|
Agnou
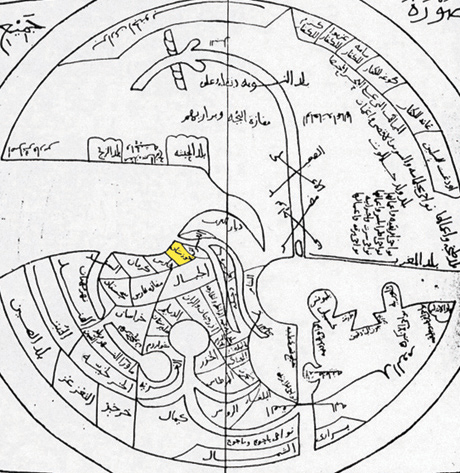
Agnou (, , ) was an ancient city and bishopric in Egypt. It was located on the strip of land between the lake Burullus and the Mediterranean Sea, near the modern village al-Hanafi al-Kubra (). It remains a Latin Catholic titular see. History Agnou was important enough in the late Roman province of Aegyptus Primus to be one of the many suffragan of the Metropolitan (becoming Patriarchate) of capital Alexandria, yet was to fade. Al-Maqrizi describes Agnou as a fortified coastal city and says that during the Arab conquest of Egypt the ruler of the city named Talma () had a dispute with Amr ibn al-As concerning the payment of jizya, which led to him rebelling and joining the Byzantine forces marching from Alexandria to Nikiou, after they recaptured the city in 646. They plundered and looted villages on their way, causing a major insurrection and shift of loyalty among the Egyptian population. The Byzantines were ultimately defeated and Talma himself was captured by the Arabs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ') is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was known as ''mḥw'' which means "north". Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into a number of regions or nomes () – '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences'' 24:4, Oxford; pp. 99–100. and the application of jizya varied in the course of Islamic history. However, scholars largely agree that early Muslim rulers adapted some of the existing systems of taxation and modified them according to Islamic religious law.online Historically, the jizya tax has been understood in Islam as a fee for protection provided by the Muslim ruler to non-Muslims, for the exemption from military service for non-Muslims, for the permission to practice a non-Muslim faith with some communal autonomy in a Muslim state, and as material proof of the non-Muslims' allegiance to the Muslim state and its laws. The majority of Muslim jurists required adult, free, sane men, males among the dhimma community to pay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Basil The Great
The Order of Saint Basil the Great (; , abbreviated OSBM), also known as the Basilian Order of Saint Josaphat, is a Greek Catholic monastic order of pontifical right that works actively among Ukrainian Catholics and other Greek-Catholic churches in central and Eastern Europe. The order received approbation on August 20, 1631, and is based at the Monastery of the Holy Trinity, Vilnius. History Revival In the 16th century, with the efforts of Metropolitan of Kiev Josyf Veliamyn Rutsky and Archbishop of Polotsk Josaphat Kuntsevych, the monastic order was revived on territory of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Following World War II, the order was eliminated by the Russian Orthodox from its original territory and forced into exile. With the fall of the Soviet Union, it was reestablished again in modern Ukraine as part of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church. Besides the Order of Saint Basil the Great, there is a smaller order of Studite Monks that was revived at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havryil Blazhovskyi
Havryil Heorhiy Blazhovskyi, O.S.B.M. (born as Juraj Mankovič; , , , c. 1705 – 20 December 1742) was the bishop of the Vicariate Apostolic for the Ruthenians in Mukacheve from 1738 to his death in 1742. Life Heorhiy Blazhovskyi was born on about 1705 in the village of Blažov, from which he took his surname (which originally was ''Mankovič''). He studied philosophy in Košice and then in the Jesuit college of Trnava. At the end of his studies, he was ordained secular priest in 1729 by Bishop Hennadiy Bizantsiy and assigned to the Vicariate Apostolic of Mukacheve. At the death of his predecessor, he was appointed, on 14 January 1738 as general vicar by the Latin bishop of Eger. He received the titular see of Agnus on 12 September 1738 and was consecrated bishop on 27 December 1738 by the Metropolitan of Kiev and all Rus', Atanasiy Sheptytskyi in Lviv. A few time before consecration, Heorhiy Blazhovskyi entered in the Order of Saint Basil the Great and took the religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titular Bishopric
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbishop" (intermediary rank) or " titular bishop" (lowest rank), which normally goes by the status conferred on the titular see. Titular sees are dioceses that no longer functionally exist, often because the territory was conquered by Muslims or because it is schismatic. The Greek–Turkish population exchange of 1923 also contributed to titular sees. The see of Maximianoupolis along with the town that shared its name was destroyed by the Bulgarians under Emperor Kaloyan in 1207; the town and the see were under the control of the Latin Empire, which took Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Parthenia, in north Africa, was abandoned and swallowed by desert sand. Catholic Church During the Muslim conquests of the Midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ya'qubi
ʾAbū al-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer. Life Ya'qubi was born in Baghdad to a family of noble background, his great-grandfather was Wadih, the freedman of the caliph Al-Mansur and ruler of Egypt during the reign of al-Mahdi. Until 873, he lived in Armenia and Khorasan, working under the patronage of the Tahirid Governors; then he traveled to India, Egypt and the Maghreb. In 872, he listed the kingdoms of Bilād as-Sūdān, including Ghana, Gao, and Kanem. His methodical approach to writing history includes personal observations and interviews to close relations on topics that Yaqubi could not encounter first-hand. He covered topics of natural, human and economic geography as well as noting down cultural, historical and topographic information. His sympathies with Ahl al-Bayt are found throughout his works. He d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosetta
Rosetta ( ) or Rashid (, ; ) is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799. Founded around the 9th century on the site of the ancient town of Bolbitine, Rosetta boomed with the decline of Alexandria following the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517, only to wane in importance after Alexandria's revival. During the 19th century, it was a popular British tourist destination, known for its Ottoman mansions, citrus groves and relative cleanliness. Etymology The name of the town most likely comes from an Arabic name '' Rašīd'' (meaning "guide") and was transcribed and corrupted in numerous ways – the name ''Rexi'' was used by the Crusaders in Middle Ages and ''Rosetta'' or ''Rosette'' ("little rose" in Italian and French respectively) was used by the French at the time of Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in Egypt. The latter lent its name to the Rosetta Stone (), which was found by French sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Al-Jazira (caliphal province), Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled from AD 943 to 969.Ludwig W. Adamec (2009), ''Historical Dictionary of Islam'', p.137. Scarecrow Press. . His famous work, written in 977, is called ''Surat Al-Ard'' (; "The face of the Earth"). The date of his death, known from his writings, was after Anno Hegirae, AH 368/AD 978. Biography Details known of Ibn Hawqal's life are extrapolated from his book. He spent the last 30 years of his life traveling to remote parts of Asia and Africa, and writing about different things he saw during his journey. One journey brought him 20° south of the equator along the East African coast where he discovered large populations in regions the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek writers had deemed uninhabitable. Ṣūrat al-’Arḍ Ibn Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Of Cyprus
George of Cyprus (; Latinized as ''Georgius Cyprius'') was a Greek Byzantine geographer of the early seventh century. Nothing is known of his life save that he was a Byzantine Greek born at Lapithos in the island of Cyprus. He is known for his ''Descriptio orbis Romani'' ("Description of the Roman world"), written in the decade 600–610. It is written in Greek, and lists cities, towns, fortresses and administrative divisions of the Eastern Roman Empire. The list begins with Italy and moves counterclockwise along the Mediterranean, from Africa, Egypt and Oriens. The surviving list is evidently incomplete, as the Balkans are excluded. The ''Descriptio'' only survived in a compilation, probably from the 9th century, along with other lists such as ecclesiastical ''notitiae''. It is possible that the compiler, usually thought to be the Armenian Basil of Ialimbana, altered George's text.Kazhdan (1991), pp. 837–838 Publications * '' Georgii Cyprii Descriptio Orbis Romani'' (Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Alexandria (641)
Forces of the Rashidun Caliphate seized the major Mediterranean port of Alexandria away from the Eastern Roman Empire in the middle of the 7th century AD. Alexandria had been the capital of the Byzantine province of Egypt. This ended Eastern Roman maritime control and economic dominance of the Eastern Mediterranean and thus continued to shift geopolitical power further in favor of the Rashidun Caliphate. Historical overview With the death of Muhammad in 632 AD, the Muslim world began a period of rapid expansion. Under the rule of the first caliphs, the Rashidun, Muslim armies began assaulting the borders of both Sassanid Persia and the Byzantine Empire. Neither of the two former powers was prepared for the aggressive expansion of the Arabs, as both underestimated Islam and its growing support; this is best depicted by the views held by the Byzantines and the slow reaction of the Sassanids. After smashing both the Byzantines at Battle of Yarmouk, Yarmuk (636) and the Persians at Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zawyat Razin
Zawyat Razin (; ), formerly Shubra al-Laun () and Ibshāda (; ) known in Antiquity as Nikiû, Nikiou or Nikious (, , , ), is a city in the Monufia Governorate, Egypt. The region hosted Fort Nikiou which was built by Emperor Trajan. The city witnessed the Battle of Nikiou between the Rashidun Caliphate and Byzantine Empire in May of 646. According to an old Christian tradition, the Holy Family stayed here for a week during their Flight into Egypt. The first church was built here in the 3rd century. Etymology D.Meeks proposed an Egyptian origin for Nikiou, based a Shoshenqid donation stele in the Western Delta mentioning a Libyan settlement of Pr-Niȝk. This might have been transcribed into Greek as Νικίου. However, a more likely origin is Hellenic, with the toponym Νικίου πολίς likely being formed from the anthroponym Nikias. Nikias could have been the name of the lieutenant of Chabrias, who also gave his name to the "village of Nikias" on the road between A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |