|
Adverb
An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by answering questions such as ''how'', ''in what way'', ''when'', ''where'', ''to what extent''. This is called the adverbial function and may be performed by an individual adverb, by an adverbial phrase, or by an adverbial clause. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Modern linguists note that the term ''adverb'' has come to be used as a kind of "catch-all" category, used to classify words with various types of syntactic behavior, not necessarily having much in common except that they do not fit into any of the other available categories (noun, adjective, preposition, etc.). Functions The English word ''adverb'' derives (through French) from Latin ''adverbium'', from ''ad-'' ('to'), ''verbum'' ('word', 'ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adverbial Phrase
In linguistics, an ''adverbial phrase'' ("AdvP") is a multi-word expression operating adverbially: its syntactic function is to modify other expressions, including verbs, adjectives, adverbs, adverbials, and sentences. Some grammars use the label adverb phrase to denote an adverbial phrase composed entirely of adverbs versus an ''adverbial phrase'', which might not contain an adverb. Adverbial phrases can be divided into two types: complementary phrases and modifying phrases. For example, ''very well'' is a complementary adverbial phrase that complements "sang" in the sentence "She sang ''very well''". More specifically, the adverbial phrase ''very well'' contains two adverbs, ''very'' and ''well'': while ''well'' qualifies the verb to convey information about the manner of singing. By contrast, ''almost always'' is a modifying adverbial phrase that modifies "skip" in the sentence "I ''almost always'' skip breakfast." The following examples illustrate some of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
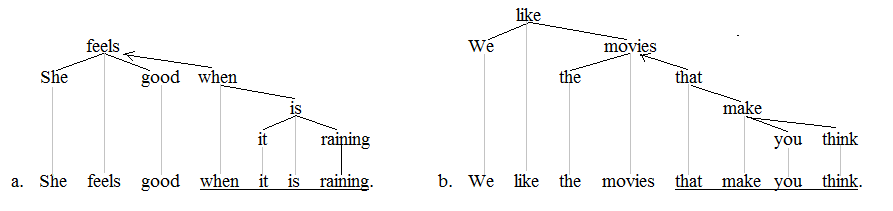
Adverbial Clause
An adverbial clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb. That is, the entire clause modifies a separate element within a sentence or the sentence itself. As with all clauses, it contains a subject and predicate, though the subject as well as the (predicate) verb are omitted and implied if the clause is reduced to an adverbial phrase as discussed below. Adverbial clause versus adverbial phrase Adverbial clauses An adverbial clause begins with a subordinating conjunction—sometimes called a trigger word. In the examples below, the adverbial clause is italicized and the subordinating conjunction is bolded: :Mary, the aspiring actress, became upset as soon ''as she saw the casting list''. ::(subject: ''she''; predicate: ''saw the casting list''; the clause modifies the verb ''became'') :Peter, the drama teacher, met with Mary ''after she calmed down''. ::(explicit subject: ''she''; predicate: ''calmed down''; predicate (verb): ''calmed''; the clause modifies the verb ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
English Adverbs
English adverbs are words such as ''so'', ''just'', ''how'', ''well'', ''also'', ''very'', ''even'', ''only'', ''really'', and ''why'' that Head (linguistics), head Adverbial phrase, adverb phrases, and whose most typical members function as modifiers in verb phrases and clauses, along with Adjective phrase, adjective and adverb phrases. The category is highly heterogeneous, but a large number of the very typical members are derived from adjectives + the suffix ''-ly'' (e.g., ''actually'', ''probably'', ''especially'', & ''finally'') and modify any word, phrase or clause other than a noun. Adverbs form an open lexical category in English. They do not typically license or function as complements in other phrases. Semantically, they are again highly various, denoting manner, degree, duration, frequency, domain, modality, and much more. History of the concept in English One of the first records we have of the word ''adverb'' used in English is from c1425. William Bullokar wrote th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flat Adverb
In English grammar, a flat adverb, bare adverb, or simple adverb is an adverb that has the same form as the corresponding adjective,Garner's Modern American Usage p. 897 so it usually does not end in ''-ly'', e.g. "drive ''slow''", "drive ''safe''", "dress ''smart''", etc. The term includes words that naturally end in -ly in both forms, e.g. "drive ''friendly''". Flat adverbs were once quite common but have been largely replaced by their ''-ly'' counterparts. In the 18th century, grammarians believed flat adverbs to be adjectives, and insisted that adverbs needed to end in ''-ly''. According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, "It's these grammarians we have to thank for ... the sad lack of flat adverbs today". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adjective, as in a ''laughing face''". "Participle" is a traditional grammatical term from Greek and Latin that is widely used for corresponding verb forms in European languages and analogous forms in Sanskrit and Arabic grammar. In particular, Greek and Latin participles are inflected for gender, number and case, but also conjugated for tense and voice and can take prepositional and adverbial modifiers. Cross-linguistically, participles may have a range of functions apart from adjectival modification. In European and Indian languages, the past participle is used to form the passive voice. In English, participles are also associated with periphrastic verb forms ( continuous and perfect) and are widely used in adverbial clauses. In non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parts Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adverbial
In English grammar, an adverbial ( abbreviated ) is a word (an adverb) or a group of words (an adverbial clause or adverbial phrase) that modifies or more closely defines the sentence or the verb. (The word ''adverbial'' itself is also used as an adjective, meaning "having the same function as an adverb".) Look at the examples below: :''Danny speaks fluently.'' (telling more about the verb) :''Lorna ate breakfast yesterday morning''. (telling when the verb's action occurred) The form of adverbials Adverbials most commonly take the form of adverbs, adverb phrases, temporal noun phrases or prepositional phrases. Many types of adverbials (for instance: reason and condition) are often expressed by clauses In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), .... :''James answered immedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Preposition
Adpositions are a part of speech, class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various thematic relations, semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complement) and postpositions (which follow their complement). An adposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement (grammar), complement, or sometimes object (grammar), object. English language, English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in, under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as "in England", "under the table", "of Jane" – although there are a few exceptions including ''ago'' and ''notwithstanding'', as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead (like Turkic languages) or have both types (like Finnish language, Finnish). The phrase form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |