|
Adit
An adit (from Latin ''aditus'', entrance) or stulm is a horizontal or nearly horizontal passage to an underground mine. Miners can use adits for access, drainage, ventilation, and extracting minerals at the lowest convenient level. Adits are also used to explore for mineral veins. Although most strongly associated with mining, the term ''adit'' is sometimes also used in the context of underground excavation for non-mining purposes; for example, to refer to smaller underground passageways excavated for underground metro systems, to provide pedestrian access to stations (pedestrian adits), and for access required during construction (construction adits). Construction Adits are driven into the side of a hill or mountain, and are often used when an ore body is located inside the mountain but above the adjacent valley floor or coastal plain. In cases where the mineral vein outcrops at the surface, the adit may follow the lode or vein until it is worked out, in which case the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great County Adit
The Great County Adit, sometimes called the County Adit, or the Great Adit was a system of interconnected adits that helped drain water from the tin and copper mines in the Gwennap area of Cornwall, in the United Kingdom. Construction started in 1748 and it eventually reached a length of over of a tunnel, providing drainage to over 100 mines at an average depth of . The adit was the brainchild of John Williams (born 1714) of Scorrier who was the manager of Poldice mine. Although work was started in 1748, it did not reach Poldice mine until the late 1760s. By 1778 the adit had been extended past Wheal Busy to Wheal Peevor, and another branch, known as the Consols Adit was driven west in the 1770s and 80s to drain the Consolidated Mines and United Mines. By 1792 a branch from Poldice extended to Wheal Unity. The portal of the adit is in the Carnon Valley below the hamlet of Twelveheads. In 1839, probably at its peak, it discharged over 14.5 million gallons (66 million litr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesterfield Canal
The Chesterfield Canal is a narrow canal in the East Midlands of England and it is known locally as 'Cuckoo Dyke'. It was one of the last of the canals designed by James Brindley, who died while it was being constructed. It was opened in 1777 and ran for from the River Trent at West Stockwith, Nottinghamshire to Chesterfield, Derbyshire, passing through the Norwood Tunnel at Kiveton Park, at the time one of the longest tunnels on the British canal system. The canal was built to export coal, limestone, and lead from Derbyshire, iron from Chesterfield, and corn, deals, timber, groceries and general merchandise into Derbyshire. The stone for the Palace of Westminster was quarried in North Anston, Rotherham, and transported via the canal. It was reasonably profitable, paying dividends from 1789, and with the coming of the railways, some of the proprietors formed a railway company. It became part of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway company, and although there w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining In Cornwall And Devon
Mining in Cornwall and Devon, in the southwest of Britain, is thought to have begun in the early-middle Bronze Age with the exploitation of cassiterite. Tin, and later copper, were the most commonly extracted metals. Some tin mining continued long after the mining of other metals had become unprofitable, but ended in the late 20th century. In 2021, it was announced that a new mine was extracting battery-grade lithium carbonate, more than 20 years after the closure of the last South Crofty tin mine in Cornwall in 1998. Historically, tin and copper as well as a few other metals (e.g. arsenic, silver, and zinc) have been mined in Cornwall and Devon. Tin deposits still exist in Cornwall, and there has been talk of reopening the South Crofty tin mine. In addition, work has begun on re-opening the Hemerdon tungsten and tin mine in southwest Devon. In view of the economic importance of mines and quarries, geological studies have been conducted; about forty distinct minerals have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Car (railway)
A cable car (usually known as a cable tram outside North America) is a type of cable railway used for Public transport, mass transit in which rail cars are hauled by a continuously moving Wire rope, cable running at a constant speed. Individual cars stop and start by releasing and gripping this cable as required. Cable cars are distinct from funiculars, where the cars are permanently attached to the cable. History The first cable-operated railway to use a moving rope that could be picked up or released by a Cable grip, grip on the cars was the Fawdon Wagonway, a colliery railway line that opened in 1826. Another began operation in 1840: the London and Blackwall Railway, which hauled passengers in east London, England. The rope available at the time proved too susceptible to wear and the system was abandoned in favour of steam locomotives after eight years. In America, the first cable car installation in operation probably was the IRT Ninth Avenue Line, West Side and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the ninth-least densely populated U.S. state. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's population live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); due to the presidency of Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft Mining
Shaft mining or shaft sinking is the action of excavating a mine shaft from the top down, where there is initially no access to the bottom. Shaft (civil engineering), Shallow shafts, typically sunk for civil engineering projects, differ greatly in execution method from deep shafts, typically sunk for mining projects. Shaft sinking is one of the most difficult of all mining development methods: restricted space, gravity, groundwater and specialized procedures make the task quite formidable. Shafts may be sunk by conventional drill and blast or mechanised means. Historically, mine shaft sinking has been among the most dangerous of all the mining occupations and the preserve of mining contractors called sinker (mining), sinkers. Today shaft sinking contractors are concentrated in Canada, Germany, China and South Africa. The modern shaft sinking industry is gradually shifting further towards greater mechanisation. Recent innovations in the form of full-face shaft boring (akin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
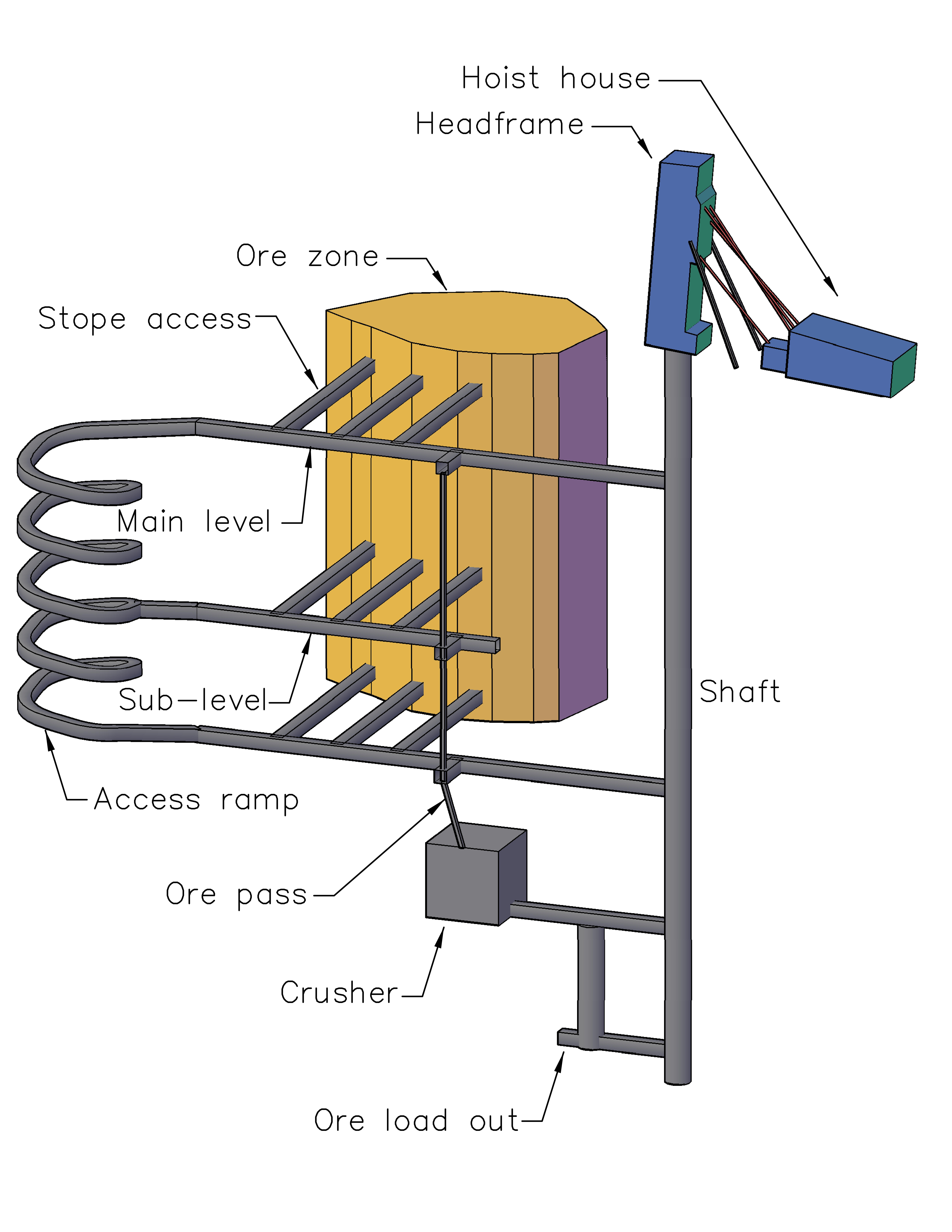
Underground Mining (hard Rock)
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shafts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollingwood
Hollingwood is a small village approximately four miles north east of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England. Description Hollingwood and Barrow Hill were built in c.1900 when the Staveley Coal and Iron Company was formed and built homes there for the workers. It is alleged that Hollingwood was the first village in the country to have hot running water via a ring main from a central boiler house in the village. This boiler house was shut down in the very early 1980s when gas and electric boilers became readily available. It is surrounded by Brimington (where the population is included), Barrow Hill, and Inkersall. Between Barrow Hill and Hollingwood runs the Chesterfield Canal which is currently being regenerated by the Chesterfield Canal Trust. The canal house at Hollingwood has been renovated as a visitor centre and a very popular cafe, as well as being the headquarters of the Trust. The remains of the entrance to the Hollingwood Common Canal, originally a navigable adit, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollingwood Common Canal
The Hollingwood Common Canal (alternatively the Hollingwood Common Canal Tunnel or the Hollingwood Common Tunnel) is a disused navigable coal mine adit which terminated at the Chesterfield Canal at Hollingwood, near Staveley, Derbyshire. History The Hollingwood Common canal tunnel was long, and measured high, with of water. Its water level was lower than that of the Chesterfield canal, requiring the trans-shipment of coal at a wharf constructed at the terminus. The water level in the tunnel was maintained lower than the canal by a culvert that ran beneath the canal. The wharf was on the old line of the Chesterfield Canal, prior to the 1892 cut being constructed. The entrance to the tunnel is still visible, though is gated off. Boats used were loaded underground within the coal mine the tunnel served; these boats were long and wide, and held seven cones or boxes containing twenty to twenty two hundredweight of coal each. Remains The wharf where the coal was transhipped was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutro Tunnel
The Sutro Tunnel is a drainage tunnel (adit) connected to the Comstock Lode in Northern Nevada. It begins at Dayton, Nevada, and connects Northwest to the Savage mine in Virginia City, Nevada. The Sutro Tunnel pioneered the excavation of large drainage and access tunnels in the US. Later US mine drainage tunnels included the Argo Tunnel at Idaho Springs, Colorado, the Leadville and Yak tunnels at Leadville mining district, Leadville, Colorado, and the Roosevelt tunnel in the Cripple Creek district, Colorado. History The tunnel was proposed by Adolph Sutro, a Prussian Jewish mining entrepreneur, in 1860. He promoted the drainage tunnel to allow access to deeper mineral exploration in the Comstock. Flooding and inadequate pumps had inhibited some exploration until that time. By 1865, Sutro's idea had gained the approval of the state and US federal governments. The mining interests of the Comstock initially supported the project, but later opposed the idea. They feared that an alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |