|
Aldbourne, Wiltshire
Aldbourne ( ) is a village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish about north-east of Marlborough, Wiltshire, England. It is in a valley on the south slope of the Lambourn Downs – part of the North Wessex Downs AONB, North Wessex Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. From here an unnamed winterbourne (stream), winterbourne flows south to join the River Kennet away near Ramsbury. The United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census recorded the parish population as 1,833. The parish includes the hamlets of Upper Upham and Woodsend and part of the hamlet of Preston, which straddles the boundary with Ramsbury. The village of Snap, Wiltshire, Snap became deserted in the early 20th century. History Early periods Evidence of prehistoric activity on the chalk downs includes a Barrow (archaeology), barrow cemetery north-west of the village, a Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age cross dyke to the north, and a field system in the valley around Snap. There are extensive prehistoric or Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
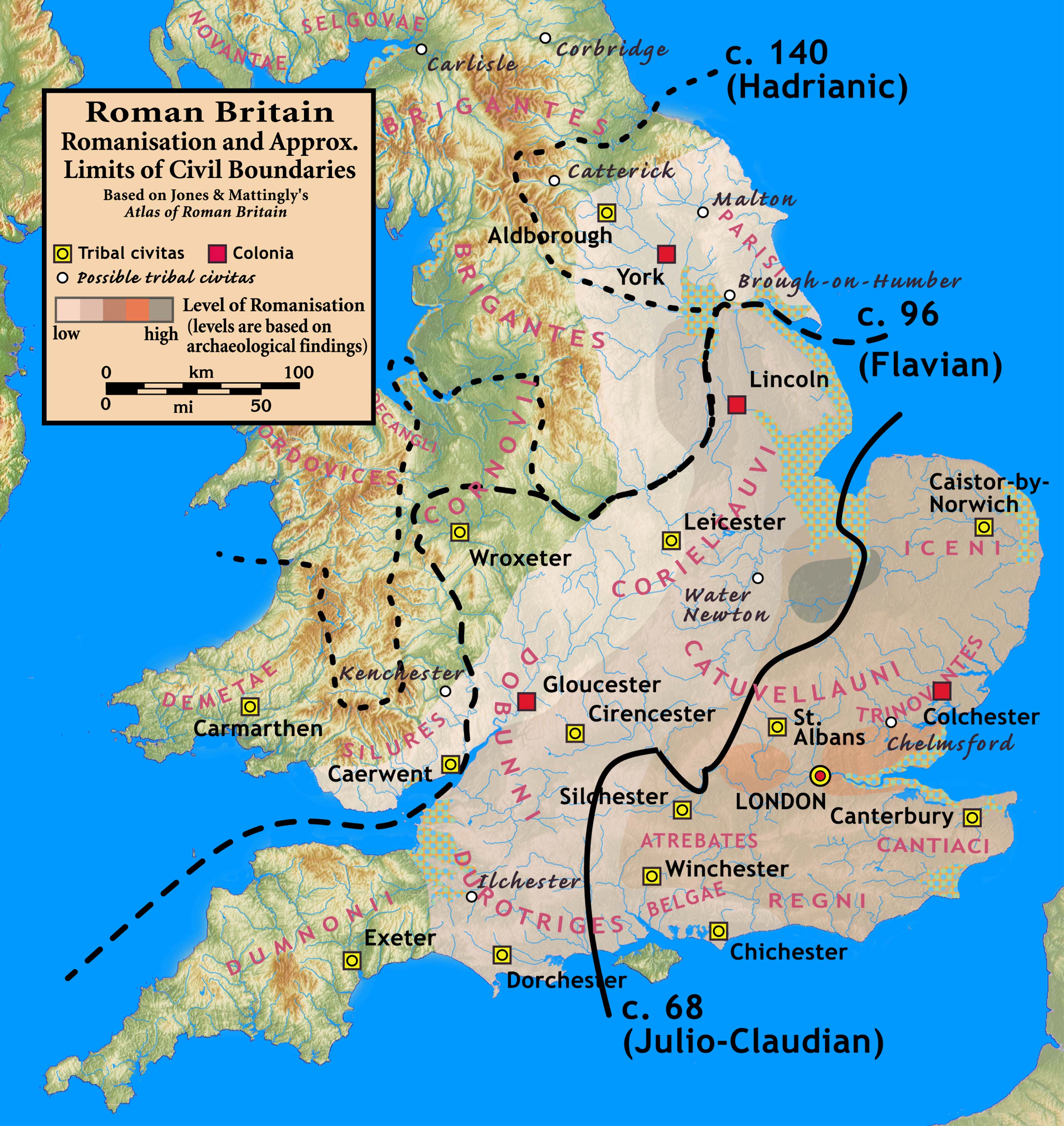
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goddard Family
The Goddard family were a prominent landed gentry, landed family chiefly living in the northern regions of the English counties of Wiltshire and Hampshire and the western part of Berkshire, between the Tudor period and the early 20th century. The Goddards were established at manors in Upper Upham, near Aldbourne, and at Clyffe Pypard (both in Wiltshire) from at least the late 15th century. From 1563 until 1927, the family were Lord of the Manor, lords of the manor of Swindon, living on the Goddard Estate at the house known as The Lawn. Other important manors included Ogbourne St George in Wiltshire, Standen at Hungerford in Berkshire and Stargroves at East Woodhay in Hampshire. Wiltshire Goddards Upper Upham The manor of Upper Upham, in Aldbourne parish south-east of Swindon, was held by Lacock Abbey (monastery), Lacock Abbey from the 13th century until the Dissolution of the monasteries, dissolution, then in 1540 was purchased by John Goddard (died 1557). His grandson Ric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacock Abbey
Lacock Abbey in the village of Lacock, Wiltshire, England, was founded in the early 13th century by Ela, Countess of Salisbury, as a nunnery of the Augustinian order. The abbey remained a nunnery until the Dissolution of the monasteries in the 16th century; it was then sold to Sir William Sharington who converted the convent into a residence where he and his family lived. It was fortified and remained loyal to the crown during the English Civil War, but surrendered to the Parliamentary forces once Devizes had fallen in 1645. The house was built over the old cloisters and its main rooms are on the first floor. It is a stone house with stone slated roofs, twisted chimney stacks and mullioned windows. Throughout the life of the building, many architectural alterations, additions, and renovations have occurred so that the house is a mish-mash of different periods and styles. The Tudor stable courtyard to the north of the house has retained many of its original features includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of London
The City of London, also known as ''the City'', is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and Districts of England, local government district with City status in the United Kingdom, city status in England. It is the Old town, historic centre of London, though it forms only a small part of the larger Greater London metropolis. The City of London had a population of 8,583 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, however over 500,000 people were employed in the area as of 2019. It has an area of , the source of the nickname ''the Square Mile''. The City is a unique local authority area governed by the City of London Corporation, which is led by the Lord Mayor of London, Lord Mayor of the City of London. Together with Canary Wharf and the West End of London, West End, the City of London forms the primary central business district of London, which is one of the leading financial centres of the world. The Bank of England and the London Stock Exchange are both ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Longespée, 3rd Earl Of Salisbury
William Longespée, 3rd Earl of Salisbury (In or before 11677 March 1226) ("Long Sword", Latinised to ''de Longa Spatha'') was an Anglo-Norman nobleman, primarily remembered for his command of the English forces at the Battle of Damme and for remaining loyal to his half-brother, King John, until shortly before John's death. His nickname "Longespée" is generally taken as a reference to his great physical height and the oversized weapons that he used. Early life William was an illegitimate son of Henry II, King of England. His mother was unknown for many years until the discovery of a charter William made that mentions "''Comitissa Ida, mater mea''" (Countess Ida, my mother). This referred to Ida de Tosny, a member of the prominent Tosny (or Toesny) family, who had married Roger Bigod, 2nd Earl of Norfolk in 1181. In 1188, William was recognized as son of King Henry II and received the honour of Appleby, Lincolnshire. Eight years later, his half brother King Richard I mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotrou IV, Count Of Perche
Rotrou IV (1135-1191), was the Count of Perche. He joined Louis VII of France in a war against Henry II of England, in which he lost lands to the English. Rotrou later went on crusade with Philip II of France and died after the Siege of Acre in 1191. Biography Born in 1135, Rotrou was the son of Rotrou III, Count of Perche, and Hawise, daughter of Walter of Salisbury, and Sibilla de Chaworth. Upon the death of his father in 1144, Rotrou continued the fight against his archenemy, William III Talvas, Count of Ponthieu and Lord of Alençon. Aside from this long-running blood feud, his uncle Patrick had married William Talvas' daughter Adela. His mother Hawise and her second husband, Robert I of Dreux, served as regents at Perche until he reached the age of maturity. Rotrou aided Louis VII the Younger against Henry II of England in an ineffective war that saw their troops routed, lands ravaged and property stolen. He was forced to yield the communes of Moulins and Bonsmoulins to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiltshire Victoria County History
The Wiltshire Victoria County History, properly called The Victoria History of the County of Wiltshire but commonly referred to as VCH Wiltshire, is an encyclopaedic history of the county of Wiltshire in England. It forms part of the overall Victoria County History of England founded in 1899 in honour of Queen Victoria. With eighteen volumes published in the series, it is now the most substantial of the Victoria County Histories. Overview A set of Wiltshire volumes was planned from the start; the authors engaged included Maud Davies, who began writing in 1906. However, the VCH central office ran into financial difficulty in 1908, and although work resumed in 1910 in ten counties, Wiltshire was not among them. In 1947 the Wiltshire project was revived, leading to publication of the first volume in 1953. For many years the project was chiefly funded by Wiltshire County Council and other Wiltshire local authorities and managed by the Wiltshire Victoria County History Committee. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewisham Castle - Geograph
Lewisham ( ) is an area of southeast London, England, south of Charing Cross. It is the principal area of the London Borough of Lewisham, and was within the historic county of Kent until 1889. It is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London, with a large shopping centre and street market. Lewisham had a population of 60,573 in 2011. History The earliest written reference to Lewisham – – is from a charter from 862 which established the boundaries with neighbouring Bromley. Lewisham is sometimes said to have been founded, according to Bede, by a pagan Jute, Leof, who settled (by burning his boat) near St Mary's Church (Ladywell) where the ground was drier, in the 6th century, but there seems to be no solid source for this speculation, and there is no such passage in Bede's history. As to the etymology of the name, Daniel Lysons (1796) wrote: :"In the most ancient Saxon records this place is called ''Levesham'', that is, the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringwork
A ringwork is a form of fortified defensive structure, usually circular or oval in shape. Ringworks are essentially motte-and-bailey castles without the motte. Defences were usually earthworks in the form of a ditch and bank surrounding the site. Ringworks originated in Germany in the 10th century as an early form of medieval castle and at first were little more than a fortified manor house A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were usually held the lord's manorial courts, communal mea .... They appeared in England just prior to the Norman conquest and large numbers were built during the late 11th and early 12th centuries. More elaborate versions (such as Stansted Mountfitchet Castle) comprise a ringwork and bailey, the ringwork replacing the more usual motte and the bailey acting as a military stronghold. A survey published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name , meaning "Book of Winchester, Hampshire, Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him. Written in Medieval Latin, it was Scribal abbreviation, highly abbreviated and included some vernacular native terms without Latin equivalents. The survey's main purpose was to record the annual value of every piece of landed property to its lord, and the resources in land, labour force, and livestock from which the value derived. The name "Domesday Book" came into use in the 12th century. Richard FitzNeal wrote in the ( 1179) that the book was so called because its de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |