|
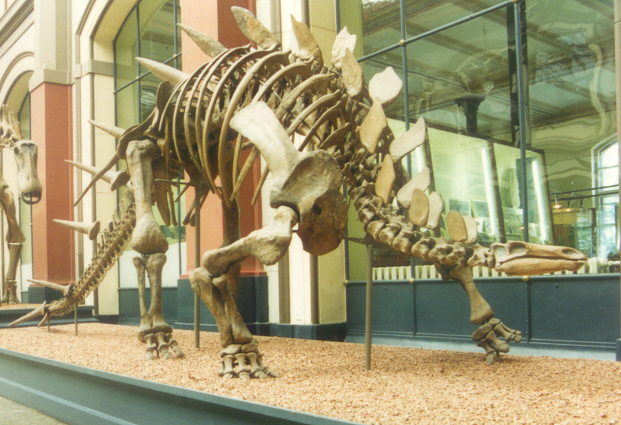
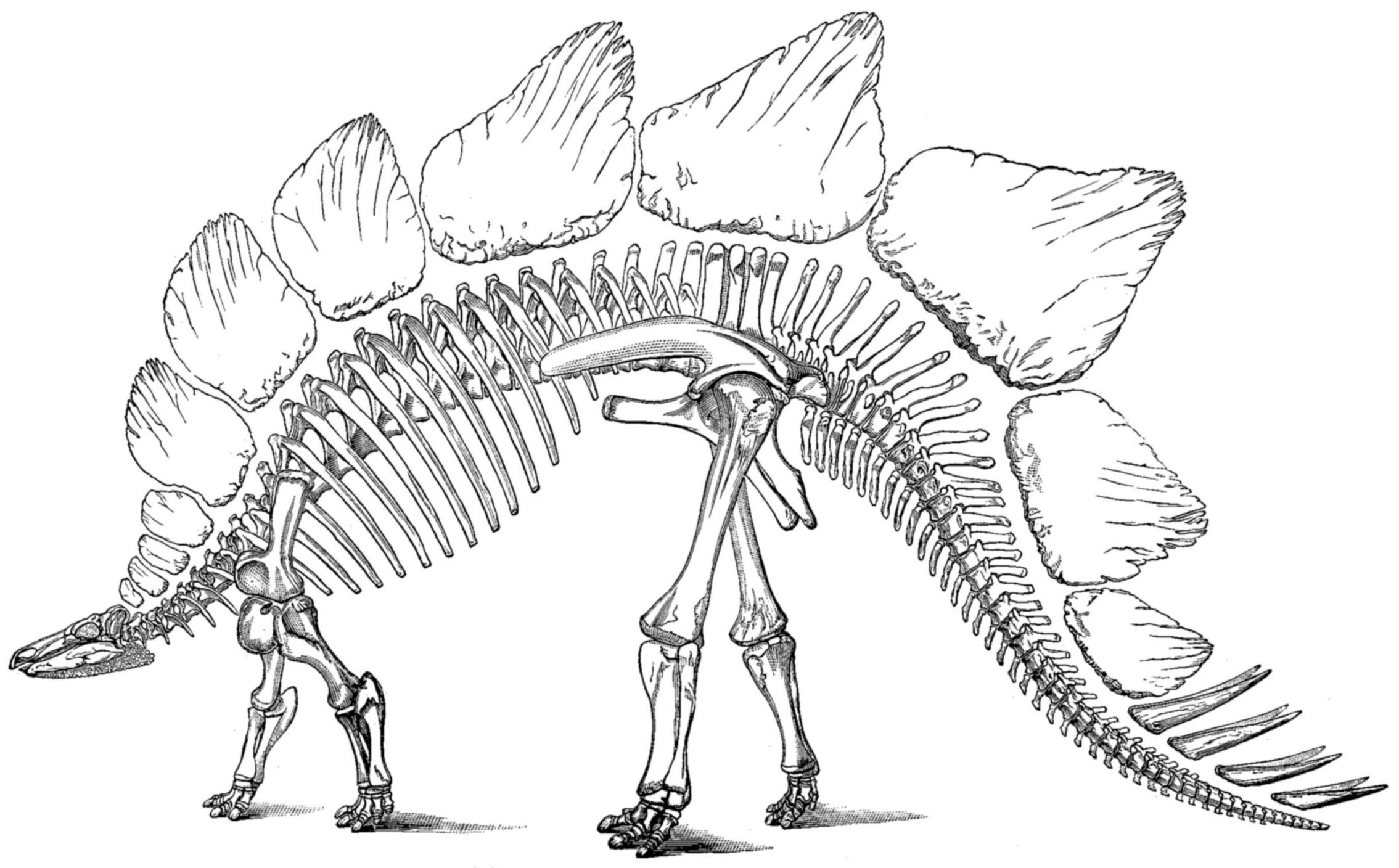
Alcovasaurus
''Alcovasaurus'', alternatively known as ''Miragaia longispinus'', is a genus of herbivorous thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic. It was found in the Morrison Formation of Natrona County, Wyoming, United States. The type species is ''Stegosaurus longispinus'', later given the genus ''Alcovasaurus'', and in 2019 recombined as ''Miragaia longispinus''. Discovery and naming In July 1908, Professors William Harlow Reed and A.C. Dart of the University of Wyoming, in the Alcova Quarry in Natrona County, Wyoming, uncovered the skeleton of a stegosaurian. This would be the last major excavation of a dinosaur in which Reed was personally involved. In 1914, the find was named and described as ''Stegosaurus longispinus'' by Charles Whitney Gilmore on the basis of holotype UW 20503 (originally UW D54), a partial postcranial skeleton of an adult individual consisting of forty-two vertebrae, a fragmentary sacrum, two ischia, a portion of one pubis, the right femu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcovasaurus Scale
''Alcovasaurus'', alternatively known as ''Miragaia longispinus'', is a genus of herbivorous thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic. It was found in the Morrison Formation of Natrona County, Wyoming, United States. The type species is ''Stegosaurus longispinus'', later given the genus ''Alcovasaurus'', and in 2019 recombined as ''Miragaia longispinus''. Discovery and naming In July 1908, Professors William Harlow Reed and A.C. Dart of the University of Wyoming, in the Alcova Quarry in Natrona County, Wyoming, uncovered the skeleton of a stegosaurian. This would be the last major excavation of a dinosaur in which Reed was personally involved. In 1914, the find was named and described as ''Stegosaurus longispinus'' by Charles Whitney Gilmore on the basis of holotype UW 20503 (originally UW D54), a partial postcranial skeleton of an adult individual consisting of forty-two vertebrae, a fragmentary sacrum, two ischia, a portion of one pubis, the right femur, several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miragaia (dinosaur)
''Miragaia'' (named after Miragaia, the parish in Portugal and geologic unit where its remains were found) is a long-necked stegosaurid dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in Upper Jurassic rocks in Portugal (Lourinhã Formation, Sobral Unit) and possibly also Wyoming, United States (Morrison Formation). ''Miragaia'' has the longest neck known for any stegosaurian, which included at least seventeen vertebrae. Discovery ''Miragaia'' is based on holotype ML 433, a nearly complete anterior half of a skeleton with partial skull (the first cranial material for a European stegosaurid). The remains were found after the construction of a road between the villages of Miragaia and Sobral. The rear half of the skeleton was probably destroyed by the roadcut. The fossils were dug up in August 1999 and August 2001. Among the recovered bones were most of the snout, a right postorbital, both angulars of the lower jaws, fifteen neck vertebrae (the first two, which articulated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentrosaurus
''Kentrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of stegosaurid dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. The type species is ''K. aethiopicus'', named and described by German palaeontologist Edwin Hennig in 1915. Often thought to be a "primitive" member of the Stegosauria, several recent cladistic analyses find it as more derived than many other stegosaurs, and a close relative of ''Stegosaurus'' from the North American Morrison Formation within the Stegosauridae. Fossils of ''K. aethiopicus'' have been found only in the Tendaguru Formation, dated to the late Kimmeridgian and early Tithonian ages, about 152 million years ago. Hundreds of bones were unearthed by German expeditions to German East Africa between 1909 and 1912. Although no complete skeletons are known, the remains provided a nearly complete picture of the build of the animal. In the Tendaguru Formation, it coexisted with a variety of dinosaurs such as the carnivorous theropods ''Elaphrosaurus'' and '' Veterupri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been found in the western United States and in Portugal, where they are found in Kimmeridgian- to early Tithonian-aged strata, dating to between 155 and 145 million years ago. Of the species that have been classified in the upper Morrison Formation of the western US, only three are universally recognized: ''S. stenops'', ''S. ungulatus'' and ''S. sulcatus''. The remains of over 80 individual animals of this genus have been found. ''Stegosaurus'' would have lived alongside dinosaurs such as ''Apatosaurus'', '' Diplodocus'', '' Brachiosaurus'', '' Ceratosaurus'', and ''Allosaurus''; the latter two may have preyed on it. They were large, heavily built, herbivorous quadrupeds with rounded backs, short fore limbs, long hind limbs, and tails held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Publication
Electronic publishing (also referred to as publishing, digital publishing, or online publishing) includes the digital publication of e-books, digital magazines, and the development of digital libraries and catalogues. It also includes the editing of books, journals, and magazines to be posted on a screen (computer, e-reader, tablet, or smartphone). About Electronic publishing has become common in scientific publishing where it has been argued that peer-reviewed scientific journals are in the process of being replaced by electronic publishing. It is also becoming common to distribute books, magazines, and newspapers to consumers through tablet reading devices, a market that is growing by millions each year, generated by online vendors such as Apple's iTunes bookstore, Amazon's bookstore for Kindle, and books in the Google Play Bookstore. Market research suggested that half of all magazine and newspaper circulation would be via digital delivery by the end of 2015 and that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age. In the past, ''Malm'' was also used to indicate the unit of geological time, but this usage is now discouraged to make a clear distinction between lithostratigraphic and geochronologic/chronostratigraphic units. Subdivisions The Late Jurassic is divided into three ages, which correspond with the three (faunal) stages of Upper Jurassic rock: Paleogeography During the Late Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea broke up into two supercontinents, Laurasia to the north, and Gondwana to the south. The result of this break-up was the spawning of the Atlantic Ocean. However, at this time, the Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow. Life forms of the epoch This epoch is well known for many famous types of din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISSN
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature. The ISSN system was first drafted as an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) international standard in 1971 and published as ISO 3297 in 1975. ISO subcommittee TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for maintaining the standard. When a serial with the same content is published in more than one media type, a different ISSN is assigned to each media type. For example, many serials are published both in print and electronic media. The ISSN system refers to these types as print ISSN (p-ISSN) and electronic ISSN (e-ISSN). Consequently, as defined in ISO 3297:2007, every serial in the ISSN system is also assigned a linking ISSN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Malcolm Galton
Peter Malcolm Galton (born 14 March 1942 in London) is a British vertebrate paleontologist who has to date written or co-written about 190 papers in scientific journals or chapters in paleontology textbooks, especially on ornithischian and prosauropod dinosaurs. With Robert Bakker in a joint article published in ''Nature'' in 1974, he argued that dinosaurs constitute a natural monophyletic group, in contrast to the prevailing view that considered them polyphyletic as consisting of two different not closely related orders Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ..., thus initiating a revolution in dinosaur studies and contributing to the revival of the popularity of dinosaurs in the field of paleontology. Publications * * * Galton, P.M., 1974, "The ornithischian dinosaur '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |