|
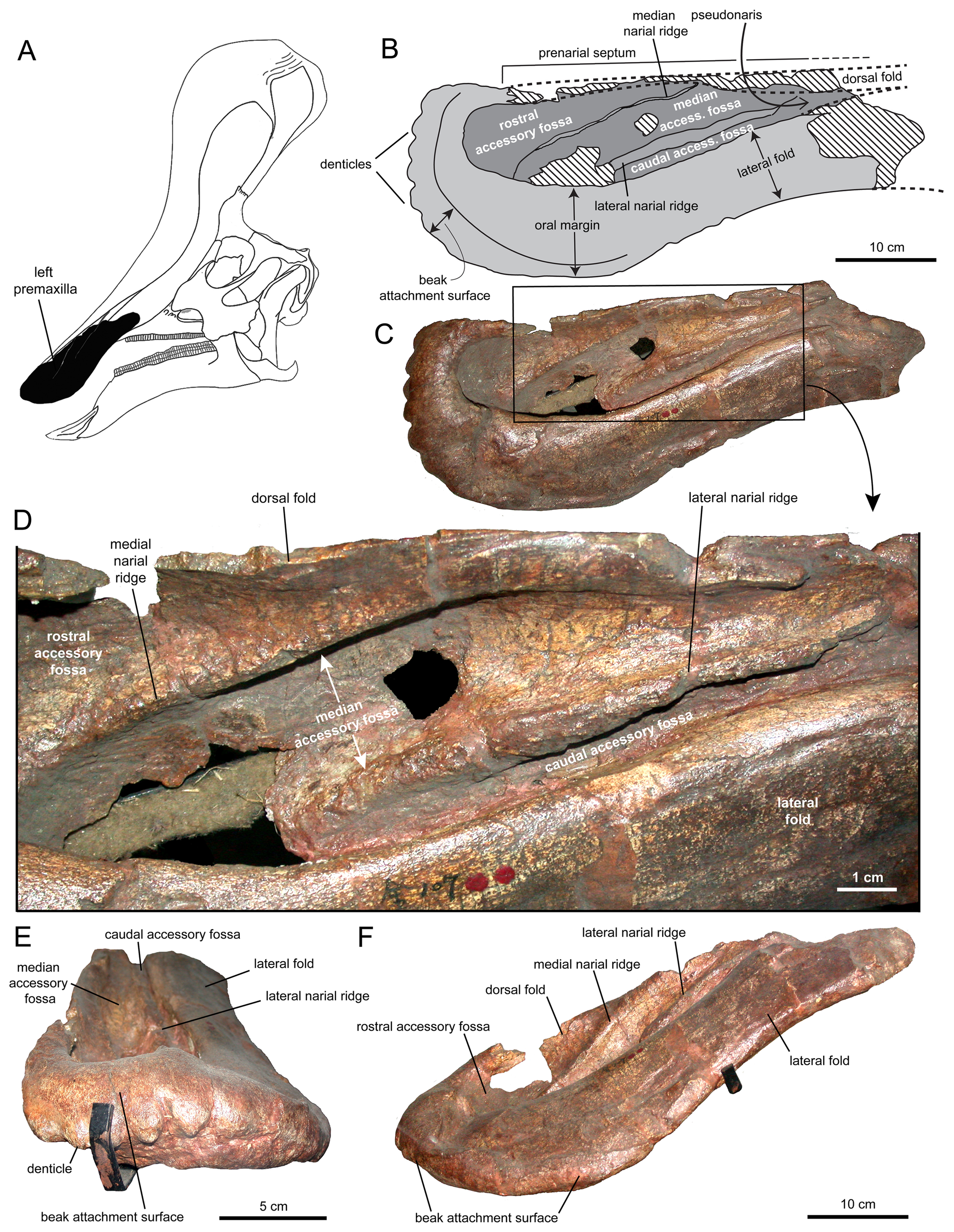
Adynomosaurus LM
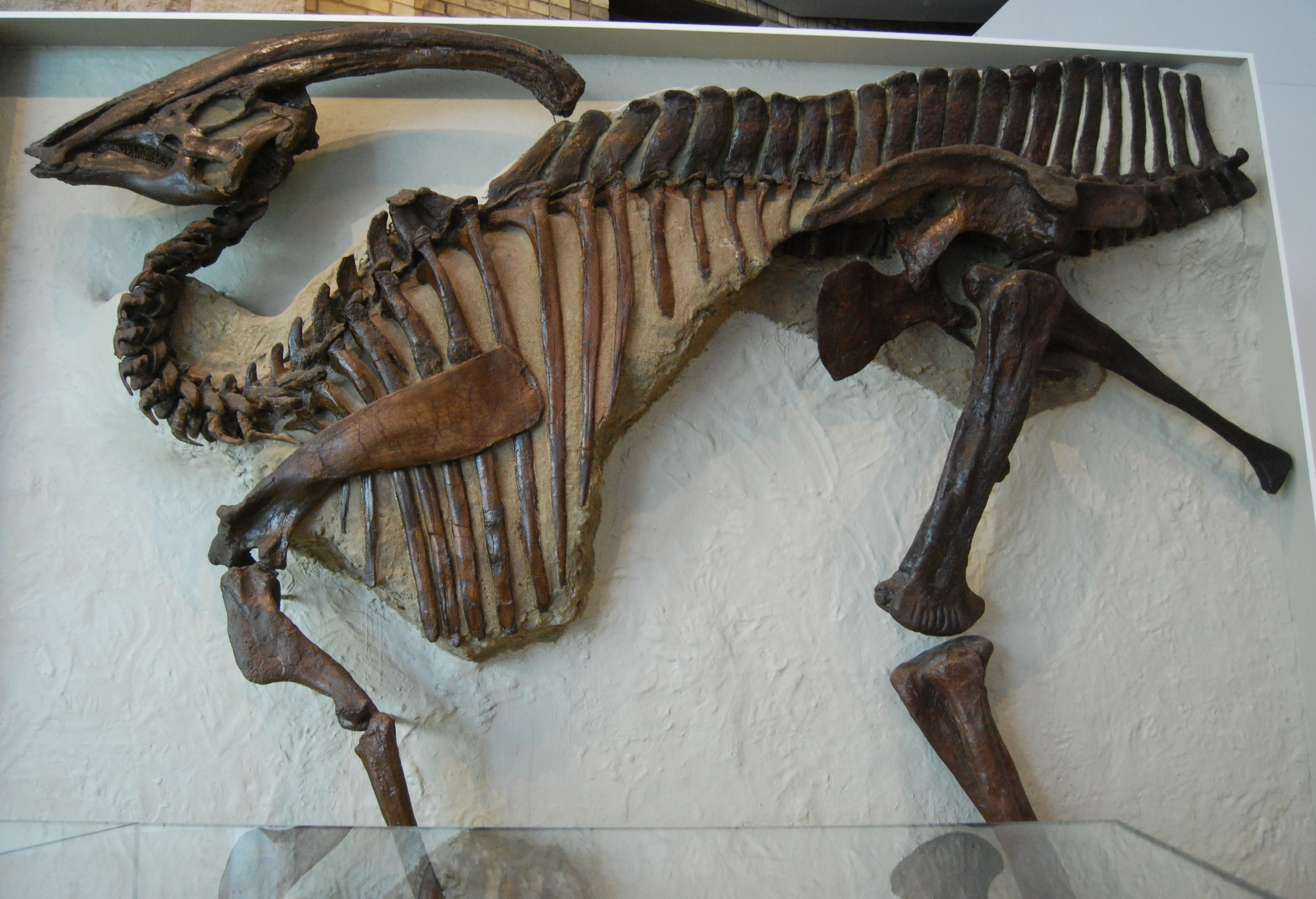
''Adynomosaurus'' is a genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of what is now Catalonia, Spain. First discovered in 2012, it was named in 2019 with the type and only species ''Adynomosaurus arcanus'', as an addition to the very incomplete fossil record of hadrosaurides dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of Europe. It is only known from scant material, but is distinguished from other hadrosaurs by its weakly developed shoulder blade which would have had underdeveloped musculature, which lends it its scientific name, partially from the Greek word for "weak". Its exact relationships with other hadrosaurs remain unresolved, with it not consistently being recovered as a relative of any other specific genera, though some studies have allied it with Tsintaosaurini or even found it outside of Hadrosauridae. It would have lived as part of a diverse coastal estuaryweak ecosystem, made up of meandering rivers and mud flats, and fits into a picture of major ecological turnove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myology
Myology is the study of the muscular system, including the study of the structure, function and diseases of muscle. The muscular system consists of skeletal muscle, which contracts to move or position parts of the body (e.g., the bones that articulate at joints), smooth and cardiac muscle that propels, expels or controls the flow of fluids and contained substance. See also *Myotomy Myotomy is a surgical procedure in which muscle Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells o ... * Oral myology References External links British Myology Society Physiology {{Muscle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basturs Poble Bonebed
The Basturs Poble bonebed is a mega-bonebed of hadrosaur dinosaur fossils, discovered in Catalonia, Spain. Hundreds of hadrosaur fossils have been found at the site, which would have been on a large island during the Late Cretaceous when the animals preserved were alive. Despite the enormous amount of specimens, taxonomically informative material has been scarce at the site, leading to extensive debate as to its nature. The number of species present, age of the individuals present in the sample, and taxonomic identity of the remains have been the primary matters of debate. Previous considered to represent ''Koutalisaurus'', ''Pararhabdodon'', or multiple, perhaps dwarf species, it is currently thought that a single, indeterminate species of lambeosaurine was present at the site, and that individuals of many different ages were present. Discovery and extent Marc Boada discovered, in the late 1990s, a new fossil-bearing locality from the village of Basturs, Catalonia. As the village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to the focal taxon (which may be a species, family or in general any clade). It can therefore be considered an apomorphy in relation to a single taxon. The word ''autapomorphy'', first introduced in 1950 by German entomologist Willi Hennig, is derived from the Greek words αὐτός, ''autos'' "self"; ἀπό, ''apo'' "away from"; and μορφή, ''morphḗ'' = "shape". Discussion Because autapomorphies are only present in a single taxon, they do not convey information about relationship. Therefore, autapomorphies are not useful to infer phylogenetic relationships. However, autapomorphy, like synapomorphy and plesiomorphy is a relative concept depending on the taxon in question. An autapomorphy at a given level may well be a synapomorphy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasaurolophus Cyrtocristatus
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to ''Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, about 76.5–73 million years ago. It was a herbivore that walked both as a biped and as a quadruped. Three species are universally recognized: ''P. walkeri'' (the type species), ''P. tubicen'', and the short-crested ''P. cyrtocristatus''. Additionally, a fourth species, ''P. jiayinensis'', has been proposed, although it is more commonly placed in the separate genus '' Charonosaurus''. Remains are known from Alberta (Canada), New Mexico and Utah (United States), and possibly Heilongjiang (China). The genus was first described in 1922 by William Parks from a skull and partial skeleton found in Alberta. ''Parasaurolophus'' was a hadrosaurid, part of a diverse family of Cretaceous dinosaurs known for their range of bizarre head adornme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsintaosaurus Spinorhinus
''Tsintaosaurus'' (; meaning " Qingdao lizard", after the old transliteration "Tsingtao") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about long and weighed . The type species is ''Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus'', first described by Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young in 1958. A hadrosaur, ''Tsintaosaurus'' had a characteristic 'duck bill' snout and a battery of powerful teeth which it used to chew vegetation. It usually walked on all fours, but could rear up on its hind legs to scout for predators and flee when it spotted one. Like other hadrosaurs, ''Tsintaosaurus'' probably lived in herds. Discovery and naming In 1950, at Hsikou, near Chingkangkou, in Laiyang, Shandong, in the eastern part of China, various remains of large hadrosaurids were uncovered. In 1958 these were described by Chinese paleontologist Yang Zhongjian ("C.C. Young") as the type species ''Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus''. The generic name is derived from the city of Qingdao, earlier often transl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasisaurus
''Blasisaurus'' is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It is known from a partial skull and skeleton found in late Maastrichtian-age rocks of Spain. The type species is ''Blasisaurus canudoi'', described in 2010 by Penélope Cruzado-Caballero, Xabier Pereda-Suberbiola and José Ignacio Ruiz-Omeñaca, a group of researchers from Spain. Naming and discovery The generic name refers to the ''Blasi 1'' site where the fossil was found. The specific epithet honours paleontologist José Ignacio Canudo. The holotype, MPZ99/667, is housed in Huesca. It was found in a layer of the Arén Formation dating from the upper Maastrichtian, about 66 million years ago. It consists of a skull with fragmentary lower jaws. Description ''Blasisaurus'' was a medium-sized ornithopod. Its describers identified two distinct features: the cheekbone has a rear projection with a hook-shaped upper edge and the lower sleep window is narrow and D-shaped. From the same forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arenysaurus
''Arenysaurus'' is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (66 million years ago), being one of the last non-avian dinosaurs and it went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. It is known from a partial skull and skeleton found in the late Maastrichtian-age Tremp Formation of the Pyrenees Mountains in Spain. The type species is ''A. ardevoli'', described in 2009 by Pereda-Suberbiola ''et al.'', a group of researchers from Spain. The genus name refers to Arén, where it was found, and the specific epithet honours geologist Lluís Ardèvol. ''Arenysaurus'' was a lambeosaurine, a member of the hadrosaurid subfamily with hollow and decorative cranial crests. It is one of the most complete and best dated ever found in the Late Cretaceous period. Description ''Arenysaurus'' was a medium-sized hadrosaur, measuring long and weighing . Its fossils were found in a small village (350 inhabitants) in the Aragonese Pyrenees called Arén (Areny in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koutalisaurus
''Koutalisaurus'' (meaning "spoon lizard", in reference to the shape of the dentary) is a potentially dubious genus of extinct hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Arenysaurini. It is based on a mostly complete dentary from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Formation near the town of Abella de la Conca, Lleida, Spain. Discovery and naming The holotype dentary, IPS SRA 27, had previously been referred to ''Pararhabdodon'' in 1999,Casanovas, M.L, Pereda-Suberbiola, X., Santafé, J.V., and Weishampel, D.B. (1999). First lambeosaurine hadrosaurid from Europe: palaeobiogeographical implications. ''Geological Magazine'' 136(2):205-211. but comes from a different locality, is based on non-comparable material, and has unusual characteristics, leading Prieto-Marquez ''et al.'' (2006) to place the dentary in the new species ''Koutalisaurus kohleorum''.Prieto-Marquez, A., Gaete, R., Rivas, G., Galobart, Á., and Boada, M. (2006). Hadrosauroid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapulae Of Olorotitan Arharensis Godefroit, Bolotsky & Alifanov, 2003
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |