|
Aging Movement Control
Normal aging movement control in humans is about the changes in the muscles, motor neurons, nerves, sensory functions, gait, fatigue, visual and manual responses, in men and women as they get older but who do not have neurological, muscular (atrophy, dystrophy...) or neuromuscular disorder. With aging, neuromuscular movements are impaired, though with training or practice, some aspects may be prevented. Force production For voluntary force production, action potentials occur in the cortex. They propagate in the spinal cord, the motor neurons and the set of muscle fibers they innervate. This results in a twitch which properties are driven by two mechanisms: motor unit recruitment and rate coding. Both mechanisms are affected with aging. For instance, the number of motor units may decrease, the size of the motor units, i.e. the number of muscle fibers they innervate may increase, the frequency at which the action potentials are triggered may be reduced. Consequently, force produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Strength
Physical strength is the measure of an individual's exertion of force on physical objects. Increasing physical strength is the goal of strength training. Overview An individual's physical strength is determined by two factors: the cross-sectional area of muscle fibers recruited to generate force and the intensity of the recruitment. Individuals with a high proportion of Muscle fibre#Type I, type I slow twitch muscle fibers will be relatively weaker than a similar individual with a high proportion of Muscle fibre#Type II, type II fast twitch fibers, but would have greater endurance. The genetic inheritance of muscle fiber type sets the outermost boundaries of physical strength possible (barring the use of enhancing agents such as testosterone), although the unique position within this envelope is determined by training. Individual muscle fiber ratios can be determined through a muscle biopsy. Other considerations are the ability to recruit muscle fibers for a particular activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antagonist Muscle
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Types There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or "voluntary muscle", is a striated muscle tissue that primarily joins to bone with tendons. Skeletal muscle enables movement of bones, and Proprioception#Reflexes, maintains posture. The widest part of a muscle that pulls on the tendons is known as the belly. Muscle slip A muscle slip is a slip of muscle that can either be an anatomical variant, or a branching of a muscle as in rib connections of the serratus anterior muscle. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in parts of the body where it conveys action without conscious intent. The majority of this type of muscle tissue is found in the digestive system, digestive and urinary systems where it acts by propelling forward foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extension (kinesiology)
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
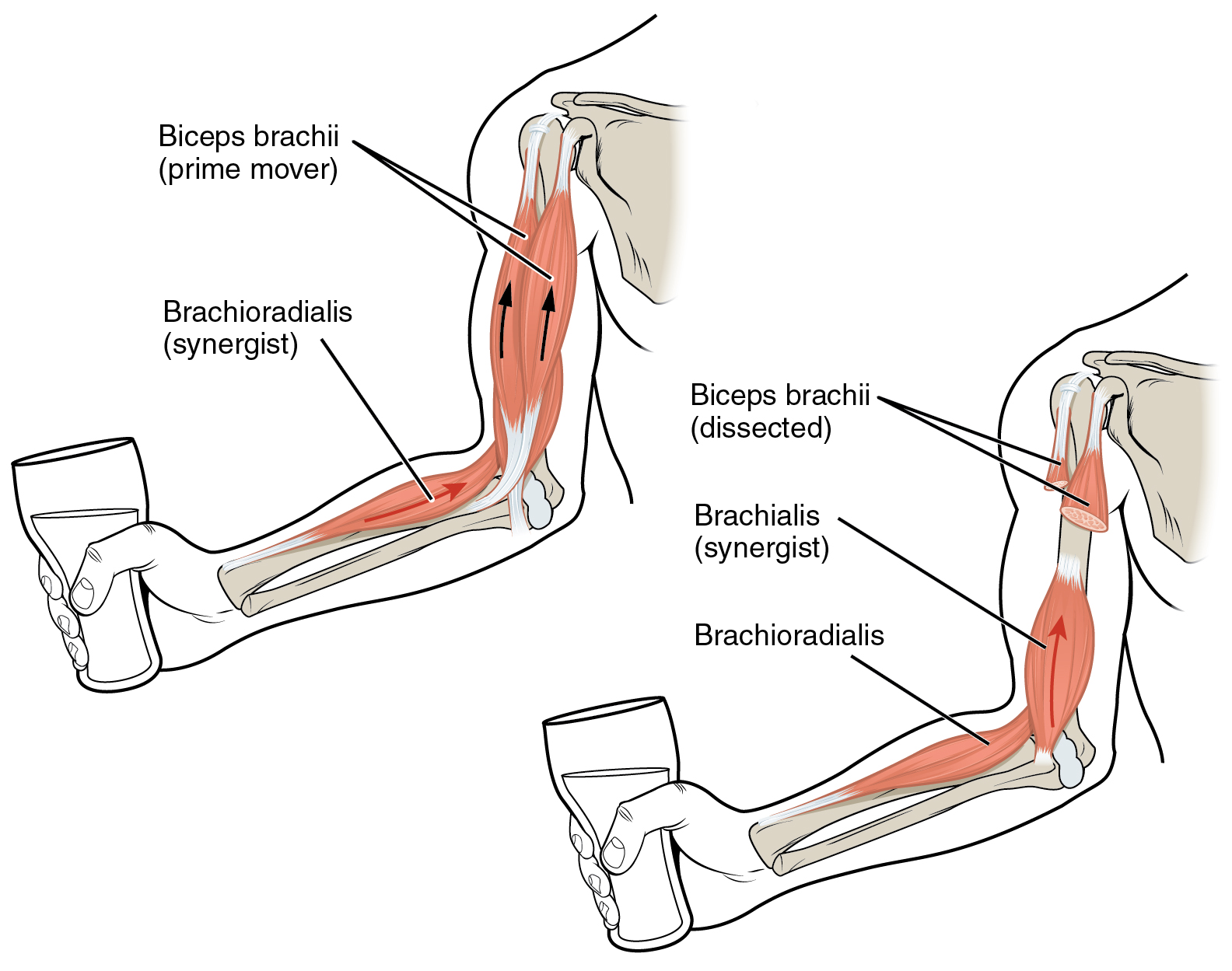
Elbow
The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennate Muscle
A pennate or pinnate muscle (also called a penniform muscle) is a type of skeletal muscle with fascicles that attach obliquely (in a slanting position) to its tendon. This type of muscle generally allows higher force production but a smaller range of motion. When a muscle contracts and shortens, the pennation angle increases. Etymology The term "pennate" comes from the Latin ''pinnātus'' ("feathered, winged"), from ''pinna'' ("feather, wing"). Types of pennate muscle In skeletal muscle tissue, 10-100 endomysium-sheathed muscle fibers are organized into perimysium-wrapped bundles known as fascicles. Each muscle is composed of a number of fascicles grouped together by a sleeve of connective tissue, known as an epimysium. In a pennate muscle, aponeuroses run along each side of the muscle and attach to the tendon. The fascicles attach to the aponeuroses and form an angle (the pennation angle) to the load axis of the muscle. If all the fascicles are on the same side of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Coding
Neural coding (or neural representation) is a neuroscience field concerned with characterising the hypothetical relationship between the stimulus and the neuronal responses, and the relationship among the electrical activities of the neurons in the ensemble. Based on the theory that sensory and other information is represented in the brain by networks of neurons, it is believed that neurons can encode both digital and analog information. Overview Neurons have an ability uncommon among the cells of the body to propagate signals rapidly over large distances by generating characteristic electrical pulses called action potentials: voltage spikes that can travel down axons. Sensory neurons change their activities by firing sequences of action potentials in various temporal patterns, with the presence of external sensory stimuli, such as light, sound, taste, smell and touch. Information about the stimulus is encoded in this pattern of action potentials and transmitted into and aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
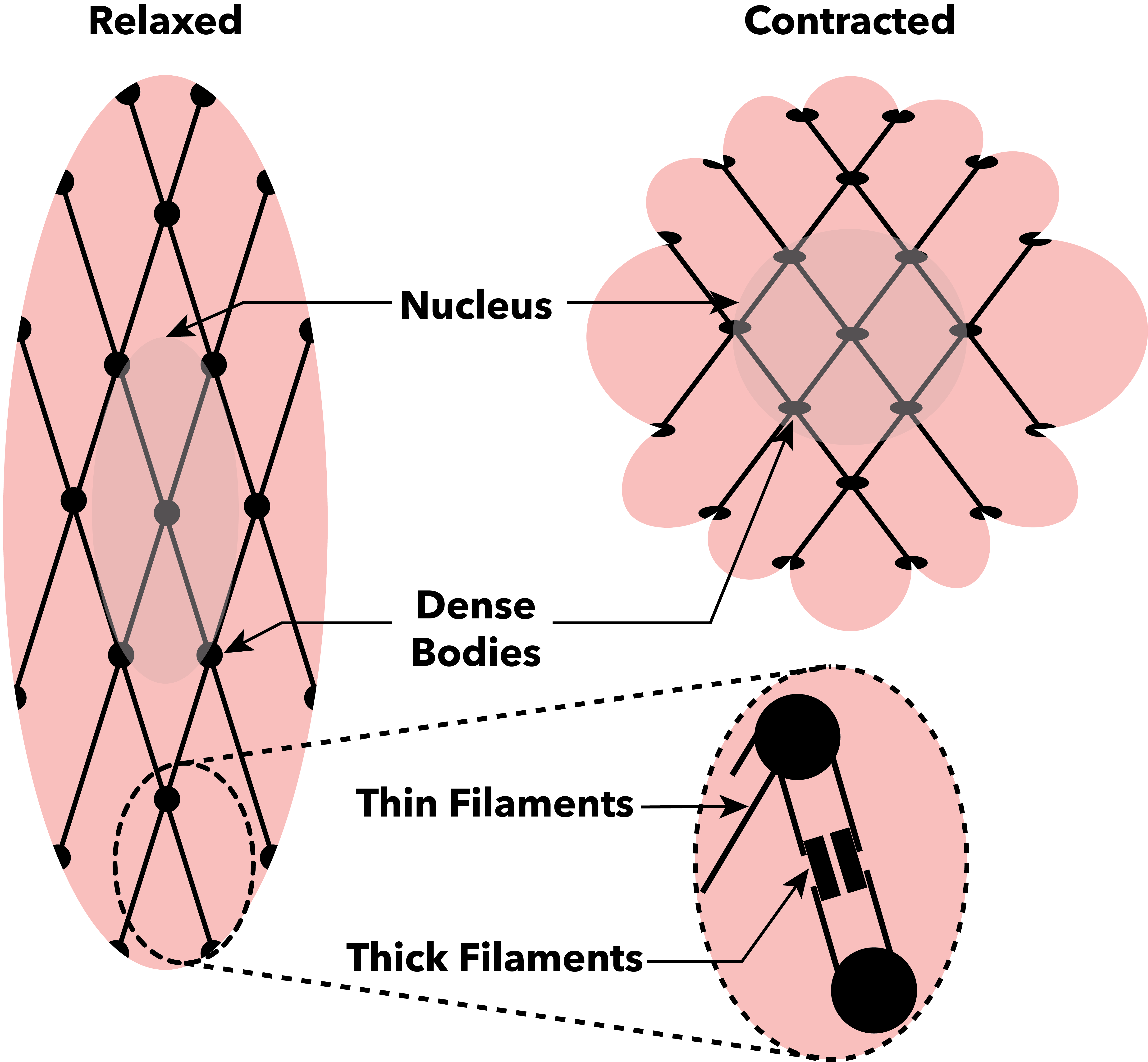
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Interossei Of The Hand
In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from the hand's midline (ray of middle finger) and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow ... joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers. Structure There are four dorsal interossei in each hand. They are specified as 'dorsal' to contrast them with the palmar interossei, which are located on the anterior side of the metacarpals. The dorsal interosseous muscles are bipennate, with each muscle arising by two heads from the adjacent sides of the metacarpal bones, but more extensively from the metacarpal bone of the finger into whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachialis Muscle
The brachialis (brachialis anticus) is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow pit). It originates from the anterior aspect of the distal humerus; it inserts onto the tuberosity of the ulna. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, and commonly also receives additional innervation from the radial nerve."Brachialis Muscle." Kenhub. Kenhub, Aug. 2001 The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion generating about 50% more power than the biceps.Saladin, Kenneth S, Stephen J. Sullivan, and Christina A. Gan. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 2015. Print. Structure Origin The brachialis originates from the anterior surface of the distal half of the humerus, near the insertion of the deltoid muscle, which it embraces by two angular processes. Its origin extends below to within 2.5 cm of the margin of the articular surface o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |