|
Ad Deir
Ed-Deir (, ), also spelled el-Deir and ad-Deir/ad-Dayr, is a monumental building carved out of rock in the ancient city of Petra in southern Jordan. The Deir was probably carved in the mid-first century AD. Arguably one of the most iconic ancient Arab monuments in the Petra Archaeological Park, the monastery is located high in the hills northwest of the Petra city center. It is the second most commonly visited monument in Petra, after the Khazneh or "Treasury". The huge façade, the inner chamber and the other structures next to it or in the wider area around the Deir probably originally served a complex religious purpose, and was possibly repurposed as a church in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine period. Location The monastery can be reached by ascending a nearly 800-step path (40-minute walking time) from the Basin. The Wadi Kharrubeh, the Lion's tomb, and small Klinai, biclinia and grottos can be seen en route to the monastery. From the monastery, one can view the valleys o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
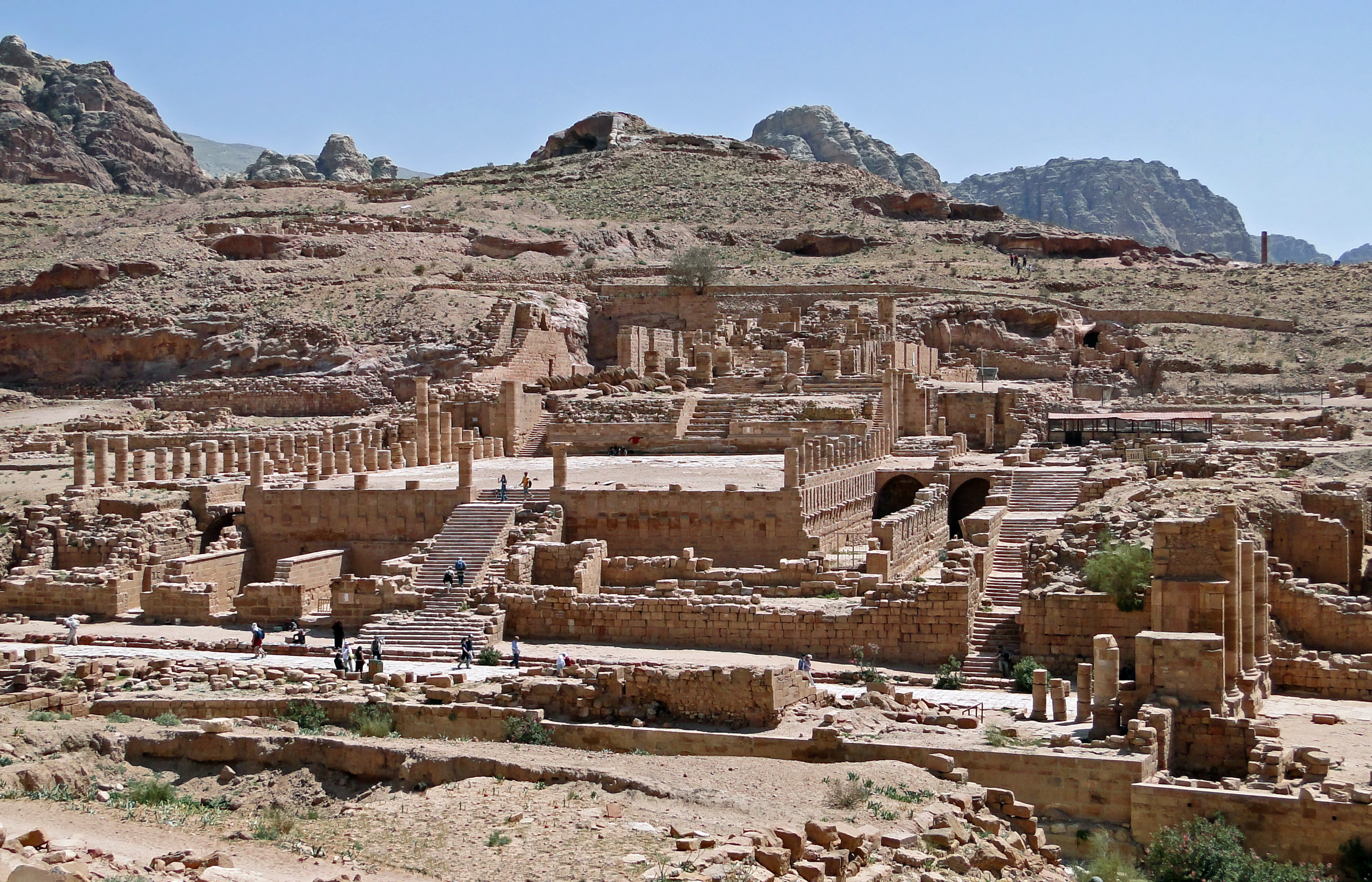
Petra
Petra (; "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu (Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: or , *''Raqēmō''), is an ancient city and archaeological site in southern Jordan. Famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit systems, Petra is also called the "Rose City" because of the colour of the sandstone from which it is carved. The city is one of the New 7 Wonders of the World and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and was settled by the Nabataeans, a nomadic Arab people, in the 4th century BC. Petra would later become the capital city of the Nabataean Kingdom in the second century BC. The Nabataeans invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub, which gained them considerable revenue. Unlike their enemies, the Nabataeans were accustomed to living in the barren deserts and thus were able to defend their kingdom. They were particularly sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Style
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture. A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or ''caulicoles''), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or they may be extravagantly drilled and undercut, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavra
A lavra or laura (; Cyrillic: Ла́вра) is a type of monastery consisting of a cluster of cells or caves for hermits, with a church and sometimes a refectory at the center. Lavra monasteries operate within the Orthodox and other Eastern Christian traditions; the name is also used by some Catholic communities. The term in Greek initially meant a narrow lane or an alley in a city.. In a later Eastern Orthodox context, the term took the new meaning of large and important monastery. History Byzantine laura/lavra From the fifth century the Greek term ''laura'' could refer specifically to the semi-eremitical monastic settlements of the Judaean Desert, where lauras were very numerous. The first lauras of Palestine were founded by Chariton the Confessor (born 3rd century, died c. 350): the Laura of Pharan (now Wadi Qelt) northeast of Jerusalem, the Laura of Douka on the Mount of Temptation west of Jericho, and Souka Laura or Old Laura in the area of Tuqu' in Wadi Khureitun. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenobite
Cenobitic (or coenobitic) monasticism is a monastic tradition that stresses community life. Often in the West the community belongs to a religious order, and the life of the cenobitic monk is regulated by a religious rule, a collection of precepts. The older style of monasticism, to live as a hermit, is called eremitic. A third form of monasticism, found primarily in Eastern Christianity, is the skete. The English words ''cenobite'' and ''cenobitic'' are derived, via Latin, from the Greek words (, ), and (, ). The adjective can also be cenobiac () or cœnobitic (obsolete). A group of monks living in community is often referred to as a cenobium (Latin, from Greek ''koinobion''). Cenobitic monasticism appears in several religious traditions, though most commonly in Buddhism and Christianity. Origins The word ''cenobites'' was initially applied to the followers of Pythagoras in Crotone, Italy, who founded a commune not just for philosophical study but also for the "amicable s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermit
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions. Description In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Christian who lives the eremitic life out of a religious conviction, namely the Catholic spirituality#Desert spirituality, Desert Theology of the Old Testament (i.e., the 40 years wandering in the Zin Desert, desert that was meant to bring about a change of heart). In the Christian tradition the eremitic life is an early form of Monk, monastic living that preceded the monastic life in the cenobium. In chapter 1, the Rule of St Benedict lists hermits among four kinds of monks. In the Roman Catholic Church, in addition to hermits who are members of religious institutes, the Canon law (Catholic Church), Canon law (canon 603) recognizes also Consecrated life#Other forms of consecrated life, diocesan hermits under the direction of their diocesan b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Orthodox
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Roman Empire. * The broader meaning refers to "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also called 'Eastern Orthodox', 'Greek Catholic', or generally 'the Greek Church. * A second, narrower meaning refers to "any of several independent churches within the worldwide communion of (Eastern) Orthodox Christianity that retain the use of the Greek language in formal ecclesiastical settings". In this sense, the Greek Orthodox Churches are the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople and its dependencies, the Patriarchates of Alexandria, Antioch and Jerusalem, the Church of Greece and the Church of Cyprus. * The third meaning refers to the Church of Greece, an Eastern Orthodox Church operating within the modern bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religion, religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, Church (building), churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, and modern paganism. Many historical-medieval faiths also made use of them, including the Religion in ancient Rome, Roman, Religion in ancient Greece, Greek, and Norse paganism, Norse religions. Etymology The modern English language, English word ''wikt:altar#English, altar'' was derived from Middle English ''wikt:alter#Latin, altar'', from Old English ''wikt:alter, alter'', taken from Latin ''wikt:altare#Latin, altare'' ("altar"), probably related to ''wikt:adolere#Etymology 2, adolere'' ("burn"); thus "burning place", influenced by ''wikt:altus#Latin, altus'' ("high"). It displaced the native Old English word ''wikt:weofod#Old English, wēofod''. Altars in antiquity In antiquity, alta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of The Winged Lions
The Temple of the Winged Lions is a large Nabatean temple complex located in Petra, Jordan, and dated to the reign of King Aretas IV (9 BCE–40 CE). The temple is located in Petra's so-called Sacred Quarter, an area situated at the end of Petra's main Colonnaded Street consisting of two majestic temples, the Qasr al-Bint and, opposite, the Temple of the Winged Lions on the northern bank of Wadi Musa. The temple is likely dedicated to the supreme goddess figure of the Nabateans, but the exact identity of this goddess is uncertain. Temple of Winged Lions was ultimately destroyed in the massive earthquake of 363 CE. Analyses of the architecture, goods, and practices associated with the Temple of the Winged Lions afford valuable insights into Nabataean religion, economy, and culture. Inscription found at the temple offer a glimpse into the details of Nabataean law and order associated with religious ritual, worship, and the allocation and generation of temple revenue. Construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyton
In Classical architecture, the ''adyton'' ( , 'innermost sanctuary, shrine', ) or (Latin) was a restricted area within the ''cella'' of a Greek temple, Greek or Roman temple. The ''adyton'' was frequently a small area at the farthest end of the cella from the entrance; at Delphi it measured just . The ''adyton'' often would house the cult image of the deity. ''Adyta'' were spaces reserved for oracles, priestesses, priests, or acolytes, and not for the general public. ''Adyta'' were found frequently associated with temples of Apollo, as at Didyma, Bassae, Clarus, Delos, and Delphi, although they were also said to have been natural phenomena (see the story of Nyx (mythology), Nyx). Those sites often had been dedicated to deities whose worship preceded that of Apollo and may go back to prehistoric eras, such as Delphi, but who were supplanted by the time of Classical Greek culture. In modern scholarship, the term may denote the innermost sacred space of a temple in the Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of The Roman Soldier
The Tomb of the Roman Soldier, also called the Tomb of the Soldier, is one of the best-preserved tombs in the ancient city of Petra, in what is now Jordan. Although its façade is its most recognizable feature — with three carved figures inset between columns — the tomb complex consists of several different architectural elements with varying degrees of preservation. In addition to the tomb façade, there is an associated courtyard, the remains of several two-story buildings, rock-cut rooms, a triclinium (or formal dining room), and several large cisterns. The main building phase of the tomb complex took place during the third quarter of the 1st century AD. Location The Tomb of the Soldier is located on the southeastern outskirts of the city center of Petra, in the valley known as Wadi Farasa. Its position between eastern Wadi Farasa and the path up to a major high place of sacrifice, leads archaeologists to speculate that it may have acted as a territorial marker or gatew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Khazneh
Al-Khazneh (; , "The Treasury"), also known as Khazneh el-Far'oun (treasury of the pharaoh), is one of the most elaborate rock-cut tombs in Petra, a city of the Nabatean Kingdom inhabited by the Arabs in ancient times. As with most of the other buildings in this ancient town, including the Monastery (Arabic: Ad Deir), this structure was carved out of a sandstone rock face. It is thought that Al-Khazneh was built as a mausoleum and crypt at the beginning of the 1st century AD during the reign of Aretas IV Philopatris. It is one of the most popular tourist attractions in both Jordan and the region. Name Al-Khazneh means "The Treasury" in Arabic, a name derived from legends regarding the decorative stone urn high on the second level, which in reality is solid sandstone. It came to be called "Al-Khazneh" in the early 19th century by the area's Bedouins as they had believed it contained treasures. One legend is that the Egyptian Pharaoh and some of his armies escaped the clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |