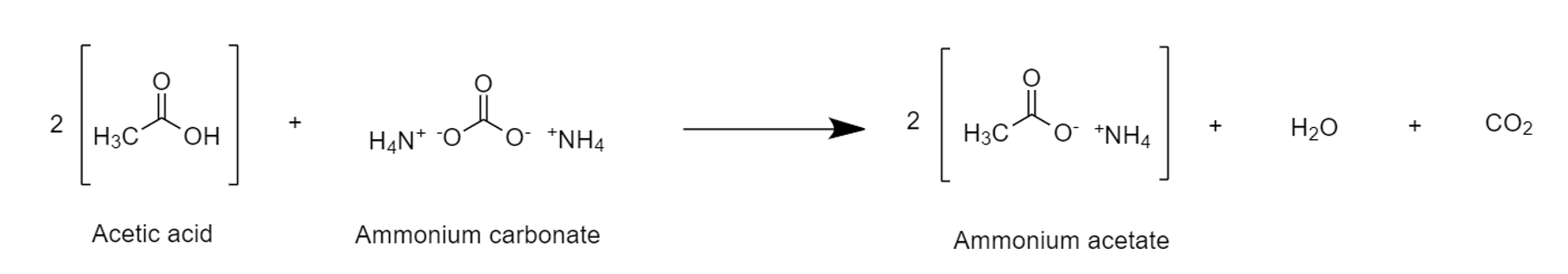
Carboxylic Acid React With Ammonium Carbonate
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Acetate
Ammonium acetate, also known as spirit of Mindererus in aqueous solution, is a chemical compound with the formula NH4CH3CO2. It is a white, hygroscopic solid and can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is available commercially. History The synonym Spirit of Mindererus is named after R. Minderer, a physician from Augsburg. Uses It is the main precursor to acetamide: :NH4CH3CO2 → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O It is also used as a diuretic. Buffer As the salt of a weak acid and a weak base, ammonium acetate is often used with acetic acid to create a buffer solution. Ammonium acetate is volatile at low pressures. Because of this, it has been used to replace cell buffers that contain non-volatile salts in preparing samples for mass spectrometry. It is also popular as a buffer for mobile phases for HPLC with ELSD and CAD-based detection for this reason. Other volatile salts that have been used for this include ammonium formate. When dissolving ammonium acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |