|
Accessory Muscle
An accessory muscle is a relatively rare anatomical variation where duplication of a muscle may appear anywhere in the muscular system. Treatment is not indicated unless the accessory muscle interferes with normal function. Examples Examples are the accessory soleus muscle in the calf or ankle, the extensor digitorum brevis manus in the hand and epitrochleoanconeus muscle of the upper arm. Additional examples in the hand include Flexor carpi radialis brevis which can compress the anterior interosseous nerve. Also see palmaris profundus muscle. On the extensor side: extensor digitorum brevis manus,extensor carpi radialis intermedius extensor medii proprius muscle Accessory muscles of the anterior thoracic wall include the sternalis muscle, the axillary arch (Langer's), variations of pectoralis major such as the ''pectoralis minimus'', ''pectoralis quartus'', and ''pectoralis intermedius'', the ''chondrocoracoideus'' and ''chondrofascialis''. The whole pectoral region is subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with Morphology (biology), morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categorized into three types including morphometric (size or shape), consistency (present or absent), and spatial (proximal/distal or right/left). Variations are seen as normal in the sense that they are found consistently among different individuals, are mostly without symptoms, and are termed anatomical variations rather than abnormalities. Anatomical variations are mainly caused by genetics and may vary considerably between different populations. The rate of variation considerably differs between single organ (anatomy), organs, particularly in muscles. Knowledge of anatomical variations is important in order to distinguish them from pathological conditions. A very early paper published in 1898, presented anatomic var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of Respiration
The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during quiet breathing. The elasticity of these muscles is crucial to the health of the respiratory system and to maximize its functional capabilities. Diaphragm The diaphragm is the major muscle responsible for breathing. It is a thin, dome-shaped muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, so that its center moves caudally (downward) and its edges move cranially (upward). This compresses the abdominal cavity, raises the ribs upward and outward and thus expands the thoracic cavity. This expansion draws air into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, elastic recoil of the lungs causes the thoracic cavity to contract, forcing air out of the lungs, and returning to its dome-sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Muscles Of The Human Body
This is a table of skeletal muscles of the human anatomy, with muscle counts and other information. Table Table explanation and summary The muscles are described using anatomical terminology. The columns are as follows: For Origin, Insertion and Action please name a specific Rib, Thoracic vertebrae or Cervical vertebrae, by using C1-7, T1-12 or R1-12. Summary in numbers There does not appear to be a definitive source counting all skeletal muscles. Different sources group muscles differently, regarding physical features as different parts of a single muscle or as several muscles. There are also vestigial muscles that are present in some people but absent in others, such as the palmaris longus muscle. There are between 600 and 840 muscles within the typical human body, depending on how they are counted. In the present table, using statistical counts of the instances of each muscle, and ignoring gender-specific muscles, there are 753 skeletal muscles. Sometimes mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
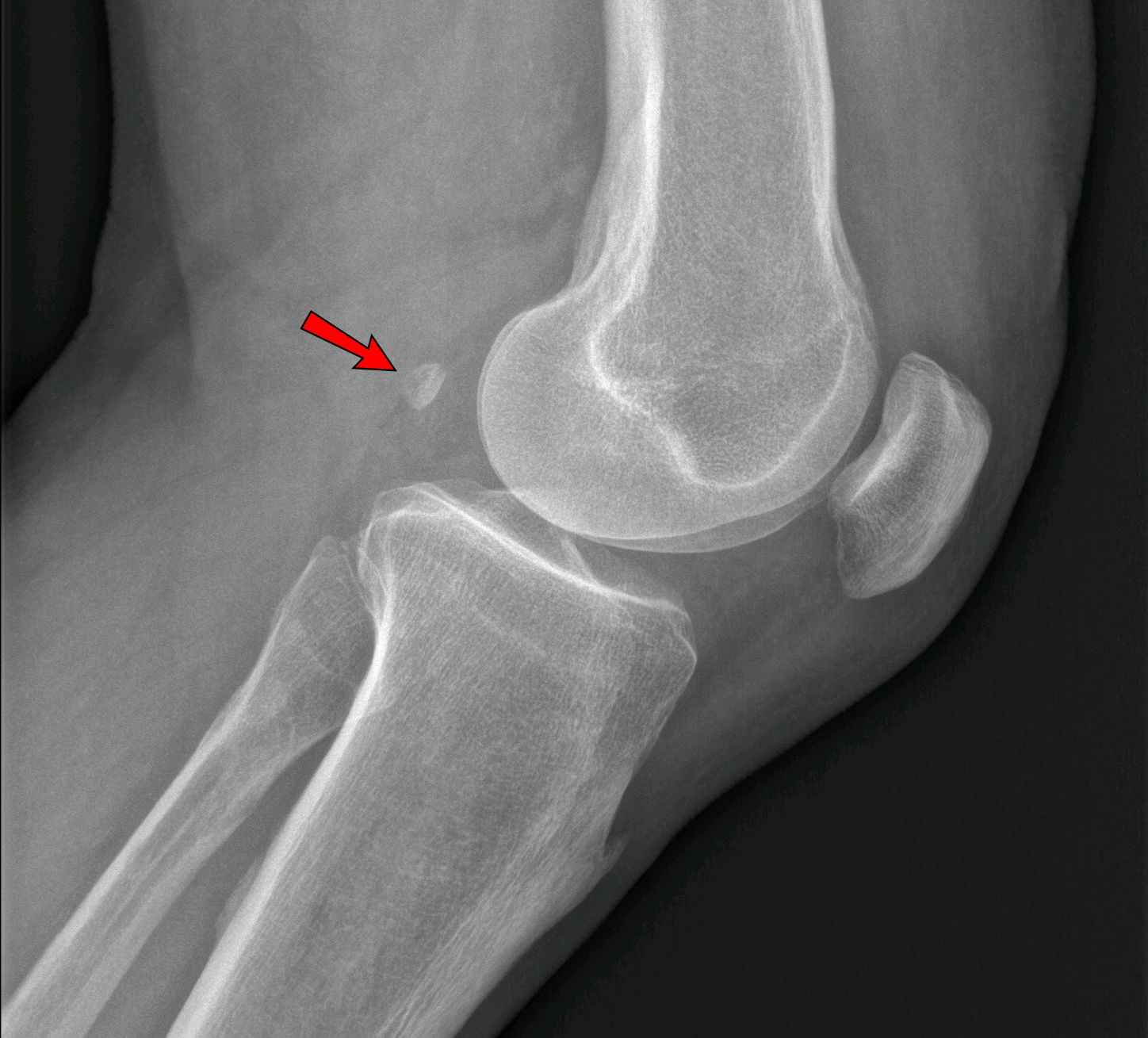
Accessory Bone
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a anatomical variation, variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosis, misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography. Wrist and hand Os ulnostyloideum The ''os ulnostyloideum'' is an ulnar styloid process that is not fused to the rest of the ulna bone.R. O'Rahilly. ''A survey of carpal and tarsal anomalies.'' J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953; 35: 626–642 On X-rays, an ''os ulnostyloideum'' is sometimes mistaken for an avulsion fracture of the styloid process. However, the distinction between these is extremely difficult.T.E. Keats, M.W. Anderson. ''Atlas of normal roentgen variants that may simulate disease''. 7th edition, Mosby Inc. 2001 It is alleged that the os ulnostyloideum has a close relationship with or is synonymous with the os triquetrum secundarium. Os centrale The ''os carpi centrale'' (also briefly ''os centrale'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
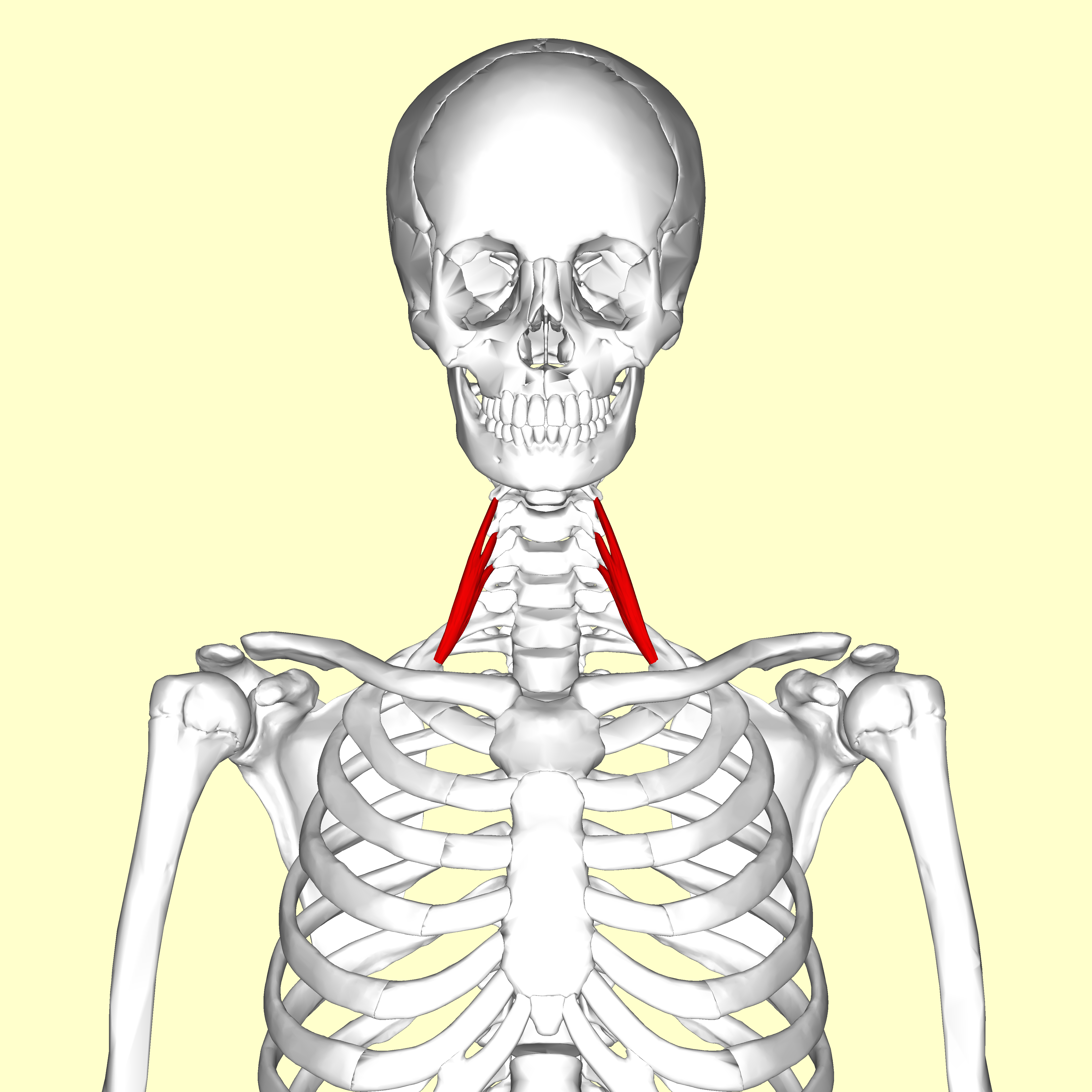
Scalenus Posterior
The scalene muscles are a group of three muscles on each side of the neck, identified as the anterior, the middle, and the posterior. They are innervated by the third to the eighth cervical spinal nerves (C3-C8). The anterior and middle scalene muscles lift the first rib and bend the neck to the side they are on. The posterior scalene lifts the second rib and tilts the neck to the same side. The muscles are named from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'uneven'. Structure The scalene muscles are attached at one end to bony protrusions on vertebrae C2 to C7 and at the other end to the first and second ribs. Anterior scalene The anterior scalene muscle (), lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its center, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |