|
Acculturation
Acculturation refers to the psychological, social, and cultural transformation that takes place through direct contact between two cultures, wherein one or both engage in adapting to dominant cultural influences without compromising their essential distinctiveness. It occurs when an individual acquires, adopts, or adjusts to a new cultural environment as a result of being placed into another culture or when another culture is brought into contact. This balancing process can result in a mixed society with prevailing and blended features or with splintered cultural changes, depending on the sociopolitical atmosphere. Individuals from other cultures work toward fitting into a more prevalent culture by selectively integrating aspects of the dominant culture, such as its Cultural trait, cultural traits and Social norm, social norms, while still holding onto their original cultural values and traditions. The impacts of acculturation are experienced differently at various levels by both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enculturation
Enculturation is the process by which people learn the dynamics of their surrounding culture and acquire values and norms appropriate or necessary to that culture and its worldviews. Definition and history of research The term enculturation was used first by sociologist of science Harry Collins to describe one of the models whereby scientific knowledge is communicated among scientists. The ingredients discussed by Collins for enculturation are # Learning by Immersion: whereby aspiring scientists learn by engaging in the daily activities of the laboratory, interacting with other scientists, and participating in experiments and discussions. # Tacit Knowledge: highlighting the importance of tacit knowledge—knowledge that is not easily codified or written down but is acquired through experience and practice. # Socialization: where individuals learn the social norms, values, and behaviours expected within the scientific community. # Language and Discourse: Scientists must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assimilation (sociology)
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or fully adopts the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group. The melting pot model is based on this concept. A related term is cultural integration, which describes the process of becoming economically and socially integrated into another society while retaining elements of one’s original culture. This approach is also known as cultural pluralism, and it forms the basis of a cultural mosaic model that upholds the preservation of cultural rights. Another closely related concept is acculturation, which occurs through cultural diffusion and involves changes in the cultural patterns of one or both groups, while still maintaining distinct characteristics. There are various types of cultural assimilation, including full assimilation and forced assimilation. Full assimilation is common, as it occurs spontaneously. Assimilation can also involve what is call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
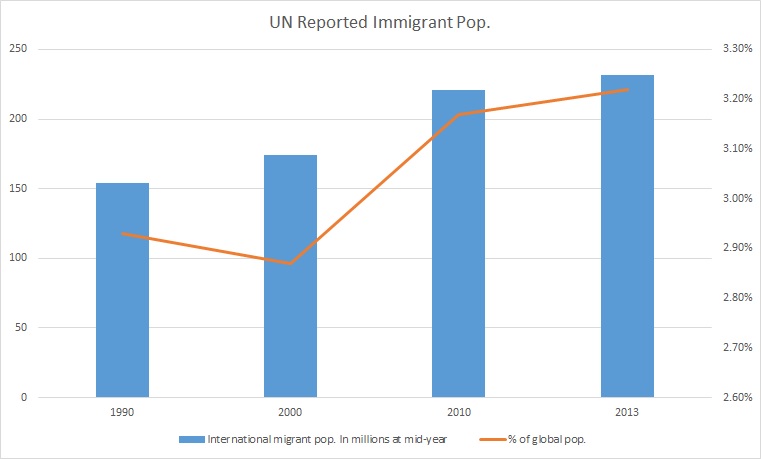
Immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-born persons in criminal justice, business, the economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton Gordon
Milton Myron Gordon (October 3, 1918 – June 4, 2019) was an American sociologist. He was most noted for having devised a theory on the Seven Stages of Assimilation. He was born in Gardiner, Maine. Gordon died on June 4, 2019, at the age of 100. # Acculturation: newcomers adopt language, dress, and daily customs of the host society (including values and norms). # Structural assimilation: large-scale entrance of minorities into cliques, clubs and institutions in the host society. # Marital assimilation: widespread intermarriage. # Identification assimilation: the minority feels bonded to the dominant culture. # Attitude reception assimilation refers to the absence of prejudice. # Behavior reception assimilation refers to the absence of discrimination. # Civic assimilation occurs when there is an absence of value conflicts and power struggles. Bibliography * * * * *''Assimilation in Native and Immigrant groups'', special editor, Andres Suarez, Seminar presented June 9, 2008, Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's Dominant culture, majority group or fully adopts the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group. The melting pot model is based on this concept. A related term is cultural integration, which describes the process of becoming economically and socially integrated into another society while retaining elements of one’s original culture. This approach is also known as cultural pluralism, and it forms the basis of a cultural mosaic model that upholds the preservation of cultural rights. Another closely related concept is acculturation, which occurs through cultural diffusion and involves changes in the cultural patterns of one or both groups, while still maintaining distinct characteristics. There are various types of cultural assimilation, including full assimilation and forced assimilation. Full assimilation is common, as it occurs spontaneously. Assimilation can also invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Trait
A cultural trait is a single identifiable material or non-material element within a culture, and is conceivable as an object in itself. Huxley, Julian S. 1955. "Guest Editorial: Evolution, Cultural and Biological." ''Yearbook of Anthropology'', 2–25. Similar traits can be grouped together as components, or subsystems of culture;https://www.heritage.nf.ca/nl-studies-2205/chapter-1-topic-1.pdf the terms sociofact and mentifact (or psychofact) were coined by biologist Julian Huxley as two of three subsystems of culture—the third being ''artifacts''—to describe the way in which cultural traits take on a life of their own, spanning over generations. In other words, cultural traits can be categorized into three interrelated components: # Artifacts — the objects, material items, and technologies created by a culture, or simply, things people make. They provide basic necessities, recreation, entertainment, and most of the things that make life easier for people. Examples includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucifix
A crucifix (from the Latin meaning '(one) fixed to a cross') is a cross with an image of Jesus on it, as distinct from a bare cross. The representation of Jesus himself on the cross is referred to in English as the (Latin for 'body'). The crucifix emphasizes Jesus' sacrifice, including his death by crucifixion, which Christians believe brought about the redemption of mankind. Most crucifixes portray Jesus on a Latin cross, rather than a Tau cross or a Coptic cross. The crucifix is a principal symbol for many groups of Christians, and one of the most common forms of the Crucifixion in the arts. It is especially important in the Catholic Church, and is also used in the Lutheran Churches, Anglican Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church, and in most Oriental Orthodox Churches (except the Armenian Church and Syriac Church). The symbol is less common in churches of other Protestant denominations, and in the Assyrian Church of the East and Armenian Apostolic Church, which prefer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganesh
Ganesha or Ganesh (, , ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped Deva (Hinduism), deities in the Hindu deities, Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in the Ganapatya sect. His depictions are found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends Ganesha in world religions, to Jains and Buddhists and beyond India. Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his Asiatic Elephant, elephant head and four arms. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and bringer of good luck; the patron of The arts, arts and Science, sciences; and the Deva (Hinduism), deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked during writing sessions as a patron of letters and learning., Vigna means obstacles Nasha means destroy. These ideas ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Differences
Cultural diversity is the quality of diverse or different cultures, as opposed to Monoculturalism, monoculture. It has a variety of meanings in different contexts, sometimes applying to cultural products like art works in museums or entertainment available online, and sometimes applying to the variety of human cultures or traditions in a specific region, or in the world as a whole. It can also refer to the inclusion of different cultural perspectives in an organization or society. Cultural diversity can be affected by political factors such as censorship or the protection of the rights of artists, and by economic factors such as free trade or protectionism in the market for cultural goods. Since the middle of the 20th century, there has been a concerted international effort to protect cultural diversity, involving the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) and its member states. This involves action at international, national, and local le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Mumford
Lewis Mumford (October 19, 1895 – January 26, 1990) was an American historian, sociologist, philosopher of technology, and literary critic. Particularly noted for his study of cities and urban architecture, he had a broad career as a writer. He made significant contributions to social philosophy, American literary and cultural history, and the history of technology. Mumford was influenced by the work of Scottish theorist Sir Patrick Geddes and worked closely with his associate the British sociologist Victor Branford. Mumford was also a contemporary and friend of Frank Lloyd Wright, Clarence Stein, Frederic Osborn, Edmund N. Bacon, and Vannevar Bush. Life Early life and education Mumford was born in Flushing, Queens, New York, and graduated from Stuyvesant High School in 1912. He studied at the City College of New York and The New School for Social Research, but became ill with tuberculosis and never finished his degree. In 1918 he joined the Navy to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Gebser
Jean Gebser (; August 20, 1905 as Hans Karl Hermann Rudolph Gebser – May 14, 1973) was a Swiss philosopher, linguist, and poet who described the structures of human consciousness. Biography Gebser was born Hans Karl Hermann Rudolph Gebser in Posen in Imperial Germany (now Poland). His father was lawyer Frederich Gebser and mother was Margaretha Grundmann. He was a cousin of World War I-era chancellor Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg. He left Germany in 1929, living for a time in Italy and then in France. He then moved to Spain, mastered the Spanish language in a few months and entered the Spanish Civil Service where he rose to become a senior official in the Ministry of Education. Before the Spanish Civil War began, he moved to Paris, and then to Southern France. It was here that he changed his German first name "Hans" to the French "Jean." He lived in Paris for a while but saw the unavoidability of a German invasion. He fled to Switzerland in 1939, escaping only hours before t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |