|
Al-Hasakah Governorate Campaign (2012–13)
Al-Hasakah (; / ; ) is a city in northeastern Syria and the capital of the Al-Hasakah Governorate. With a 2023 estimated population of 422,445, Al-Hasakah is populated by Kurds, Arabs, Assyrian people, Assyrians and a smaller number of Armenians in Syria, Armenians and Chechens in Syria, Chechens. Al-Hasakah is south of the city of Qamishli. The Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River, a tributary of the Euphrates, Euphrates River, flows west–east through the city. The Jaghjagh River flows into the Khabur from the north at Al-Hasakah. The city (and the surrounding countryside) is controlled by the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES). History An ancient Tell (archaeology), tell has been identified in the city centre by Dominique Charpin as the location of the city of Qirdahat. Another possibility is that it was the site of the ancient Arameans, Aramean city of Magarisu, mentioned by the Assyrian king Ashur-bel-kala, who fought the Arameans near the city. The et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Syria
The country of Syria is Administrative division, administratively subdivided into Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates, which are sub-divided into Districts of Syria, 65 districts, which are further divided into 284 sub-districts. Each of the governorates and districts has its own centre or capital city, except for Rif Dimashq Governorate and Markaz Rif Dimashq district. All the sub-districts have their own centres as well. Each district bears the same name as its administrative centre, with the exception of Mount Simeon District where the centre is the city of Aleppo. The same applies to all ''nahiyas'' (sub-districts), except for the Mount Simeon Nahiyah where the centre is the city of Aleppo. Governorate and district capital cities Sixty-four of the 65 districts of Syria have a city that serves as the regional capital (administrative centre); Markaz Rif Dimashq is a district with no official regional centre. The city of Damascus functions as a governorate, a district and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Islam
The history of Islam is believed, by most historians, to have originated with Muhammad's mission in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE, although Muslims regard this time as a return to the original faith passed down by the Abrahamic prophets, such as Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, David, Solomon, and Jesus, with the submission () to the will of God. According to the traditional account, the Islamic prophet Muhammad began receiving what Muslims consider to be divine revelations in 610 CE, calling for submission to the one God, preparation for the imminent Last Judgement, and charity for the poor and needy. As Muhammad's message began to attract followers (the ''ṣaḥāba'') he also met with increasing hostility and persecution from Meccan elites. In 622 CE Muhammad migrated to the city of Yathrib (now known as Medina), where he began to unify the tribes of Arabia under Islam, returning to Mecca to take control in 630 and order the destruction of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. The Middle Assyrian Empire was Assyria's first period of ascendancy as an empire. Though the empire experienced successive periods of expansion and decline, it remained the dominant power of northern Mesopotamia throughout the period. In terms of Assyrian history, the Middle Assyrian period was marked by important social, political and religious developments, including the rising prominence of both the Assyrian King, Assyrian king and the Assyrian national deity Ashur (god), Ashur. The Middle Assyrian Empire was founded through Assur, a city-state through most of the preceding Old Assyrian period, and the surrounding territories achieving independence from the Mitanni kingdom. Under Ashur-uballit, Assyria began to expand and assert its pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
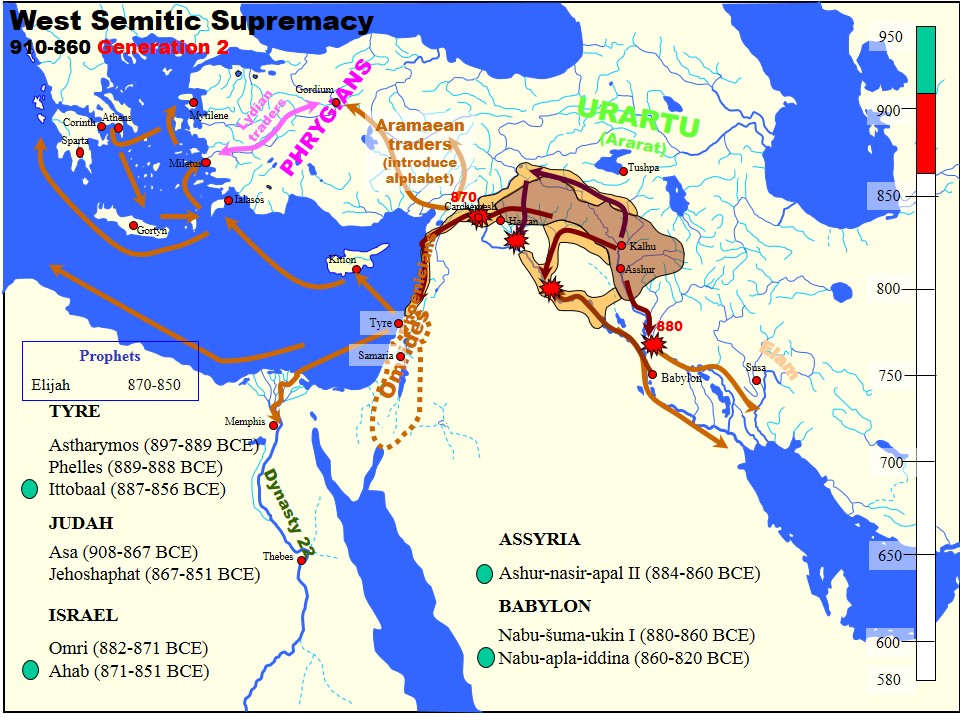
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was the third king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III and his queen was Mullissu-mukannišat-Ninua. Reign During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. The palaces, temples and other buildings raised by him bear witness to a considerable development of wealth and art. Cruelty Ashurnasirpal II was notorious for his brutality, using enslaved captives to build a new Assyrian capital at Kalhu (Nimrud) in Mesopotamia where he built many impressive monuments. He was also a shrewd administrator, who realized that he could gain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukulti-Ninurta II
Tukulti-Ninurta II (meaning: "my trust is in he warrior godNinurta") was King of Assyria from 890 BCE to 884 BCE. He was the second king of the Neo Assyrian Empire. History His father was Adad-nirari II, the first king of the Neo-Assyrian period. Tukulti-Ninurta consolidated the gains made by his father over the Neo-Hittites, Babylonians and Arameans, and successfully campaigned in the Zagros Mountains of Iran, subjugating the newly arrived Iranian peoples of the area, the Persians and Medes, during his brief reign. Tukulti-Ninurta II was victorious over Ammi-Ba'al, the king of Bit-Zamani, and then entered into a treaty with him (which included prohibitions against selling horses to Assyria's foes), as a result of which Bit-Zamani became an ally, and in fact a vassal of Assyria. Ammi-Ba'al remained in power, but from that moment on, he had to support Tukulti-Ninurta II during his military expeditions to the Upper Tigris against the Hurrians and Urartians in Nairi. Tukulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years. Aramaic served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires, particularly the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire, and Achaemenid Empire, and also as a language of divine worship and religious study within Judaism, Christianity, and Gnosticism. Several modern varieties of Aramaic are still spoken. The modern eastern branch is spoken by Assyrians, Mandeans, and Mizrahi Jews.{{cite book , last1=Huehnergard , first1=John , author-link1=John Huehnergard , last2=Rubin , first2=Aaron D. , author-link2=Aaron D. Rubin , date=2011 , editor-last=Weninger , editor-first=Stefan , title=The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook , pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashur-bel-kala
Aššūr-bēl-kala, inscribed m''aš-šur-''EN''-ka-la'' (meaning " Aššur is lord of all"), was the king of Assyria in 1074/3–1056 BC, the 89th to appear on the ''Assyrian Kinglist''. He was the son of Tiglath-Pileser I, succeeded his brother Asharid-apal-Ekur who had briefly preceded him, and he ruled for 18 years''Assyrian Kinglist'', iii 29-30, 31, 35. He was the last king of the Middle Assyrian Empire, and his later reign was preoccupied with a revolution against his rule led by one Tukulti-Mer, which, by the end of his reign, allowed hordes of Arameans to press in on Assyria's western borders. He is perhaps best known for his zoological collection. Biography His reign marks the point at which the tide turned against the middle Assyrian empire, and substantial Levantine territory to the west was captured by the invading Arameans. Aššūr-bēl-kala was the last of the monarchs of the second millennium for whom there are any significant surviving inscriptions. His annals ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magarisu
Al-Hasakah (; / ; ) is a city in northeastern Syria and the capital of the Al-Hasakah Governorate. With a 2023 estimated population of 422,445, Al-Hasakah is populated by Kurds, Arabs, Assyrians and a smaller number of Armenians and Chechens. Al-Hasakah is south of the city of Qamishli. The Khabur River, a tributary of the Euphrates River, flows west–east through the city. The Jaghjagh River flows into the Khabur from the north at Al-Hasakah. The city (and the surrounding countryside) is controlled by the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES). History An ancient tell has been identified in the city centre by Dominique Charpin as the location of the city of Qirdahat. Another possibility is that it was the site of the ancient Aramean city of Magarisu, mentioned by the Assyrian king Ashur-bel-kala, who fought the Arameans near the city. The etymology of ''Magarisu'' is Aramaic (from the root ''mgrys'') and means "pasture land". The city was the capital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered central regions of what is now Syria. The Arameans were not a single nation or group; Aram was a region with local centers of power spread throughout the Levant. That makes it almost impossible to establish a coherent ethnic category of "Aramean" based on extralinguistic identity markers, such as material culture, lifestyle, or religion. The people of Aram were called "Arameans" in Assyrian texts and the Hebrew Bible, but the terms "Aramean" and “Aram” were never used by later Aramean dynasts to refer to themselves or their country, except the king of Aram-Damascus, since his kingdom was also called Aram. "Arameans" is merely an appellation of the geographical term Aram given to 1st millennium BCE inhabitants of Syria. At the begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |