|
Aluminaut
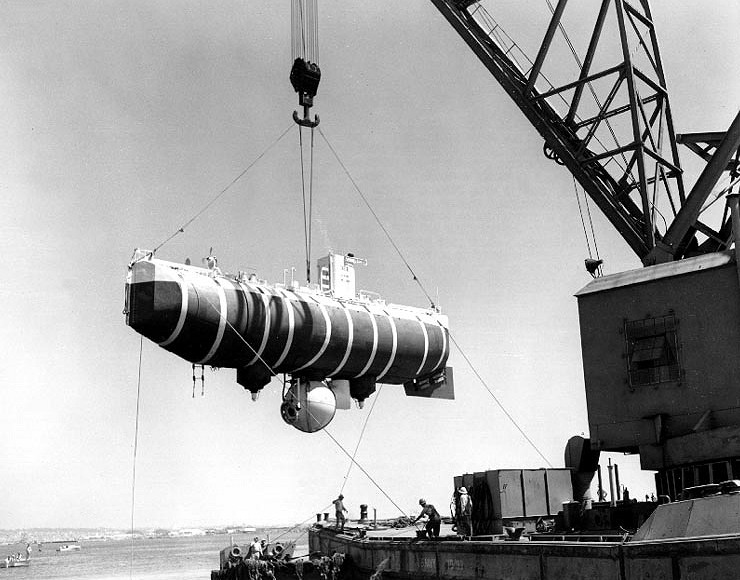
''Aluminaut'' (built in 1964) was the world's first aluminum submarine. An experimental vessel, the 80-ton, crewed deep-ocean research submersible was built by Reynolds Metals Company, which was seeking to promote the utility of aluminum. ''Aluminaut'' was based in Miami, Florida, and was operated from 1964 to 1970 by Reynolds Submarine Services, doing contract work for the U.S. Navy and other organizations, including marine biologist Jacques Cousteau. ''Aluminaut'' is best known for helping recover a lost unarmed U.S. hydrogen bomb in 1966 and recovering its smaller fellow deep-submergence vehicle, DSV ''Alvin'' in 1969, after ''Alvin'' had been lost and sank in the Atlantic Ocean the previous year. After retirement, ''Aluminaut'' was donated to the Science Museum of Virginia in Richmond, where it is on permanent display. 1964: World's first aluminium submarine Reynolds Metals was an early developer and manufacturer of aluminium products, including aluminium buses and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynolds Metals
Reynolds Group Holdings was a New Zealand–based packaging company with roots in the former Reynolds Metals Company, which was the second-largest aluminum company in the United States, and the third-largest in the world. Reynolds Metals was acquired by Alcoa in Reynolds Group Holdings became Pactiv Evergreen through an IPO in 2020. Reynolds Metals became known for the consumer product Reynolds Wrap foil, as well as for developing and promoting new uses for aluminum. Its RV '' Aluminaut'' submarine was operated by Reynolds Submarine Services Corporation. It was headquartered for most of its existence in Richmond, Virginia; the Modernist style Reynolds Metals Company International Headquarters was built there in 1958. History The Reynolds Metals Company was founded in 1919 as the U.S. Foil Company in Louisville, Kentucky, by Richard S. Reynolds Sr., nephew of tobacco king R. J. Reynolds. Initially, the new company supplied lead and tin foil wrappers to cigarette and candy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSV Alvin
''Alvin'' (DSV-2) is a crewed deep-ocean research submersible owned by the United States Navy and operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) of Woods Hole, Massachusetts. The original vehicle was built by General Mills' Electronics Group in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Named to honor the prime mover and creative inspiration for the vehicle, Allyn Vine, ''Alvin'' was commissioned on June 5, 1964. The submersible is launched from the deep submergence support vessel , which is also owned by the U.S. Navy and operated by WHOI. The submersible has made more than 5,200 dives, carrying two scientists and a pilot, observing the lifeforms that must cope with super-pressures and move about in total darkness, as well as exploring the wreck of ''Titanic''. Research conducted by ''Alvin'' has been featured in nearly 2,000 scientific papers. Design ''Alvin'' was designed as a replacement for bathyscaphes and other less maneuverable oceanographic vehicles. Its more nimble de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1966 Palomares B-52 Crash
The Palomares incident occurred on 17 January 1966, when a United States Air Force Boeing B-52 Stratofortress#Variants, B-52G bomber collided with a Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker, KC-135 tanker during Aerial refueling, mid-air refueling at over the Mediterranean Sea, near the Spanish village of Palomares, Almería, Palomares in Province of Almería, Almería province. The collision destroyed the tanker, killing all four crew members, and caused the bomber to break apart, resulting in the deaths of three of its seven crew members. The B-52G was participating in Operation Chrome Dome, a Cold War airborne alert mission involving continuous flights of nuclear-armed bombers. At the time of the accident, the B-52G was carrying four B28 nuclear bomb, B28FI Mod 2 Y1 Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear bombs. Three of these bombs fell on land near Palomares; the conventional explosives in two detonated upon impact, dispersing plutonium and Radioactive contamination, contaminating approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep-submergence Vehicle
A deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) is a deep-diving crewed submersible that is self-propelled. Several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs. DSVs are commonly divided into two types: research DSVs, which are used for exploration and surveying, and DSRVs ( deep-submergence rescue vehicles), which are intended to be used for rescuing the crew of a sunken navy submarine, clandestine (espionage) missions (primarily installing wiretaps on undersea communications cables), or both. DSRVs are equipped with docking chambers to allow personnel ingress and egress via a manhole. Strictly speaking, bathyscaphes are not submarines because they have minimal mobility and are built like a balloon, using a habitable spherical pressure vessel hung under a liquid hydrocarbon filled float drum. In a DSV/DSRV, the passenger compartment and the ballast tank functionality is incorporated into a single structure to afford more habitable space (up to 24 people in the case of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Museum Of Virginia
The Science Museum of Virginia is a science museum located in Richmond, Virginia. Established in 1970, it is an agency of the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is housed in the former Broad Street Station, built in 1917. History Early proposals In 1906, the Virginia General Assembly approved funds for the construction of a simple "exhibits center" to display mineral and timber exhibits being assembled for the Jamestown Exposition of 1907. After the exposition ended, many of the items were moved to Richmond's Capitol Square. The "State Museum" as it came to be known opened in 1910, adding displays of natural historical specimens from a variety of state agencies to its collection over the years. In 1942, the General Assembly created a study commission to consider establishing an official State science museum. That commission succeeded in endorsing the creation of a "Virginia Museum of Science" in 1943. The fiscal restraints and pressing concerns of World War II – and the rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by joints allowing either rotational motion (such as in an articulated robot) or translational (linear) displacement. The links of the manipulator can be considered to form a kinematic chain. The terminus of the kinematic chain of the manipulator is called the end effector and it is analogous to the human hand. However, the term "robotic hand" as a synonym of the robotic arm is often proscribed. Types * Cartesian robot / Gantry robot: Used for pick and place work, application of sealant, assembly operations, handling machine tools and arc welding. It is a robot whose arm has three prismatic joints, whose axes are coincident with a Cartesian coordinator. * Collaborative robot / Cobot: Cobot applications contrast with traditional industri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI, acronym pronounced ) is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering. Established in 1930 in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, it is the largest independent oceanographic research institution in the U.S., with staff and students numbering about 1,000. Constitution The institution is organized into six departments, the Cooperative Institute for Climate and Ocean Research, and a marine policy center. Its shore-based facilities are located in the village of Woods Hole, Massachusetts, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, United States and a mile and a half away on the Quissett Campus. The bulk of the institution's funding comes from grants and contracts from the National Science Foundation and other government agencies, augmented by foundations and private donations. WHOI scientists, engineers, and students collaborate to develop theories, test ideas, build seagoing instruments, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conning Tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armoured, from which an officer in charge can conn (nautical), conn (conduct or control) the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and ground tackle. It is usually located as high on the ship as is practical, to give the conning team good visibility of the entirety of the ship, ocean conditions, and other vessels. The naval term "conn" may derive from the Middle English ''conne'' (study, become acquainted with) or French ''conduire'' from Latin ''conducere'' (conduct). Surface ships On surface ships, the conning tower was a feature of all battleships and armored cruiser, armoured cruisers from about 1860 to the early years of World War II. Located at the front end of the superstructure, the conning tower was a heavily armored cylinder, with tiny slit windows on three sides providing a reasonable field of view. Designed to shield j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woods Hole
Woods Hole is a census-designated place in the town of Falmouth in Barnstable County, Massachusetts, United States. It lies at the extreme southwestern corner of Cape Cod, near Martha's Vineyard and the Elizabeth Islands. The population was 781 at the 2010 census. It is the site of several marine science institutions, including Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, the Marine Biological Laboratory, the Woodwell Climate Research Center, NOAA's Northeast Fisheries Science Center (which started the Woods Hole scientific community in 1871), the Woods Hole Science Aquarium, a USGS coastal and marine geology center, and the home campus of the Sea Education Association. Woods Hole is also the site of United States Coast Guard Sector Southeastern New England (formerly USCG Group Woods Hole), the Nobska Light lighthouse, and the terminus of the Steamship Authority ferry route between Cape Cod and the island of Martha's Vineyard. History Historically, Woods Hole included one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |