|
Affection (linguistics)
Affection (also known as vowel affection, infection or vowel mutation), in the linguistics of the Celtic languages, is the change in the quality of a vowel under the influence of the vowel of the following final syllable. It is a type of anticipatory (or regressive) assimilation at a distance. The vowel that triggers the change was later normally lost. Some grammatical suffixes cause i-affection. In Welsh, "word" and "device suffix" yield "dictionary", with in becoming . The two main types of affection are a-affection and i-affection.Benjamin W. Fortson, ''Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction''. 2nd edition. Blackwell, 2010. , p. 317, 321, 328. There is also u-affection, which is more usually referred to as u-infection. I-affection is an example of i-mutation and may be compared to the Germanic umlaut The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut (linguistics), umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Languages
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves Pezron, who made the explicit link between the Celts described by classical writers and the Welsh and Breton languages. During the first millennium BC, Celtic languages were spoken across much of Europe and central Anatolia. Today, they are restricted to the northwestern fringe of Europe and a few diaspora communities. There are six living languages: the four continuously living languages Breton, Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh, and the two revived languages Cornish and Manx. All are minority languages in their respective countries, though there are continuing efforts at revitalisation. Welsh is an official language in Wales and Irish is an official language across the island of Ireland and of the European Union. Welsh is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in Vowel length, quantity (length). They are usually voice (phonetics), voiced and are closely involved in Prosody (linguistics), prosodic variation such as tone (linguistics), tone, intonation (linguistics), intonation and Stress (linguistics), stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (, , , , , and sometimes and ). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one Phonetics, phonetic and the other Phonology, phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English language, English "ah" or "oh" , produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllable
A syllable is a basic unit of organization within a sequence of speech sounds, such as within a word, typically defined by linguists as a ''nucleus'' (most often a vowel) with optional sounds before or after that nucleus (''margins'', which are most often consonants). In phonology and studies of languages, syllables are often considered the "building blocks" of words. They can influence the rhythm of a language, its prosody, its poetic metre; properties such as stress, tone and reduplication operate on syllables and their parts. Speech can usually be divided up into a whole number of syllables: for example, the word ''ignite'' is made of two syllables: ''ig'' and ''nite''. Most languages of the world use relatively simple syllable structures that often alternate between vowels and consonants. Despite being present in virtually all human languages, syllables still have no precise definition that is valid for all known languages. A common criterion for finding syllable bound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assimilation (linguistics)
In phonology, assimilation is a sound change in which some phonemes (typically consonants or vowels) change to become more similar to other nearby sounds. This process is common across languages and can happen within a word or between words. For example, in English "handbag" (), the often shifts to in rapid speech, becoming , because and are both bilabial (produced with both lips), and their places of articulation are similar. It occurs in normal speech but is more frequent in faster speech. Sometimes the change is accepted as canonical, and can even become recognized in standard spelling: implosion pronounced with , composed of ''in-'' + ''-plosion'' (as in ''explosion''). Sound segments typically assimilate to a following sound, but they may also assimilate to a preceding one. Assimilation most commonly occurs between immediately adjacent sounds but may occur between sounds separated by others. For example, in "handbag," the is sometimes elided (omitted), which caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales by about 18% of the population, by some in England, and in (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). It is spoken by smaller numbers of people in Canada and the United States descended from Welsh immigrants, within their households (especially in Nova Scotia). Historically, it has also been known in English as "British", "Cambrian", "Cambric" and "Cymric". The Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011 gave the Welsh language official status in Wales. Welsh and English are ''de jure'' official languages of the Senedd (the Welsh parliament), with Welsh being the only ''de jure'' official language in any part of the United Kingdom, with English being merely ''de facto'' official. According to the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I-mutation
I-mutation (also known as umlaut, front mutation, i-umlaut, i/j-mutation or i/j-umlaut) is a type of sound change in which a back vowel is fronted or a front vowel is raised if the following syllable contains , or (a voiced palatal approximant, sometimes called ''yod'', the sound of English in ''yes''). It is a category of regressive metaphony, or vowel harmony. The term is usually used by scholars of the Germanic languages: it is particularly important in the history of the Germanic languages because inflectional suffixes with an or led to many vowel alternations that are still important in the morphology of the languages. Germanic languages ''I-mutation'' took place separately in the various Germanic languages from around 450 or 500 CE in the North Sea area and affected all the early languages, except for Gothic. It seems to have taken effect earliest and most completely in Old English and Old Norse. It took place later in Old High German; by 900, its effects a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
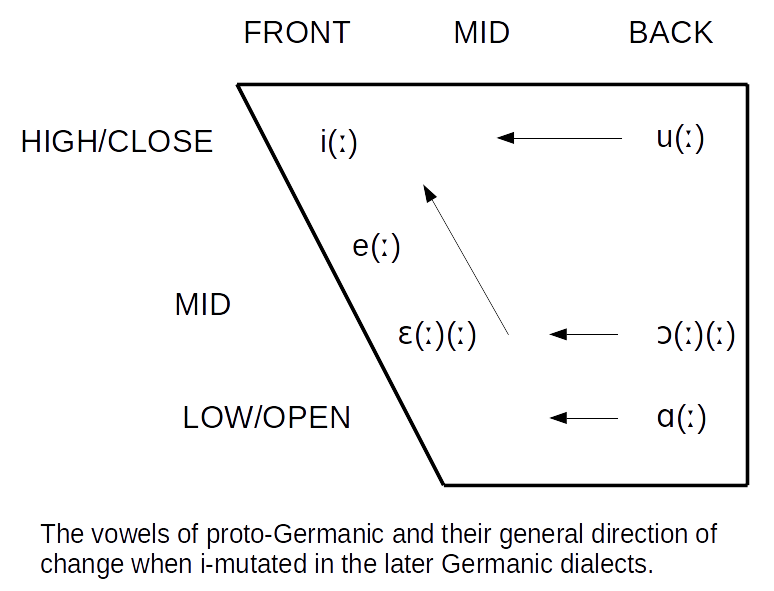
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut (linguistics), umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel (fronting (phonology), fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to (raising (phonetics), raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around 450 or 500 Common Era, CE and affected all of the early languages except Gothic language, Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation (other), u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic A-mutation
''A''-mutation is a metaphonic process supposed to have taken place in late Proto-Germanic (c. 200). General description In ''a''-mutation, a short high vowel ( or ) was lowered when the following syllable contained a non-high vowel (, or ).Gordon 1957, § 32. Thus, since the change was produced by other vowels besides */a/, the term ''a''-mutation is something of a misnomer. It has also been called "''a''-umlaut", "''a''/''o''-umlaut", "velar umlaut" and, formerly, "Brechung."Lloyd (1966), p. 738. (This last was Grimm's term, but nowadays German ''Brechung'', and its English equivalents ''breaking'' and ''fracture'', are generally restricted in use to other unrelated sound-changes which later affected individual Germanic languages.) :* > Old English "horn" :* > Old English "man" The high vowel was not lowered, however, if intervened between it and the following non-high vowel. An intervening nasal consonant followed by a consonant of any kind also blocked the process (and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umlaut (linguistics)
In linguistics, umlaut (from German language, German "sound alternation") is a sound change in which a vowel is pronounced more like a following vowel or semivowel. The term ''umlaut'' was originally coined by Jacob Grimm in connection with the study of Germanic languages, as umlaut had occurred prominently in many of their linguistic histories (see Germanic umlaut). While the common English plural is umlauts, the German plural is Umlaute. Umlaut is a form of Assimilation (linguistics), assimilation, the process of one speech sound becoming more similar to a nearby sound. Umlaut occurred in order to make words easier to pronounce. If a word has two vowels, one back in the mouth and the other forward, it takes more effort to pronounce than if those vowels were closer together. Thus, one way languages may change is that these two vowels get drawn closer together. The phenomenon is also known as vowel harmony, the complete or partial identity of vowels within a domain, typically a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocope
In phonology, apocope () is the omission (elision) or loss of a sound or sounds at the end of a word. While it most commonly refers to the loss of a final vowel, it can also describe the deletion of final consonants or even entire syllables. For instance, in many dialects the 't' in words like 'hot' remains unpronounced in contexts like 'hot potato'. Even longer words, such as 'Worcestershire', can undergo apocope, resulting in 'Worcester'. The resulting word form after apocope has occurred is called an . Etymology ''Apocope'' comes from the Greek () from () "cutting off", from () "away from" and () "to cut". Historical sound change In historical linguistics, ''apocope'' is often the loss of an unstressed vowel. Loss of an unstressed vowel or vowel and nasal * Latin → Portuguese (''sea'') * Vulgar Latin → Spanish (''bread'') * Vulgar Latin → French (''wolf'') * Proto-Germanic → Old, Middle, and Modern English ''land'' * Old English → Modern English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphony
In historical linguistics, metaphony is a class of sound change in which one vowel in a word is influenced by another in a process of assimilation. The sound change is normally "long-distance" in that the vowel triggering the change may be separated from the affected vowel by several consonants, or sometimes even by several syllables. For more discussion, see the article on vowel harmony. There are two types: *''Progressive'' (or ''left-to-right'') metaphony, in which a vowel towards the beginning of a word influences a subsequent vowel. *''Regressive'' (or ''right-to-left'') metaphony, in which a vowel towards the end of the word influences a preceding vowel. Metaphony is closely related to some other linguistic concepts: *''Vowel harmony'' is sometimes used synonymously with metaphony. Usually, however, "vowel harmony" refers specifically to a synchronic process operating in a particular language, normally requiring all vowels in a word to agree in a particular feature (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |