|
Acute Visual Loss
Acute visual loss is a rapid loss of the ability to see. It is caused by many ocular conditions like retinal detachment, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and giant cell arteritis, etc. Main causes Retinal detachment Retinal detachment should be considered if there were preceding flashes or floaters, or if there is a new visual field defect in one eye. If treated early enough, retinal tear and detachment can have a good outcome. Glaucoma Angle-closure glaucoma should be considered if there is painful loss of vision with a red eye, nausea or vomiting. The eye pressure will be very high typically greater than 40 mmHg. Emergent laser treatment to the iris may prevent blindness. Macular degeneration Wet macular degeneration should be considered in older people with new distortion of their vision with bleeding in the macula. Vision can often be regained with prompt eye injections with anti-VEGF agents. Giant cell arteritis Giant cell arteritis should be considered in an older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snellen Chart
A Snellen chart is an eye chart that can be used to measure visual acuity. Snellen charts are named after the Dutch ophthalmologist Herman Snellen who developed the chart in 1862 as a measurement tool for the acuity formula developed by his professor Franciscus_Donders, Franciscus Cornelius Donders. Many ophthalmologists and vision scientists now use an improved chart known as the LogMAR chart. History Snellen developed charts using symbols based in a 5×5 unit grid. The experimental charts developed in 1861 used abstract symbols. Snellen's charts published in 1862 used alphanumeric capitals in the 5×5 grid. The original chart shows A, C, E, G, L, N, P, R, T, 5, V, Z, B, D, 4, F, H, K, O, S, 3, U, Y, A, C, E, G, L, 2. Description The normal Snellen chart is printed with eleven lines of block letters. The first line consists of one very large letter, which may be one of several letters, for example E, H, or N. Subsequent rows have increasing numbers of letters that decrease in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-VEGF Agents
Anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy, also known as anti-VEGF () therapy or medication, is the use of medications that block vascular endothelial growth factor. This is done in the treatment of certain cancers and in age-related macular degeneration. They can involve monoclonal antibodies such as bevacizumab, antibody derivatives such as ranibizumab (Lucentis), or orally-available small molecules that inhibit the tyrosine kinases stimulated by VEGF: sunitinib, sorafenib, axitinib, and pazopanib (some of these therapies target VEGF receptors rather than the VEGFs). Both antibody-based compounds and the first three orally available compounds are commercialized. The latter two, axitinib and pazopanib, are in clinical trials. Bergers and Hanahan concluded in 2008 that anti-VEGF drugs can show therapeutic efficacy in mouse models of cancer and in an increasing number of human cancers. But, "the benefits are at best transitory and are followed by a restoration of tumour g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion
Branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO) is a rare retinal vascular disorder in which one of the branches of the central retinal artery is obstructed. Although often grouped together under one term, the condition consists of two distinct subtypes: permanent BRAO and transient BRAO. Signs and symptoms Sudden painless partial vision loss Causes Diagnosis Treatment No proven treatment exists for branch retinal artery occlusion. In the rare patient who has branch retinal artery obstruction accompanied by a systemic disorder, systemic anti-coagulation may prevent further events. Epidemiology See also * Central retinal artery occlusion Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a disease of the eye where the flow of blood through the central retinal artery is blocked (occluded). There are several different causes of this occlusion; the most common is carotid artery atheroscle ... * Central retinal vein occlusion * Branch retinal vein occlusion References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Branch retinal vein occlusion is a common retinal vascular disease of the elderly. It is caused by the occlusion of one of the branches of central retinal vein. Signs and symptoms Patients with branch retinal vein occlusion usually have a sudden onset of blurred vision or a central visual field defect. The eye examination findings of acute branch retinal vein occlusion include superficial hemorrhages, retinal edema, and often cotton-wool spots in a sector of retina drained by the affected vein. The obstructed vein is dilated and tortuous. The quadrant most commonly affected is the superotemporal (63%). Retinal neovascularization occurs in 20% of cases within the first 6–12 months of occlusion and depends on the area of retinal nonperfusion. Neovascularization is more likely to occur if more than five disc diameters of nonperfusion are present and vitreous hemorrhage can ensue. Causes Diagnosis The diagnosis of branch retinal vein occlusion is made clinically by finding r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Central retinal vein occlusion, also CRVO, is when the central retinal vein becomes occluded, usually through thrombosis. The central retinal vein is the venous equivalent of the central retinal artery and both may become occluded. Since the central retinal artery and vein are the sole source of blood supply and drainage for the retina, such occlusion can lead to severe damage to the retina and blindness, due to ischemia (restriction in blood supply) and edema (swelling). CRVO can cause ocular ischemic syndrome. Nonischemic CRVO is the milder form of the disease. It may progress to the more severe ischemic type. CRVO can also cause glaucoma. Diagnosis Despite the role of thrombosis in the development of CRVO, a systematic review found no increased prevalence of thrombophilia (an inherent propensity to thrombosis) in patients with retinal vascular occlusion. Treatment Treatment consists of Anti-VEGF drugs like Lucentis or intravitreal steroid implant (Ozurdex) and Pan-Retinal L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) is a disease of the eye where the flow of blood through the central retinal artery is blocked (occluded). There are several different causes of this occlusion; the most common is carotid artery atherosclerosis. Signs and symptoms Central retinal artery occlusion is characterized by painless, acute vision loss in one eye. Upon fundoscopic exam, one would expect to find: cherry-red spot (90%) (a morphologic description in which the normally red background of the choroid is sharply outlined by the swollen opaque retina in the central retina), retinal opacity in the posterior pole (58%), pallor (39%), retinal arterial attenuation (32%), and optic disk edema (22%). During later stages of onset, one may also find plaques, emboli, and optic atrophy. Diagnosis One diagnostic method for the confirmation of CRAO is fluorescein angiography, used to examine the retinal artery filling time after the fluorescein dye is injected into the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
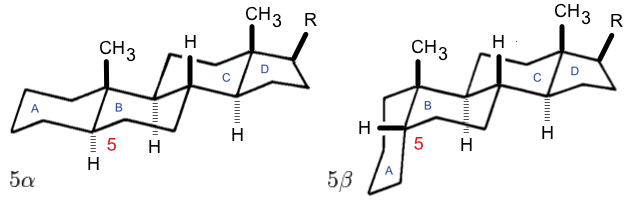
Steroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterol: cholesterol (animals), lanosterol ( opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus ( core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four fused rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaw Claudication
The jaws are a pair of opposable articulated structures at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of humans and most animals. Arthropods In arthropods, the jaws are chitinous and oppose laterally, and may consist of ''Mandible (arthropod mouthpart), mandibles'' or ''chelicerae''. These jaws are often composed of numerous Arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts. Their function is fundamentally for food acquisition, conveyance to the mouth, and/or initial processing (''mastication'' or ''chewing''). Many mouthparts and associate structures (such as pedipalps) are modified legs. Vertebrates In most vertebrates, the jaws are bone, bony or cartilage, cartilaginous and oppose vertically, comprising an ''upper jaw'' and a ''lower jaw''. The vertebrate jaw is derived from the most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macula
The macula (/ˈmakjʊlə/) or macula lutea is an oval-shaped pigmented area in the center of the retina of the human eye and in other animals. The macula in humans has a diameter of around and is subdivided into the umbo, foveola, foveal avascular zone, fovea, parafovea, and perifovea areas. The anatomical macula at a size of is much larger than the clinical macula which, at a size of , corresponds to the anatomical fovea. The macula is responsible for the central, high-resolution, color vision that is possible in good light. This kind of vision is impaired if the macula is damaged, as in macular degeneration. The clinical macula is seen when viewed from the pupil, as in ophthalmoscopy or retinal photography. The term macula lutea comes from Latin ''macula'', "spot", and ''lutea'', "yellow". Structure The macula is an oval-shaped pigmented area in the center of the retina of the human eye and other animal eyes. Its center is shifted slightly away from the optical axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision Loss
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks, including reading and walking. The terms ''low vision'' and ''blindness'' are often used for levels of impairment which are difficult or impossible to correct and significantly impact daily life. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems. The most common causes of visual impairment globally are uncorrected refractive errors (43%), cataracts (33%), and glaucoma (2%). Refractive errors include near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism (eye), astigmatism. Cataracts are the most common cause of blindness. Other disorders that may cause visual problems include age-related macular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Eye (medicine)
A red eye is an eye that appears red due to illness or injury. It is usually hyperemia, injection and prominence of the superficial blood vessels of the conjunctiva, which may be caused by disorders of these or adjacent structures. Conjunctivitis and subconjunctival hemorrhage are two of the less serious but more common causes. Management includes assessing whether emergency action (including referral) is needed, or whether treatment can be accomplished without additional resources. slit lamp, Slit lamp examination is invaluable in diagnosis but initial assessment can be performed using a careful history, testing vision (visual acuity), and carrying out a swinging-flashlight test, penlight examination. Diagnosis Particular sign (medicine), signs and symptoms may indicate that the cause is serious and requires immediate attention. Seven such signs are: * #Reduced visual acuity, Reduced visual acuity * #Ciliary flush, Ciliary flush (circumcorneal injection) * #Corneal abnormal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Field Defect
The visual field is "that portion of space in which objects are visible at the same moment during steady fixation of the gaze in one direction"; in ophthalmology and neurology the emphasis is mostly on the structure inside the visual field and it is then considered “the field of functional capacity obtained and recorded by means of perimetry”.Strasburger, Hans; Pöppel, Ernst (2002). Visual Field. In G. Adelman & B.H. Smith (Eds): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''; 3rd edition, on CD-ROM. Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam, New York. However, the visual field can also be understood as a predominantly ''perceptual'' concept and its definition then becomes that of the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments" (for example in van Doorn et al., 2013). The corresponding concept for optical instruments and image sensors is the field of view (FOV). In humans and animals, the FOV refers to the area visible when eye mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |