|
Alexander Isakov
Alexander Isakov (Russian language, Russian: Александр Степанович Иисаков, 1730 — 1794) was a major general and a military and administrative Russian figure of the 18th century. Reign He was born into the family of a clerk and served in army since 1742. In 1755, he became the captain of the garrison of the Borovska settlement, Bakhmut province of the Voronezh Governorate, during the construction of the village of Serbo-Slavyanskoye for the settlement of the Slavo-Serbia, Serbs who settled there. Participant of the Seven Years' War of 1756–1763. On March 22, 1764, he was appointed to the post of commander of the Fortress of St. Elizabeth and all the villages near that fortress that made up the Novorossiya Governorate, and consisted in this position until his resignation. Participant in the Siege of St. Elizabeth fortress (1769), first campaigns of the Russo-Turkish War (1768-1774) where he commanded the defense of the St. Elizabeth fortress. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novorossiya Governorate
Novorossiya Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (''guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1764–1783 and again in 1796–1802. It was created and governed according to the "Plan for the Colonization of New Russia Governorate" issued by the Governing Senate, Russian Senate.New Russia Governorate at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine It became the first region in Russia where Catherine the Great allowed foreign Jews to settle. Most of its territories belonged to the Zaporozhian Sich as well as the Poltava Regiment and Myrhorod Regiment of the Cossack Hetmanate. Its establishment was strategically successful and advantageous for Russia, and after the conclusion of the Russian war aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Chertkov
Vasili, Vasily, Vasilii or Vasiliy (Russian: Василий) is a Russian masculine given name of Greek origin and corresponds to ''Basil''. It may refer to: *Vasily I of Moscow Grand Prince from 1389–1425 *Vasily II of Moscow Grand Prince from 1425–1462 *Vasili III of Russia Grand Prince from 1505–1533 *Vasili IV of Russia Tsar from 1606–1610 *Basil Fool for Christ (1469–1557), also known as Saint Basil, or Vasily Blazhenny * Vasily Alekseyev (1942–2011), Soviet weightlifter *Vasily Arkhipov (1926–1998), Soviet Naval officer in the Cuban Missile Crisis *Vasily Boldyrev (1875–1933), Russian general *Vasily Chapayev (1887–1969), Russian Army commander *Vasily Chuikov (1900–1982), Soviet marshal *Vasily Degtyaryov (1880–1949), Russian weapons designer and Major General *Vasily Dzhugashvili (1921–1962), Stalin's son *Vasili Golovachov (born 1948), Russian science fiction author *Vasily Grossman (1905–1964), Soviet writer and journalist * Vasily Ignatenko (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "Canon law of the Eastern Orthodox Church, canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church, organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches, number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Unrecognised churches, autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own Primate (bishop), primate. Autocephalous churches can have Ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is the native language of the Russians. It was the ''de facto'' and ''de jure'' De facto#National languages, official language of the former Soviet Union.1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 Russian has remained an official language of the Russia, Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Russian language in Israel, Israel. Russian has over 253 million total speakers worldwide. It is the List of languages by number of speakers in Europe, most spoken native language in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakhmut
Bakhmut is a city in eastern Ukraine. It is officially the administrative center of Bakhmut urban hromada and Bakhmut Raion in Donetsk Oblast. The city is located on the Bakhmutka River, about north of Donetsk, the administrative center of the oblast. Bakhmut was designated a city of regional significance until 2020, when the designation was abolished. In January 2022, it had an estimated population of Bakhmut was originally founded in the 16th century as a minor border post on the southern border of the Russian state. Its population grew in the early 18th century, and it served as the capital of Slavo-Serbia (1753–1764), a colony in the Russian Empire established by settlers from the Balkans. It received city status in 1783, and underwent major industrialization over the following few centuries. In 1920–1924, the city was an administrative center of the newly created Donets Governorate of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. The city was known as Artemivsk or A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronezh Governorate
Voronezh Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, and the Russian SFSR, which existed from 1708 (as ''Azov Governorate'') to 1779 and again from 1796 to 1928. Its capital was located in Voronezh since 1725. The governorate was located in the south of the European part of the Russian Empire. In 1928, the governorate was abolished, and its area was included into newly established Central Black Earth Oblast. First Azov Governorate Azov Governorate, together with seven other governorates, was established on , 1708, by Tsar Peter the Great's edict.Указ об учреждении губерний и о росписании к ним городов As with the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
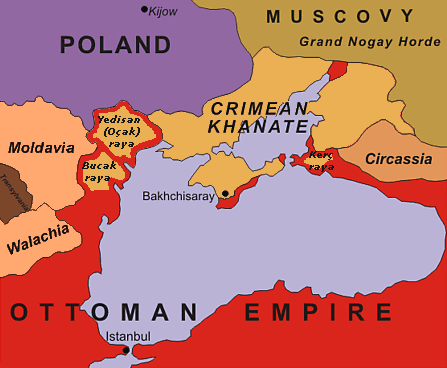
Slavo-Serbia
Slavo-Serbia or Slaveno-Serbia was a territory of Imperial Russia from 1753 to 1764. It was located to the south of the Donets River, between the Bakhmutka River and Luhan River. This area today is located within present-day Luhansk Oblast and Donetsk Oblast of Ukraine. The administrative centre of Slavo-Serbia was Bakhmut. It was bounded on the north by Slobozhanshchyna, on the west by the Cossack Hetmanate (a.k.a. the Zaporizhian Host), the Crimean Khanate to the south, and the Don Cossack Host to the southeast. Background As far back as 1723, Serb military colonists had been settling to a limited extent in the area that is now modern Ukraine. These Serbs came largely from the Military Frontier of the Habsburg Empire, where they enjoyed autonomy from the state. The abolishment of sectors of the frontier, and thus the loss of their autonomy, has been cited as a major reason for emigration to the Russian Empire. The Serbian polymath and historian Zaharije Orfelin p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia versus Kingdom of France, France and Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the respective coalitions receiving by countries including Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Spain, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, Age of Liberty, Sweden, and Russian Empire, Russia. Related conflicts include the Third Silesian War, French and Indian War, Carnatic wars, Third Carnatic War, Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763), and Spanish–Portuguese War (1762–1763), Spanish–Portuguese War. Although the War of the Austrian Succession ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), none of the signatories were happy with the terms, and it was generally viewed as a temporary armistice. It led to a strategic realignment kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortress Of St
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a border gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of St
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (military), mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1768-1774)
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of these wars ended in losses for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a period of stagnation and decline. Conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of the Russian Empire as a significant European power after Peter the Great oversaw extensive modernization efforts in the early 18th century. Ultimately, however, the end of the Russo-Turkish wars came about with the dissolution of the two belligerents' respective states as a consequence of World War I: the Russian Empire collapsed in 1917 and was ultimately succeeded by the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922; while the Ottoman Empire was partitioned between 1918 and 1922 and succeeded by the Republic of Turkey in 1923. History Initial and intermediate phases (1568–1739) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |