|
Alexander Ure, 1st Baron Strathclyde
Alexander Ure, 1st Baron Strathclyde, (22 February 1853 – 2 October 1928) was a Scottish politician, judge, and georgist land value tax activist. Life He was the son of John Ure, lord provost of Glasgow, and his wife Isabella. He studied law at the University of Glasgow he was admitted to membership of the Faculty of Advocates in 1878. He was a Liberal Member of Parliament for Linlithgowshire from 1895 to 1913. He became a queen's counsel in 1897. He provided as solicitor general for Scotland from December 1905 to 1909, and as Lord Advocate from February 1909 to 1913. He was an enthusiastic supporter of David Lloyd George's 1909–10 budget. He was sworn of the Privy Council in 1909. In 1909, he conducted the prosecution of Oscar Slater for murder; the conviction was later quashed on appeal. He lived at 31 Heriot Row, a large Georgian townhouse, in Edinburgh's Second New Town. On leaving Parliament, he was raised to the bench as Lord Strathclyde and appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' (abbreviation: The Rt Hon. or variations) is an honorific Style (form of address), style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire, and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and, to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the Grammatical person, third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leading the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom during the First World War, for social-reform policies, for his role in the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference, and for negotiating the establishment of the Irish Free State. Born in Chorlton-on-Medlock, Manchester, and raised in Llanystumdwy, Lloyd George gained a reputation as an orator and proponent of a Welsh blend of radical Liberal ideas that included support for Welsh devolution, the Disestablishment of the Church in Wales, disestablishment of the Church of England in Wales, equality for labourers and tenant farmers, and reform of land ownership. He won 1890 Caernarvon Boroughs by-election, an 1890 by-election to become the Member of Parliam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1895 United Kingdom General Election
The 1895 United Kingdom general election was held from 13 July to 7 August 1895. The result was a Conservative parliamentary majority of 153. William Ewart Gladstone, William Gladstone had retired as prime minister the previous year, and Queen Victoria, disregarding Gladstone's advice to name John Spencer, 5th Earl Spencer, Lord Spencer as his successor, appointed the Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery, Earl of Rosebery as the new prime minister. Rosebery's government found itself largely in a state of paralysis due to a power struggle between him and William Harcourt (politician), William Harcourt, the Liberal leader in the Commons. The situation came to a head on 21 June, when Parliament voted to dismiss Secretary of State for War Henry Campbell-Bannerman; Rosebery, realising that the government would likely not survive a motion of no confidence were one to be brought, promptly resigned as prime minister. Conservative Party (UK), Conservative leader Robert Arthur Talbot G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hope (MP For Linlithgowshire)
Capt Thomas Hope (3 February 1848 – 28 March 1925) was the Tory MP for Linlithgowshire, winning it in the 1893 by-election and resigning it in 1895. In Freemasonry, he was also Provincial Grand Master of the Provincial Grand Lodge of Linlithgowshire West Lothian, also known as Linlithgowshire (its official name until 1925), is a counties of Scotland, historic county in the east central Lowlands of Scotland. until 1925. It is bounded geographically by the River Avon, Falkirk, Avon to the wes ... from 1894 to 1904. Thomas Hope was elected to the newly created Linlithgowshire County Council (for Torphichen Parish) in 1889 and became its first County Convener. References External links * 1848 births 1925 deaths Scottish Freemasons Scottish Tory MPs (pre-1912) UK MPs 1892–1895 19th-century Scottish people {{Conservative-UK-MP-1840s-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterhead Prison
HMP Peterhead was a prison in Peterhead in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, operating from 1888 to 2013. Since June 2016, the former grounds operate as the Peterhead Prison Museum. History Peterhead Convict Prison was built around 1888. It was designed to hold 208 prisoners and to be Scotland's only convict prison,Scraton, P., Sim, J. & Skidmore, P. (1991) ''Prisons Under Protest'', Buckingham: Open University Press i.e. for prisoners sentenced to 'hard labour'. Occupancy averaged at around 350 however, until peaking at 455 in 1911. Additional buildings were completed in 1909, 1960 and 1962, bringing capacity up to 362. According to the Scottish Prison Service, the prison could, in 2012, accommodate up to 142 prisoners. It closed in 2013, to be replaced by the new HMP Grampian, the first prison in Scotland to jointly house youths, men and women. The first inmates transferred on to site on 2 March 2014 having been temporarily housed at other sites and connected to family with virtual v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Holmes and Dr. Watson. The Sherlock Holmes stories are milestones in the field of crime fiction. Doyle was a prolific writer. In addition to the Holmes stories, his works include fantasy and science fiction stories about Professor Challenger, and humorous stories about the Napoleonic soldier Brigadier Gerard, as well as plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction, and historical novels. One of Doyle's early short stories, "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement" (1884), helped to popularise the mystery of the brigantine ''Mary Celeste'', found drifting at sea with no crew member aboard. Name Doyle is often referred to as "Sir Arthur Conan Doyle" or "Conan Doyle", implying that "Conan" is part of a Double-barrelled name, compound surname rather than a mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helensburgh
Helensburgh ( ; ) is a town on the north side of the Firth of Clyde in Scotland, situated at the mouth of the Gareloch. Historically in Dunbartonshire, it became part of Argyll and Bute following local government reorganisation in 1996. History History context (Prehistoric–1858) Although it has long been known that there are some prehistoric remains in the Helensburgh area, recent fieldwork by the North Clyde Archaeological Society has uncovered more. However the oldest building in the town itself is Ardencaple Castle which was the ancestral home of Clan MacAulay, and the history of which may date back to the twelfth century. Today only one tower of this building remains, the rest having been demolished in 1957–59. In 1752 Sir James Colquhoun (died 1786), chief of the Clan Colquhoun of Luss, bought the land which was to become Helensburgh; at that time it was known by such names as Malig, Millig or Milligs. In 1776 he placed an advertisement in a Glasgow newspaper seekin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding valuable service in a wide range of useful activities. It comprises five classes of awards across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom#Modern honours, knight if male or a dame (title), dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with the order, but are not members of it. The order was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V, who created the order to recognise 'such persons, male or female, as may have rendered or shall hereafter render important services to Our Empire'. Equal recognition was to be given for services rendered in the UK and overseas. Today, the majority of recipients are UK citizens, though a number of Commonwealth realms outside the UK continue to make appointments to the order. Honorary awards may be made to cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark (; ), is a Counties of Scotland, historic county, Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area and registration county in the Central Lowlands and Southern Uplands of Scotland. The county is no longer used for local government purposes, but gives its name to the two modern council areas of North Lanarkshire and South Lanarkshire. The county was established as a shire (the area controlled by a sheriff principal, sheriff) in the twelfth century, covering most of the basin of the River Clyde. The area was sometimes known as Clydesdale. In the early fifteenth century the western part of the shire was removed to become Renfrewshire (historic), Renfrewshire. The historic county of Lanarkshire includes Glasgow, but the city had a separate lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy from 1893. A Lanarkshire County Council existed from 1890 until 1975, which was based in Glasgow until 1964 when it moved to Hamilton, South Lanarkshire, Hamil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Justice General
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are entitled to courtesy titles. The collective "Lords" can refer to a group or body of peers. Etymology According to the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'', the etymology of the word can be traced back to the Old English word ''hlāford'' which originated from ''hlāfweard'' meaning "loaf-ward" or "bread-keeper", reflecting the Germanic tribal custom of a chieftain providing food for his followers. The appellation "lord" is primarily applied to men, while for women the appellation "lady" is used. This is no longer universal: the Lord of Mann, a title previously held by the Queen of the United Kingdom, and female Lords Mayor are examples of women who are styled as "Lord". Historical usage Feudalism Under the feudal system, "lord" had a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
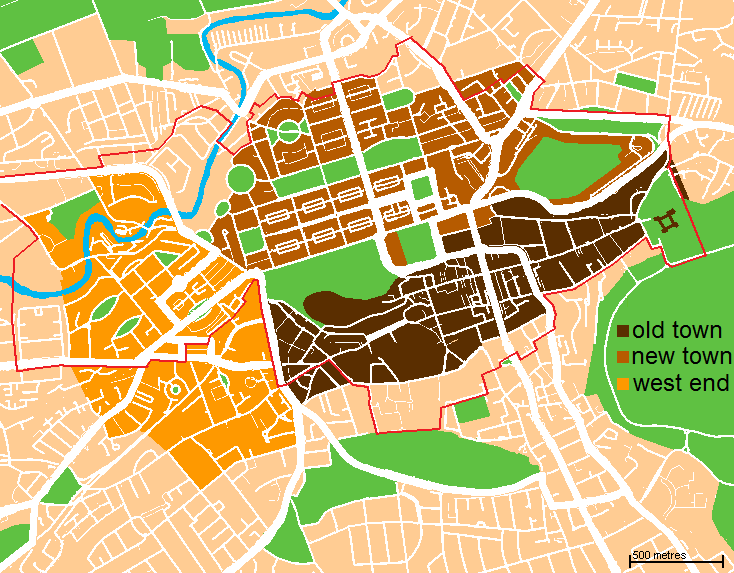
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heriot Row
Heriot Row is a highly prestigious street in central Edinburgh, virtually unchanged since its original construction in 1802. From its inception to the present day in remained a top address in the city and has housed the rich and famous of the city's elite for 200 years History Following the success of Edinburgh's First New Town (from Princes Street to Queen Street) it was proposed to expand the concept northwards onto what was then fairly open land largely owned by the Heriot Trust. The scheme was designed by William Sibbald with the young Robert Reid (architect), Robert Reid working mainly on the proportions of the palace type frontages. The project was built by John Paton and David Lind. The two main sections were complete by 1808. The short western section (linking to Darnaway Street then the Moray Estate was slightly later and was executed in 1817 to the design of Thomas Bonnar being built by William & Wallace. The original concept was for two palace-fronted blocks: Dun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |