|
Acorn Archimedes
The Acorn Archimedes is a family of personal computers designed by Acorn Computers of Cambridge, England. The systems in this family use Acorn's own ARM architecture processors and initially ran the Arthur operating system, with later models introducing RISC OS and, in a separate workstation range, RISC iX. The first Archimedes models were introduced in 1987, and systems in the Archimedes family were sold until the mid-1990s alongside Acorn's newer Risc PC and A7000 models. The first Archimedes models, featuring a 32-bit ARM2 RISC CPU running at 8 MHz, provided a significant upgrade from Acorn's previous machines and 8-bit home computers in general. Acorn's publicity claimed a performance rating of 4 MIPS.These being equivalent to VAX-11/750 instructions. Later models featured the ARM3 CPU, delivering a substantial performance improvement, and the first ARM system-on-a-chip, the ARM250. The Archimedes preserves a degree of compatibility with Acorn's earlier m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorn Computers
Acorn Computers Ltd. was a British computer company established in Cambridge, England in 1978 by Hermann Hauser, Christopher Curry (businessman), Chris Curry and Andy Hopper. The company produced a number of computers during the 1980s with associated software that were highly popular in the domestic market, and they have been historically influential in the development of computer technology like Central processing unit, processors. The company's Acorn Electron, released in 1983, and the later Acorn Archimedes, were highly popular in Britain, while Acorn's computer dominated the educational computer market during the 1980s. The company also designed the ARM architecture family, ARM architecture and the operating system for it. The architecture part of the business was spun-off as Advanced RISC Machines under a joint venture with Apple Inc., Apple and VLSI Technology, VLSI in 1990, now known as Arm Holdings, which is dominant in the mobile phone and personal digital assistant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data buses of that size. Memory addresses (and thus address buses) for 8-bit CPUs are generally larger than 8-bit, usually 16-bit. 8-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 8-bit microprocessors. The term '8-bit' is also applied to the character sets that could be used on computers with 8-bit bytes, the best known being various forms of extended ASCII, including the ISO/IEC 8859 series of national character sets especially Latin 1 for English and Western European languages. The IBM System/360 introduced byte-addressable memory with 8-bit bytes, as opposed to bit-addressable or decimal digit-addressable or word-addressable memory, although its general-purpose registers were 32 bits wide, and addresses were contained in the lower 24 bits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit computing, 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit Bus (computing), data bus (allowing the use of cheaper and fewer supporting Integrated circuit, ICs),Fewer TTL buffers, latches, multiplexers (although the amount of TTL logic was not drastically reduced). It also permits the use of cheap 8080-family ICs, where the 8254 CTC, Intel 8255, 8255 PIO, and 8259 PIC were used in the IBM PC design. In addition, it makes PCB layout simpler and boards cheaper, as well as demanding fewer (1- or 4-bit wide) DRAM chips. and is notable as the processor used in the original IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC design. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture, which eventually became Intel's most successful line of processors. On June 5, 2018, Intel released a limited-edition CPU celebrating the 40th anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range are unchanged, however. In fact, according to the Intel documentation, the 8086 and 8088 have the same execution unit (EU)—only the bus interface unit (BIU) is different. The 8088 was used in the original IBM PC and in IBM PC compatible clones. History and description The 8088 was designed at Intel's laboratory in Haifa, Israel, as were a large number of Intel's processors. The 8088 was targeted at economical systems by allowing the use of an eight-bit data path and eight-bit support and peripheral chips; complex circuit boards were still fairly cumbersome and expensive when it was released. The prefetch queue of the 8088 was shortened to four bytes, from the 8086's six bytes, and the prefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC DOS
PC or pc may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Player character or playable character, a fictional character controlled by a human player, usually in role-playing games or computer games * '' Port Charles'', an American daytime TV soap opera * Production code number, a designation used to identify television episodes * ''Pretty Cure'', a Japanese anime franchise Business and finance * Percentage (pc) * Prime cost or variable cost * Principal Consultant, a management consulting position * Professional corporation, a type of corporate entity for licensed professionals (attorneys, architects, physicians, engineers, etc.) Organizations Businesses * Pearl-Continental Hotels & Resorts, a hotel chain in Pakistan * Pirelli & C. (stock symbol: PC) * President's Choice, a private label product brand of the Canadian supermarket chain Loblaw Companies ** PC Mobile, a Canadian mobile virtual network operator ** PC Optimum, a Canadian rewards program ** President's Choice Financial, a C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the List of IBM Personal Computer models, IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers at IBM, International Business Machines (IBM), directed by William C. Lowe and Philip Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. Powered by an x86-architecture Intel 8088 processor, the machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had influence of the IBM PC on the personal computer market, a substantial influence on the personal computer market; the specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from Apple Inc., Apple's Maci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Digital Research, Inc. CP/M is a disk operating system and its purpose is to organize files on a magnetic storage medium, and to load and run programs stored on a disk. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors. CP/M's core components are the ''Basic Input/Output System'' (BIOS), the ''Basic Disk Operating System'' (BDOS), and the ''Console Command Processor'' (CCP). The BIOS consists of drivers that deal with devices and system hardware. The BDOS implements the file system and provides system services to applications. The CCP is the command-line interpreter and provides some built-in commands. CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republic after its capital city of Bonn, or as the Second German Republic. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from 12 States of Germany, states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. At the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided between the Western and Eastern Bloc, Eastern blocs. Germany was divided into the two countries. Initially, West Germany claimed an exclusive mandate for all of Germany, representing itself as the sole democratically reorganised continuation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorn Electron
The Acorn Electron (nicknamed the Elk inside Acorn and beyond) was introduced as a lower-cost alternative to the BBC Micro educational/home computer, also developed by Acorn Computers, to provide many of the features of that more expensive machine at a price more competitive with that of the ZX Spectrum. It has 32 kilobytes of random-access memory, RAM, and its read-only memory, ROM includes BBC BASIC II together with the Acorn MOS, operating system. Announced in 1982 for a possible release the same year, it was eventually introduced on 25 August 1983 priced at £199. The Electron is able to save and load programs onto compact audio cassette, audio cassette via a cable, originally supplied with the computer, connecting it to any standard tape recorder with the appropriate sockets. It is capable of bitmapped graphics, and can use either a contemporary television set, a colour (RGB) monitor or a monochrome monitor as its display. Several expansions were made available to provide m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
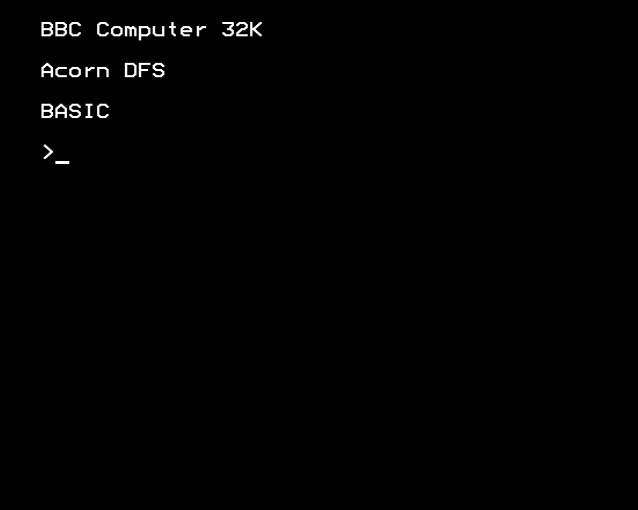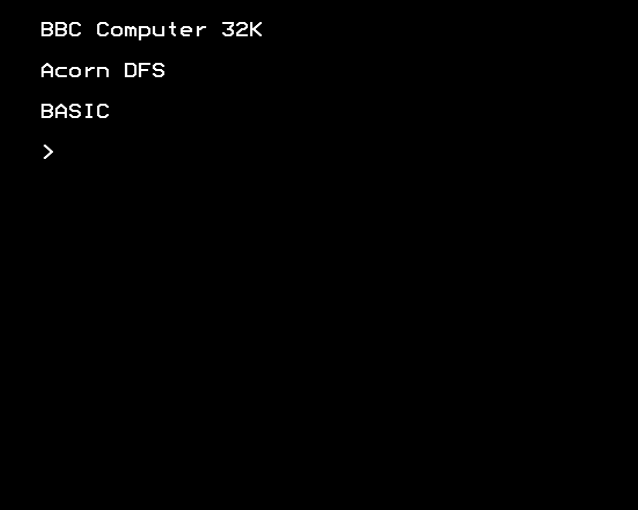
BBC BASIC
BBC BASIC is an interpreted version of the BASIC programming language. It was developed by Acorn Computers Ltd when they were selected by the BBC to supply the computer for their BBC Literacy Project in 1981. It was originally supplied on an installed ROM for the BBC Microcomputer which used a 6502 microprocessor. When Acorn produced the Archimedes computer which used their ARM processor, further versions of BBC BASIC were produced. Acorn included a built in assembler, first for the 6502 and later for the ARM2 processor. Initially the BBC specified compatibility with Microsoft BASIC. Acorn were already extending their earlier Atom BASIC to include structured programming constructs. Particularly on the later Archimedes computers as the memory constraints reduced, BBC BASIC incorporated a more complete set of structured programming constructs commonly found in the ALGOL 60 group of computer languages. Alongside Acorn's version of BBC BASIC on the Archimedes, third part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |