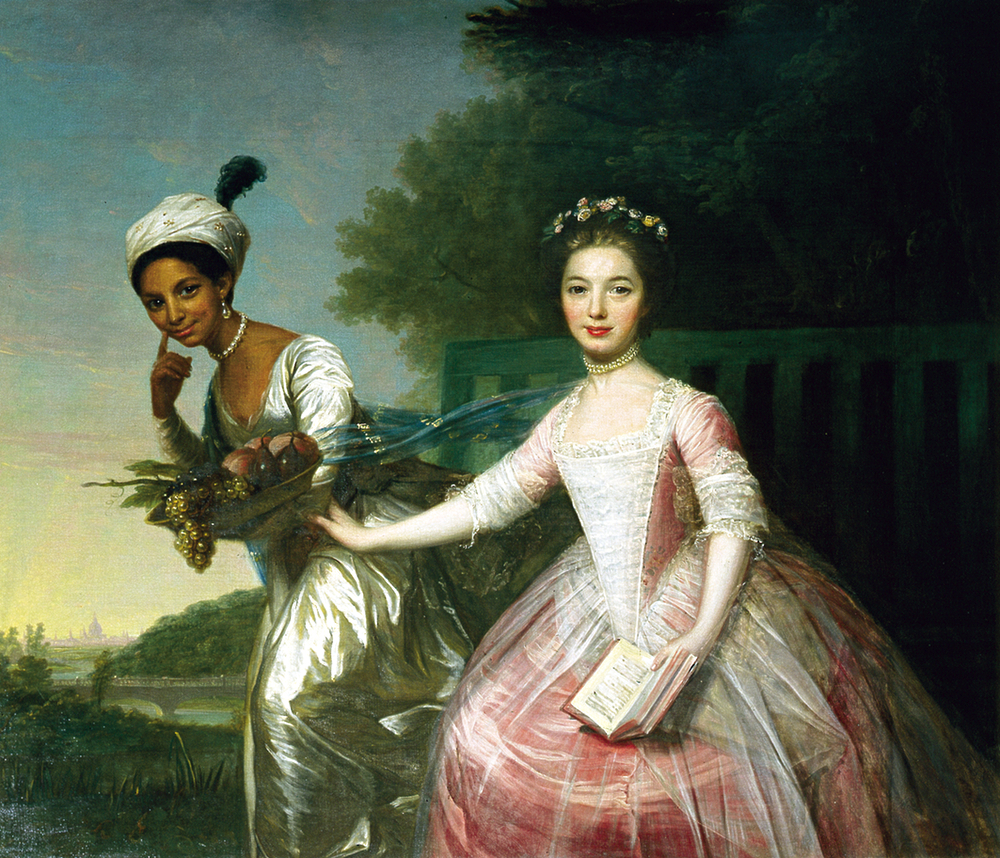|
Abolitionism In The United Kingdom
Abolitionism in the United Kingdom was the movement in the late 18th and early 19th centuries to end the practice of History of slavery, slavery, whether formal or informal, in the United Kingdom, the British Empire and the world, including ending the Atlantic slave trade. It was part of a wider abolitionism movement in Western Europe and the Americas. The trade of slaves was made illegal throughout the British Empire by 1937, with Nigeria and Bahrain being the last British territories to abolish slavery. Origins In the 17th and early 18th centuries, English Quakers and a few evangelical religious groups condemned slavery (by then applied mostly to Africans) as un-Christian. A few secular thinkers of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment criticised it for violating the rights of man. James Edward Oglethorpe was the first to act on the Enlightenment case against slavery on humanistic grounds. In his "Georgia Experiment" he convinced Parliament to ban slavery in his Province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official Medallion Of The British Anti-Slavery Society (1795)
An official is someone who holds an office (function or Mandate (politics), mandate, regardless of whether it carries an actual Office, working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority (either their own or that of their superior or employer, public or legally private). An elected official is a person who is an official by virtue of an election. Officials may also be appointed ''ex officio'' (by virtue of another office, often in a specified capacity, such as presiding, advisory, secretary). Some official positions may be Inheritance, inherited. A person who currently holds an office is referred to as an incumbent. Something "official" refers to something endowed with governmental or other authoritative recognition or mandate, as in official language, official gazette, or official scorer. Etymology The word ''official'' as a noun has been recorded since the Middle English period, first seen in 1314. It comes from the Old French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of London In 1102
__NOTOC__ The Council of London, also known as the Synod of Westminster, was a Catholic church council convened by Anselm, Archbishop of Canterbury, on Michaelmas in 1102. It marked the first major council of his episcopate, as he had been prohibited from convening any during the reign of William II of England. Anselm took the opportunity to initiate the Gregorian Reformation, prohibiting marriage, concubinage, and drunkenness to all those in holy orders, condemning sodomy and simony, and regulating clerical dress, particularly against the recent trend towards pigaches. Anselm also obtained a resolution against the slave trade in England, although this was aimed mainly at the sale of English slaves to the Irish and did not prevent the church from owning slaves. Those present included John of Tours and Roger, the latter being elected to the see of Hereford by the council. See also * Clerical celibacy Clerical celibacy is the requirement in certain religions that some or all m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habeas Corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a legal procedure invoking the jurisdiction of a court to review the unlawful detention or imprisonment of an individual, and request the individual's custodian (usually a prison official) to bring the prisoner to court, to determine whether their detention is lawful. ''Habeas corpus'' is generally enforced via writ, and accordingly referred to as a writ of ''habeas corpus''. The writ of ''habeas corpus'' is one of what are called the "extraordinary", "common law", or " prerogative writs", which were historically issued by the English courts in the name of the monarch to control inferior courts and public authorities within the kingdom. The writ was a legal mechanism that allowed a court to exercise jurisdiction and guarantee the rights of all the Crown's subjects against arbitrary arrest and detention. At common law the burden was usually on the official to prove that a detention was authorized. ''Habeas corpus'' has cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water either partially or completely, traditionally three times, once for each person of the Trinity. The synoptic gospels recount that John the Baptist baptism of Jesus, baptized Jesus., , Baptism is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance (Christian), ordinance in others. Baptism according to the Trinitarian formula, which is done in most mainstream Christian denominations, is seen as being a basis for Christian ecumenism, the concept of unity amongst Christians. Baptism is also called christening, although some reserve the word "christening" for the Infant baptism, baptism of infants. In certain Christian denominations, such as the Catholic Churches, Eastern Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Assyrian Church of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the island containing Haiti and the Dominican Republic), and southeast of the Cayman Islands (a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory). With million people, Jamaica is the third most populous English-speaking world, Anglophone country in the Americas and the fourth most populous country in the Caribbean. Kingston, Jamaica, Kingston is the country's capital and largest city. The indigenous Taíno peoples of the island gradually came under Spanish Empire, Spanish rule after the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of Africans to Jamaica as slaves. The island remained a possession of Spain, under the name Colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somersett's Case
''Somerset v Stewart'' (177298 ER 499(also known as ''Sommersett v Steuart'', Somersett's case, and the Mansfield Judgment) is a judgment of the English Court of King's Bench in 1772, relating to the right of an enslaved person on English soil not to be forcibly removed from the country and sent to Jamaica for sale. According to one reported version of the case, Lord Mansfield decided that: Lord Mansfield found that to the extent the laws of England and Wales had ever permitted slavery, those laws were superseded by later law or otherwise defunct. This absence of a current English statute ("positive law") under which the court might remand someone as a slave proved decisive, as Mansfield refused to accept any other basis for the court to order something that he considered repugnant. The case was closely followed throughout the Empire, particularly in the thirteen American colonies. Scholars have disagreed over precisely what legal precedent the case set. Facts James Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalisation
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the United Nations excludes citizenship that is automatically acquired (e.g. at birth) or is acquired by declaration. Naturalization usually involves an application or a motion and approval by legal authorities. The rules of naturalization vary from country to country but typically include a promise to obey and uphold that country's laws and taking and subscribing to an oath of allegiance, and may specify other requirements such as a minimum legal residency and adequate knowledge of the national dominant language or culture. To counter multiple citizenship, some countries require that applicants for naturalization renounce any other citizenship that they currently hold, but whether this renunciation actually causes loss of original citizens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dido Elizabeth Belle
Dido Elizabeth Belle (June 1761 – July 1804) was a British gentlewoman. She was born into slavery, an illegitimate daughter of Captain John Lindsay of the Royal Navy and Maria Belle; her mother, Maria Belle, was an enslaved Black woman in the British West Indies. Her father was Sir John Lindsay, a British career naval officer who was stationed there; later knighted and promoted to admiral. Lindsay took Dido with him when he returned to England in 1765, entrusting her upbringing to his uncle William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, and his wife Elizabeth Murray, Countess of Mansfield. The Murrays educated Belle, bringing her up as a free gentlewoman at their Kenwood House, together with another great-niece, Lady Elizabeth Murray, whose mother had died. Lady Elizabeth and Belle were second cousins. Belle lived there for 30 years. In his will of 1793, Lord Mansfield provided an outright sum and an annuity to her. Early life Dido Elizabeth Belle was born into slavery in 1761 in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Archives Of Scotland
The National Archives of Scotland (NAS) is the previous name of the National Records of Scotland (NRS), and are the national archives of Scotland, based in Edinburgh. The NAS claims to have one of the most varied collection of archives in Europe. It is the main archive for sources of the history of Scotland as an independent state (see Kingdom of Scotland), her role in the British Isles and the links between Scotland and many other countries over the centuries. The NAS changed its name from the Scottish Record Office on 7 January 1999 and is both an associated department and Executive Agency of the Scottish Government, headed by the Keeper of the Records of Scotland. The agency is responsible to the Scottish Minister for Europe, External Affairs and Culture. Its antecedents date back to the 13th century. It is responsible for selecting, preserving, and promoting and making available the national archives of Scotland. It also has a role in records management more generally. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Olusoga
David Adetayo Olusoga (born January 1970) is a British-Nigerian historian, writer, broadcaster and BAFTA winning film-maker. He is Professor of Public History at the University of Manchester. Olusoga has presented historical documentaries on the BBC and contributed to ''The One Show'' and ''The Guardian''. Early life and education David Olusoga was born in 1970 in Lagos, Nigeria, the second child to a Nigerian father and British mother.David Olusoga's Biography at biogs.com. At five years old, Olusoga migrated to the UK with his mother and grew up in , . He was one of a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh had a population of in , making it the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city in Scotland and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. The Functional urban area, wider metropolitan area had a population of 912,490 in the same year. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament, the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland, and the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch in Scotland. It is also the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The city has long been a cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |