|
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum Variables
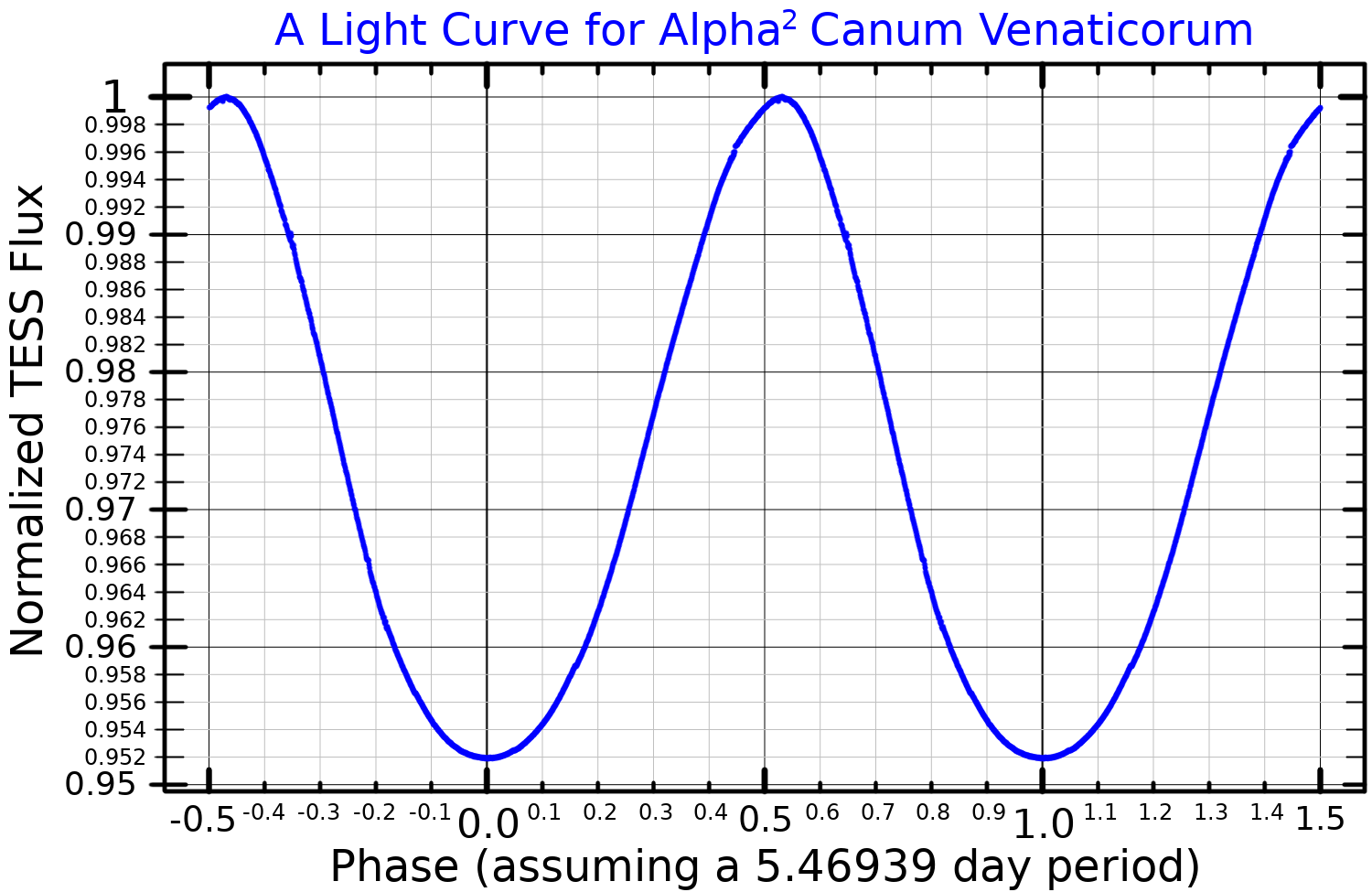
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of stellar magnetic field, magnetic variable star. These are chemically peculiar stars of the CP2 type that are Photometry (astronomy), photometrically variable. That is, they are upper main sequence stars of stellar classification, spectral class B8p to A7p, with strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chromium spectral lines. Their brightness typically varies by 0.01 to 0.1 Apparent magnitude, magnitudes over the course of 0.5 to 160 days. The first CP2 variable to be discovered was Cor_Caroli#α2_Canum_Venaticorum, α2 Canum Venaticorum, a star in the binary system of Cor Caroli, which lies in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici. Its brightness fluctuates by 0.14 magnitudes with a period of 5.47 days. This is now the prototype of the α2 CVn class of variables. In addition to their brightness, the intensities and profiles of the spectral lines of α2 CVn variables vary, as do their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha2CVnLightCurve
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first Letter (alphabet), letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter ''Aleph#Origin, aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for 'ox'. Letters that arose from alpha include the Latin script, Latin letter and the Cyrillic letter . Uses Greek In Ancient Greek, alpha was pronounced and could be either phoneme, phonemically long ([aː]) or short ([a]). Where there is ambiguity, long and short alpha are sometimes written with a Macron (diacritic), macron and breve today: . * = ' "a time" * = ' "tongue" In Modern Greek, vowel length has been lost, and all instances of alpha simply represent the open front unrounded vowel . In the polytonic Greek, polytonic orthography of Greek, alpha, like other vowel letters, can occur with several diacritic marks: any of three accent symbols (), and either of two breathing marks ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Atmosphere
The stellar atmosphere is the outer region of the volume of a star, lying above the stellar core, radiation zone and convection zone. Overview The stellar atmosphere is divided into several regions of distinct character: * The photosphere, which is the atmosphere's lowest and coolest layer, is normally its only visible part. Light escaping from the surface of the star stems from this region and passes through the higher layers. The Sun's photosphere has a temperature in the range. Starspots, cool regions of disrupted magnetic field, lie in the photosphere. * Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere. This part of the atmosphere first cools down and then starts to heat up to about 10 times the temperature of the photosphere. * Above the chromosphere lies the transition region, where the temperature increases rapidly on a distance of only around . * Additionally, many stars have a molecular layer (MOLsphere) above the photosphere and just beyond or even within the chromosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Hydrae
Beta Hydrae, Latinized from β Hydrae, is a double star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. Historically, Beta Hydrae was designated 28 Crateris, but the latter fell out of use when the IAU defined the permanent constellation boundaries in 1930. The system is faintly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude that ranges around 4.29. It is located at a distance of approximately 310 light years from the Sun based on parallax. The double nature of this system was first reported by English astronomer John Herschel in 1834. The brighter primary, designated component A, has an average visual magnitude of 4.67, while the secondary, component B, is of magnitude 5.47. As of 2002, the secondary is located at an angular separation of from the primary, along a position angle of 28.5°. The brighter component is an α2 Canum Venaticorum variable that changes in brightness with a period of 2.344 days and an amplitude of 0.04 in vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisces (constellation)
Pisces is a constellation of the zodiac. Its vast bulk – and main asterism viewed in most European cultures per Greco-Roman antiquity as a distant pair of fishes connected by one cord each that join at an apex – are in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its old astronomical symbol is (♓︎). Its name is Latin for "fishes". It is between Aquarius (constellation), Aquarius, of similar size, to the southwest and Aries (constellation), Aries, which is smaller, to the east. The ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect within this constellation and in Virgo (constellation), Virgo. The Sun subsolar point, passes directly overhead of the equator, on average, at approximately this point in the sky, at the March equinox. The right ascension/declination 00 is located within the boundaries of Pisces. Features The March equinox is currently located in Pisces, due south of Psc, and, due to precession, slowly drifting due west, just below the western fish towards Aquari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Piscium
Alpha Piscium (α Piscium) is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Pisces. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Hipparcos spacecraft, it is about from the Solar System. The two components are designated Alpha Piscium A (officially named Alrescha , the traditional name of the system) and B. Nomenclature ''α Piscium'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Piscium'') is the star's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Alpha Piscium A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The system bore the traditional name ''Alrescha'' (alternatively ''Al Rescha'', ''Alrischa'', ''Alrisha'') derived from the Arabic الرشآء ''ar-Rishā’'' "the cord" and less commonly ''Kaitain'' and ''Okda'', the latter from the Arabic عقدة ''ʽuqdah'' "knot" (see Ukdah. In 2016, the International Astronomical Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorado
Dorado (, ) is a constellation in the Southern Sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the mahi-mahi (''Coryphaena hippurus''), which is known as ''dorado'' ("golden") in Spanish, although it has also been depicted as a swordfish. Dorado contains most of the Large Magellanic Cloud, the remainder being in the constellation Mensa. The South Ecliptic pole also lies within this constellation. Even though the name Dorado is not Latin but Spanish, astronomers give it the Latin genitive form ''Doradus'' when naming its stars; it is treated (like the adjacent asterism Argo Navis) as a feminine proper name of Greek origin ending in -ō (like ''Io'' or ''Callisto'' or ''Argo''), which have a genitive ending ''-ūs''. History Dorado was one of twelve constellations named by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It appeared: * On a celestial globe published in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Doradus
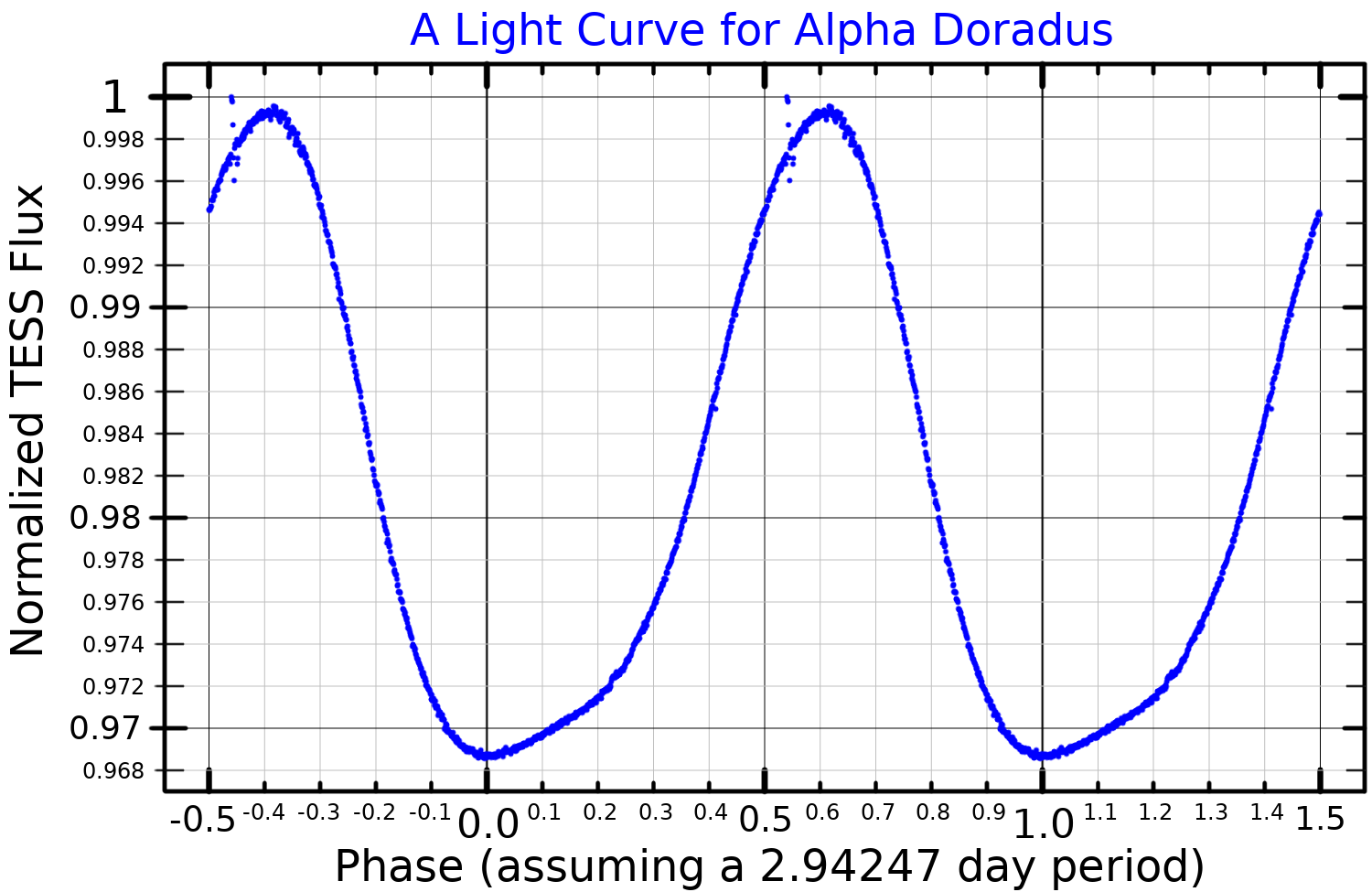
Alpha Doradus, Latinized from α Doradus, is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Dorado. The distance to this system, as measured using the parallax method, is about . This is a binary star system with an overall apparent visual magnitude that varies between 3.26 and 3.30, making this one of the brightest binary stars. The system consists of a subgiant star of spectral type B revolving around a giant star with spectral type A in an eccentric orbit with a period of about 12 years. The orbital separation varies from 2 astronomical units at periastron to 17.5 astronomical units at apastron. The primary, α Doradus A, is a chemically peculiar star whose atmosphere displays an abnormally high abundance of silicon, making this an Si star. Alpha Doradus has an optical companion, CCDM J04340-5503C, located 77 arcseconds away along a position angle In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper", "the Wagon", "Charles's Wain", or "the Plough", among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the " Little Dipper". Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alioth
Alioth , also called Epsilon Ursae Majoris, is a star in the northern constellation of Ursa Major. The designation is Latinised from ε Ursae Majoris and abbreviated Epsilon UMa or ε UMa. Despite being designated "ε" (epsilon), it is the brightest star in the constellation and at magnitude 1.77 is the thirty-third brightest star in the sky. It is the star in the tail of the bear closest to its body, and thus the star in the handle of the Big Dipper (or Plough) closest to the bowl. It is also a member of the large and diffuse Ursa Major moving group. Historically, the star was frequently used in celestial navigation in the maritime trade, because it is listed as one of the 57 navigational stars. Physical characteristics According to ''Hipparcos'', Epsilon Ursae Majoris is from the Sun. Its spectral type is A1p; the "p" stands for '' peculiar'', as its spectrum is characteristic of an α2 Canum Venaticorum variable. Epsilon Ursae Majoris, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cor Caroli
Cor Caroli is a binary star in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici. It is the brightest star in the constellation, lying at the third magnitude. The International Astronomical Union uses the name "Cor Caroli" specifically for the brighter star of the binary. The system has the Bayer designation Alpha Canum Venaticorum or α Canum Venaticorum. Nomenclature ''α Canum Venaticorum'', Romanization of Greek, Latinised to ''Alpha Canum Venaticorum'', is the system's Bayer designation. The brighter of the two stars is designated ''α2 Canum Venaticorum'', the fainter ''α1 Canum Venaticorum''. In the western world Alpha Canum Venaticorum had no name until the 17th century, when it was named ''Cor Caroli'', which means "Charles's Heart". There has been some uncertainty whether it was named in honour of King Charles I of England, who was executed in 1649 during the English Civil War, or of his son, Charles II of England, Charles II, who Stuart Restoration, restored the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naked Eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microscope, or eye protection. In astronomy, the naked eye may be used to observe celestial events and astronomical object, objects visible without equipment, such as conjunction (astronomy), conjunctions, passing comets, meteor showers, and the brightest asteroids, including 4 Vesta. Sky lore and various tests demonstrate an impressive variety of phenomena visible to the unaided eye. Basic properties Some basic properties of the human eye are: *Quick autofocus from distances of 25 cm (young people) to 50 cm (most people 50 years and older) to infinity. *Angular resolution: about 1 arcminute, approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians, which corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance. *Field of view (FOV): simultaneous visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. In its turn, the magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its angular speed decreases. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |