|
Administrative Divisions Of The Kingdom Of Hungary (1941–1945)
This article discusses the administrative divisions of the Kingdom of Hungary between 1941 and 1945. As a result of the First (1938) and Second Vienna Award (1940), territories that had been ceded by the Kingdom of Hungary at the 1920 Treaty of Trianon were partly regained from Czechoslovakia and Romania respectively. This required modification of the administrative divisions. Hungary excluding Sub-Carpathia had three levels of administrative sub-division. Level One were: County (''Vármegye'', vm) and City with Municipal Status (''Törvényhatósági Jogú Város'', tjv). Counties were divided into Districts (''Járás'', j) and Urban Districts ''Megyei Város'', mv) which constituted the second level. A third level were Sub-Districts, which were temporary entities typically created to give a position to a politician when no district leader posts were available. The City of Budapest had the unique status of Royal Seat and Capital (''székesfőváros'', szfv.) and was legally di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary 1941-44 Administrative Map
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpathian Basin by Hung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bars County
Bars (Latin: ''comitatus Barsiensis'', Hungarian: ''Bars'', Slovak: ''Tekov'', German: ''Barsch'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central and southern Slovakia. Today in Slovakia, Tekov is the informal designation of the corresponding territory. Geography Bars County shared borders with the Hungarian counties of , , , , and . It was situated along the Garam river between Hont in the east, Körmöcbánya and Felsőbesenyő in the north (which were part of the county), the Zsitva river in the west, and Zsitvabesenyő and Bény in the south (which was not part of the county). The rivers Garam and Zsitva ran through the county. The county was characterised by mining. Around 1910, its area was . Capitals The capital of the county was the Bars Castle, then the Léva Castle, then from the late 16th century Kistapolcsány and since the 18th century Aranyosmarót. History The county arose in the 11th century. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fejér County (former)
Fejér (in Latin: ''comitatus Albensis'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was slightly smaller than that of present Fejér county, today in central Hungary. The capital of the county was Székesfehérvár. Geography Fejér county shared borders with the Hungarian counties Veszprém, Komárom, Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun and Tolna. It lay southwest of Budapest, around Székesfehérvár. The river Danube formed most of its eastern border. Its area was 4129 km2 around 1910. History Fejér county arose as one of the first comitatus of the Kingdom of Hungary, in the 11th century. Székesfehérvár, as a seat for the coronation of the Hungarian monarch and location of royal burials, held a central role in the Middle Ages. The Solt region, east of the Danube river, which used to be part of Fejér county, went to Pest-Pilis-Solt county in 1569. In 1945, the city of Érd and its surroundings went to Pest county, while in 1950 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Csongrád County (former)
Csongrád ( Hungarian: ''Csongrád'', Serbian: ''Čongrad'' or ''Чонград'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was smaller than that of present-day Csongrád-Csanád County, is now part of Hungary, except a very small area which belongs to Serbia. The capital of the county was Szentes. Name The name Csongrád/Čongrad is Slavic by origin. In Slavic languages, this name means "a black city" (čon/čorni = black, grad = city/town). Indeed, the county was named after a town of Csongrád. Geography Csongrád county shared borders with the Hungarian counties Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok, Békés, Csanád, Torontál and Bács-Bodrog. The river Tisza flowed through the county. Its area was 3,544 km2 around 1910. History Csongrád county arose in the 11th century as one of the first counties of the Kingdom of Hungary. It was taken by the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century, and reconquered by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Csík County
Csík (Hungarian, in Romanian: ''Ciuc'') was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central Romania (eastern Transylvania). The capital of the county was Csíkszereda (now Miercurea Ciuc). Geography Csík county shared borders with Kingdom of Romania and the Hungarian counties of Beszterce-Naszód, Maros-Torda, Udvarhely and Háromszék. The county was situated in the Carpathian Mountains, around the sources and upper courses of the rivers Olt and Mureș. Its area was 4,859 km2 around 1910. History Csík county consisted of three former seats of the Székelys: Csíkszék, Gyergyószék and Kászonszék (the latter two as filial seats of the former). It was formed in 1876, when the administrative structure of Transylvania was changed. In 1920, by the Treaty of Trianon, the county became part of Romania. It was returned to Hungary by the Second Vienna Award of 1940. After World War II, it became again part of Romania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
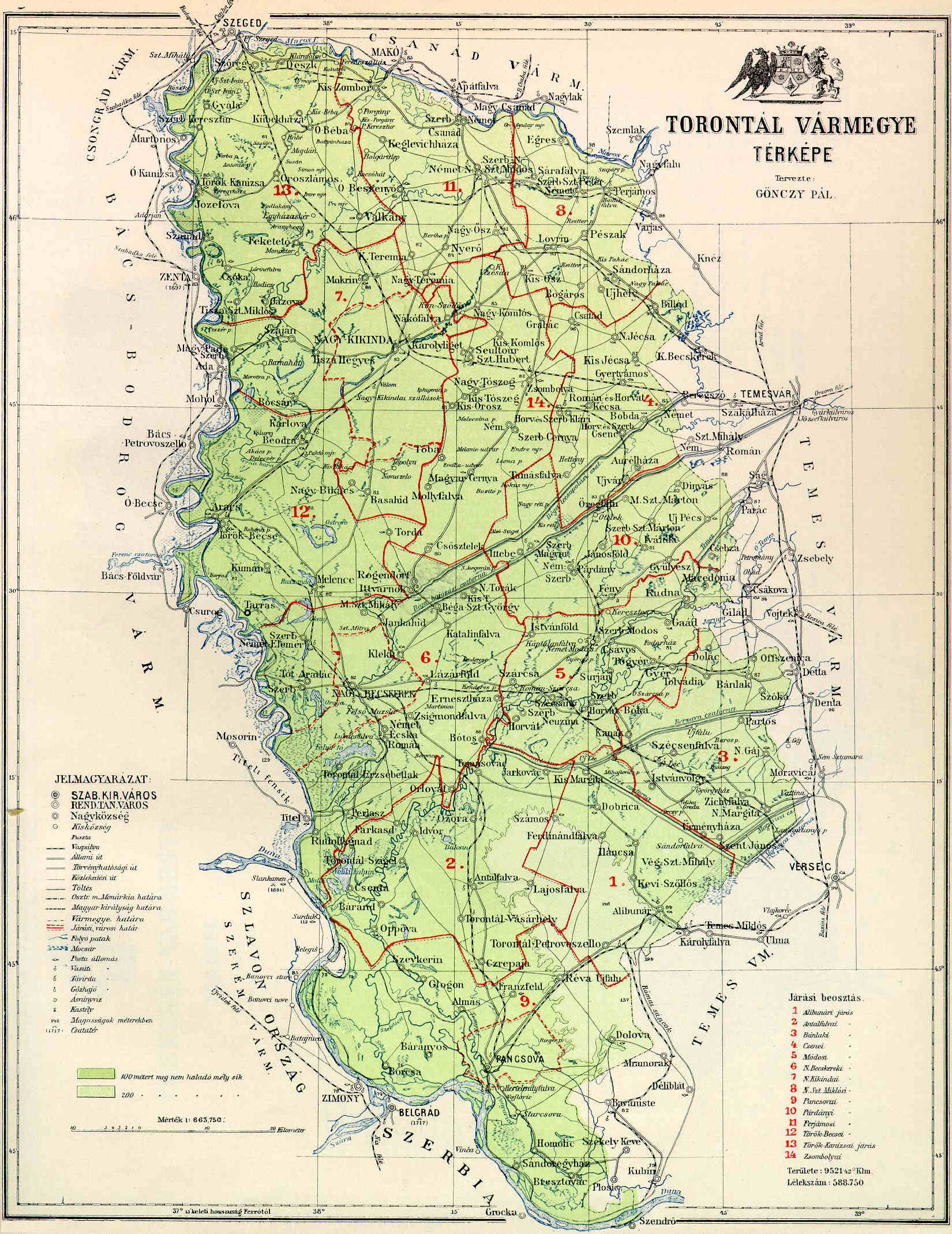
Torontál County
Torontál (, , , ) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Serbia and Romania, except for a small area which is part of Hungary. The capital of the county was Nagybecskerek (, , ), the current Zrenjanin. Geography Torontál county was located in the Banat region. From its recreation in 1779 until its partition in 1920 it shared borders with the Hungarian counties of Bács-Bodrog, Csongrád, Csanád, Arad and Temes. The Banat Military Frontier lay along its southern border until it was abolished in 1873, after which the river Danube formed its southern border, which it shared with the Principality of Serbia (Kingdom of Serbia after 1882), and the Slavonian Military Frontier ( Croatian-Slavonian county of Syrmia after 1881). The river Tisza formed its western border and the river Maros (Mureș) its northern border. The rivers Aranca, Bega, Timiș and Bârzava flowed through the county. Its area was arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arad County (former)
Arad County was an administrative unit in the Kingdom of Hungary, the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and the Principality of Transylvania. The county was established along the Maros (Mureș) river in the 11th or the , but its first head, or ''ispán'', was only mentioned in 1214. Its territory is now part of Romania, except a small area (the town of Elek and the surrounding villages) which is part of Hungary. The capital of the county was Arad. Geography The medieval Arad County was situated in the lands along both banks of the Maros (Mureș) River. The existence of arable lands, pastures, vineyards and orchards in the western lowlands in the Middle Ages is well-documented. The hilly eastern regions were sparsely populated. The total territory of the medieval county was around . In 1744, Arad County absorbed a large part of Zaránd County, including its capital Zaránd/Zărand (the remainder of Zarand County was then reorganized, with Körösbánya/Baia de Criș as the new ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Csanád County
Csanád was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now part of Hungary, except for a small area which is part of Romania. The capital of the county was Makó. Geography Csanád county shared borders with the Hungarian counties of Csongrád, Békés, Arad and Torontál. The river Maros ( Mureș) formed its southern border. Its area was 1,714 km2 around 1910. History The county's territory became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in the first half of the 11th century when Stephen I of Hungary defeated Ajtony, the local ruler. The county got its name after the commander of the royal army, Csanád. The king appointed Gerard of Csanád as the first bishop of Csanád. The county was initially much larger and included territories of the later Temes, Arad, and Torontál counties. The first seat of the county was Csanád (present-day Cenad, Romania). The county's territory became part of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borsod County
Borsod was an administrative county ( comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. The capital of the county was Miskolc. After World War II, the county was merged with the Hungarian parts of Abaúj-Torna County and Zemplén counties to form Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county. Etymology The name comes from the personal name ''Bors'' (an early medieval magnate) with the -d suffix used to derive place names in old Hungarian language. The personal name ''Bors'' could have derived from ''bors'' (Hungarian "pepper") and/or derived from Turkish (a theory of János Melich) or from the Slavic personal name ''Boriš'' (a theory of Elemér Moór). The problem has not been sufficiently resolved yet. E.g. Lajos Kiss suggests the Turkish origin, whilst Slovak scholars have been suggesting the Slavic origin since the times of Ján Stanislav who accepted Moór's theory as more reliable and pointed to several place names with similar etymology (''*Bor �a''). Ján Steinhübel points to the Czech name Bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bihar County
Bihar was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary and a county of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and Principality of Transylvania (since the 16th century, when it was under the rule of the Princes of Transylvania). Most of its territory is now part of Romania, while a smaller western part belongs to Hungary. The capital of the county was Nagyvárad (now Oradea in Romania). Albrecht Dürer's father was from this county. Geography Bihar County was situated along the upper courses of the rivers Körös, Sebes-Körös, Fekete-Körös and Berettyó. The medieval county also included ''Kalotaszeg'' region (now Țara Călatei in Romania). The total territory of the medieval county was around . After 1876, Bihar county shared borders with the Hungarian counties Békés, Hajdú, Szabolcs, Szatmár, Szilágy, Kolozs, Torda-Aranyos and Arad. The western half of the county was in the Pannonian plain, while the eastern half was part of the Apuseni mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beszterce-Naszód County
Beszterce-Naszód was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in northern Romania (north-eastern Transylvania). The capital of the county was Beszterce (now Bistrița). Geography Beszterce-Naszód county shared borders with the Kingdom of Romania, Austrian Bukovina and the Hungarian counties of Máramaros, Szolnok-Doboka, Kolozs, Maros-Torda and Csík. Its area was 4,167 km² around 1910. History Beszterce-Naszód county was formed in 1876, when the Saxon district of Bistritz/Bistrița was united with the former Transylvanian Military Frontier district of Năsăud (Romanian Border Regiment II), also joined by parts of the former Doboka and Belső-Szolnok counties. In 1920, the Treaty of Trianon assigned the territory of Beszterce-Naszód county to Romania. In 1940, by the Second Vienna Award, it was returned to Hungary and was expanded with additional territories from the former Kolozs County. After World War II, it became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |