|
Alexander Balas
Alexander I Theopator Euergetes, surnamed Balas (), was the ruler of the Seleucid Empire from 150 BC to August 145 BC. Picked from obscurity and supported by the neighboring Roman-allied Kingdom of Pergamon, Alexander landed in Phoenicia in 152 BC and started a civil war against Seleucid King Demetrius I Soter. Backed by mercenaries and factions of the Seleucid Empire unhappy with the existing government, he defeated Demetrius and took the crown in 150 BC. He married the princess Cleopatra Thea to seal an alliance with the neighboring Ptolemaic kingdom. His reign saw the steady retreat of the Seleucid Empire's eastern border, with important eastern satrapies such as Media being lost to the nascent Parthian Empire. In 147 BC, Demetrius II Nicator, the young son of Demetrius I, began a campaign to overthrow Balas, and civil war resumed. Alexander's ally, Ptolemaic king Ptolemy VI Philometor, moved troops into Coele-Syria to support Alexander, but then switched sides and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''. The remains of the ancient city of Antioch are mostly buried beneath alluvial deposits from the Orontes River. The modern city of Antakya, in Hatay Province of Turkey, lies in its place. Antioch was founded near the end of the fourth century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, as one of the tetrapoleis of Seleucis of Syria. Seleucus encouraged Greeks from all over the Mediterranean to settle in the city. The ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
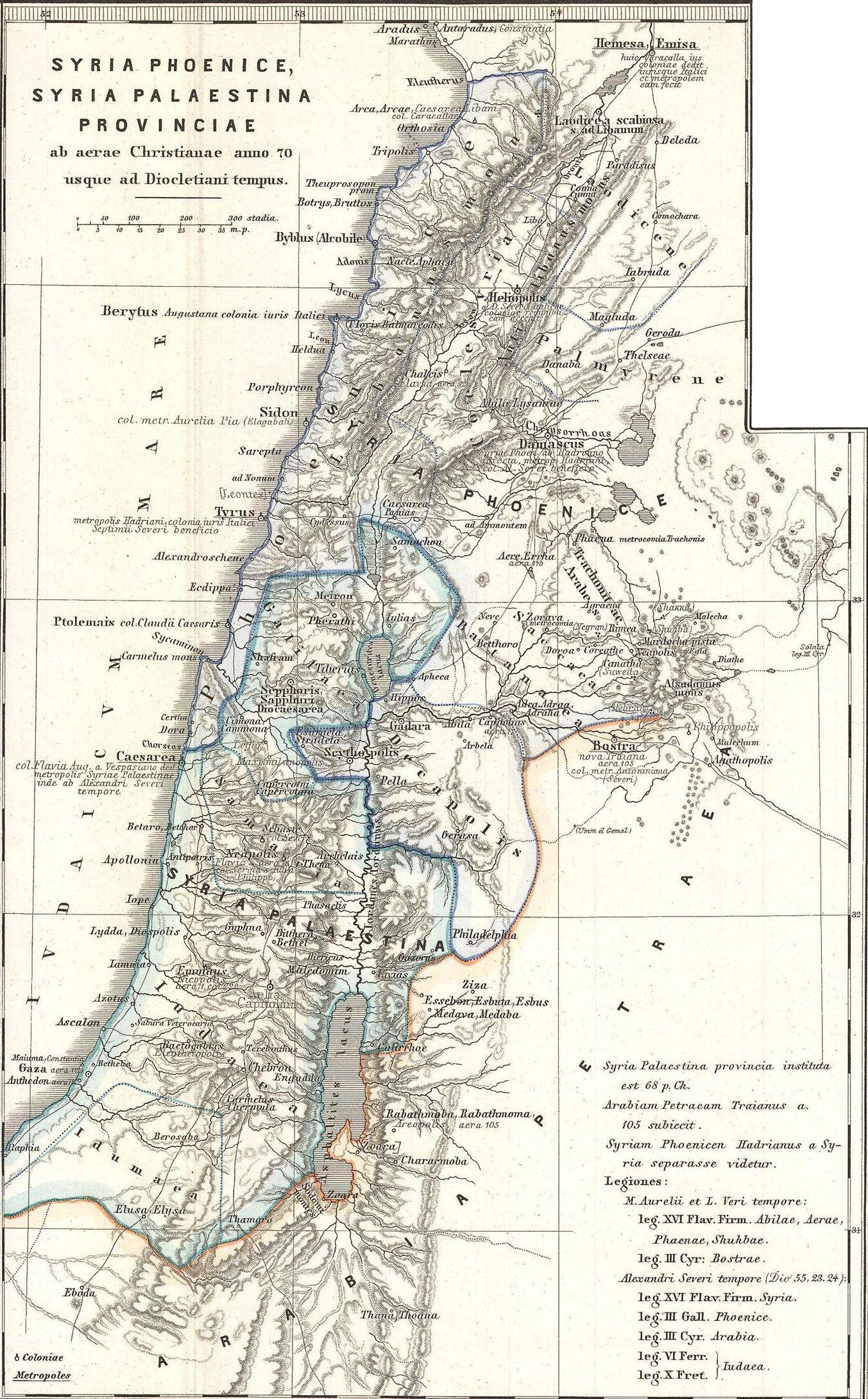
Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian coast. They developed a Maritime history, maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula, evidenced by thousands of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Phoenician inscriptions. The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions after the decline of most major Mediterranean basin cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. They called themselves Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pergamum
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north side of the river Caicus (modern-day Bakırçay) and northwest of the modern city of Bergama, Turkey. During the Hellenistic period, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Pergamon in 281–133 BC under the Attalid dynasty, who transformed it into one of the major cultural centres of the Greek world. Many remains of its monuments can still be seen and especially the masterpiece of the Pergamon Altar. Pergamon was the northernmost of the seven churches of Asia cited in the New Testament Book of Revelation. The city is centered on a mesa of andesite, which formed its acropolis. This mesa falls away sharply on the north, west, and east sides, but three natural terraces on the south side provide a route up to the top. To the west of the acropolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus (Greek: Ἄτταλος ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a ruler of the Attalid kingdom of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia. Family He was the second son of Attalus I Soter and queen Apollonis of Cyzicus, and ascended the throne first as co-ruler alongside his ailing brother Eumenes II in 160 BC, whose widow Stratonice of Pergamon he married in 158 BC upon Eumenes' death.Strabo13.4.2 Hansen, pp. 44–45; Hurwit, p. 271. Biography Prior to becoming king, Attalus was already an accomplished military commander. In 192 BC he was sent by his brother Eumenes to Rome to warn against Antiochus III. In 190 BC, he was present in the Battle of Magnesia which resulted in a defeat against the Seleucids. Around 189 BC he led his forces to fight alongside the Roman Army under Gnaeus Manlius Vulso in Galatia. From 182-179 BC, he successfully defeated the King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Men Who Would Be King
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwyn Bevan
Edwyn Robert Bevan OBE, FBA (15 February 1870 in London – 18 October 1943 in London) was a versatile British philosopher and historian of the Hellenistic world. Life Edwyn Robert Bevan was the fourteenth of sixteen children of Robert Cooper Lee Bevan, a partner in Barclays Bank, and his second wife Emma Frances Shuttleworth, daughter of Philip Nicholas Shuttleworth, Bishop of Chichester. He was educated at Monkton Combe School and at New College, Oxford. Bevan held an academic position at King's College London as Lecturer in Hellenistic History and Literature. The Arabist Anthony Ashley Bevan was his brother, the conspiracy theorist Nesta Helen Webster was his youngest sister and the artist Robert Polhill Bevan a cousin. He married Mary Waldegrave, daughter of Granville Waldegrave, 3rd Baron Radstock in 1896 and they had two daughters, Christina (born March 1897, died 1981) and Anne (born March 1898,died 1983). Bevan's name is given in a list of staff at Wellington Hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laodice VI
Laodice VI (; died 115–113 BCE) was a Greek Seleucid princess and through marriage was a queen of the Kingdom of Pontus. Biography Laodice was the daughter born from the sibling union of the Seleucid rulers Antiochus IV Epiphanes and Laodice IV, or a more obscure Seleukid relation or impostor. According to the first explanation, her grandparents were Antiochus III the Great and Laodice III. Through her mother’s previous marriages, she had various maternal half-brothers and sisters and two full blooded brothers who served as Seleucid kings Antiochus V Eupator and Alexander Balas. In 152 BC, Laodice became one of the supporters for her brother Alexander Balas, who revolted and overthrew the Seleucid king Demetrius I Soter, who was their maternal half-brother/cousin. The other alternative is Laodice appears to have come from obscure origins, connected with the same impostorship as Alexander Balas. Laodice could have been a supposed daughter of the Seleucid King Antiochus IV E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, between 60 and 30 BC. The history is arranged in three parts. The first covers mythic history up to the destruction of Troy, arranged geographically, describing regions around the world from Egypt, India and Arabia to Europe. The second covers the time from the Trojan War to the death of Alexander the Great. The third covers the period to about 60 BC. ''Bibliotheca'', meaning 'library', acknowledges that he was drawing on the work of many other authors. Life According to his own work, he was born in Agyrium in Sicily (now called Agira). With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about his life and doings beyond his written works. Only Jerome, in his '' Chronicon'' under the "year of Abraham 1968" (49 BC), writes, "D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; , ; ) was a Greek historian of the middle Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , a universal history documenting the rise of Rome in the Mediterranean in the third and second centuries BC. It covered the period of 264–146 BC, recording in detail events in Italy, Iberia, Greece, Macedonia, Syria, Egypt and Africa, and documented the Punic Wars and Macedonian Wars among many others. Polybius' ''Histories'' is important not only for being the only Hellenistic historical work to survive in any substantial form, but also for its analysis of constitutional change and the mixed constitution. Polybius' discussion of the separation of powers in government, of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", all influenced Montesquieu's '' The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's '' Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Oenoparus River
The Battle of the Oenoparus took place in 145 BC on the Oenoparus river (the modern Afrin River, Syria) in the adjoining countryside of Antioch on the Orontes, the capital of the Seleucid Empire. It was fought between a coalition of Ptolemaic Egypt led by Ptolemy VI and Seleucids who favored the royal claim of Demetrius II Nicator against Seleucids who favored the claim of Alexander Balas. Both the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic kingdom were diadochi, Greek-ruled successor states established after the conquests of Alexander the Great. The Ptolemaic force won the battle, and Balas's hopes of securing the throne were ended. However, King Ptolemy VI suffered a mortal wound in the battle. Despite the Egyptian forces winning the battle, they too would be driven out of Syria by the now unified Seleucid Empire under Demetrius II, which turned on the leaderless Egyptian force and drove them out of Seleucid territory. Background King Demetrius I Soter of the Seleucid Empire was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria () was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. The term originally referred to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges, but sometimes it was applied to a broader area of the region of Syria. The area is now part of modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ܟܠ ''kul'' , such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grabbe, p173 "Yet the suggestion is widely accepted that the name actually derives from Aramaic for "all Syria", which was then assimilated by the Greeks to a more usual pattern for place names" The word "Coele", with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy VI Philometor
Ptolemy VI Philometor (, ''Ptolemaĩos Philomḗtōr'';"Ptolemy, lover of his Mother". 186–145 BC) was a Greek king of Ptolemaic Egypt who reigned from 180 to 164 BC and from 163 to 145 BC. He is often considered the last ruler of ancient Egypt when that state was still a major power. Ptolemy VI, the eldest son of King Ptolemy V and Queen Cleopatra I, came to the throne aged six when his father died in 180 BC. The kingdom was governed by regents: his mother until her death in 178 or 177 BC and then two of her associates, Eulaeus and Lenaeus, until 169 BC. From 170 BC, his sister-wife Cleopatra II and his younger brother Ptolemy VIII were co-rulers alongside him. Ptolemy VI's reign was characterised by external conflict with the Seleucid Empire over Syria and by internal conflict with his younger brother for control of the Ptolemaic monarchy. In the Sixth Syrian War (170–168 BC), the Ptolemaic forces were utterly defeated and Egypt was twice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |