|
Abdullah Pashë Dreni
Abdullah Pashë Dreni (1820–1878) was a 19th-century Albanian tribal leader and military of the Ottoman Army. Life Abdullah Pashë Dreni was born in 1820 in Gjakova. He served in the Ottoman Empire military, where he notably fought in the Siege of Plevna, a major battle of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), after which he received the title of pasha. Mehmed Ali Pasha, Marshal, Chief of Staff of the Ottoman Empire was residing in Dreni's house, when both of them, as well as Dreni's son, were killed under an armed attack of Albanian rebels, which is known as Gjakova's attack in Albanian's historiography. He is mentioned in Gjergj Fishta's Lahuta e Malcís, a national epic poem In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to ..., where Dreni is described as forced to defend his un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, and they also live in the neighboring countries of Albanians in North Macedonia, North Macedonia, Albanians in Montenegro, Montenegro, Albanians in Greece, Greece, and Albanians in Serbia, Serbia, as well as in Albanians in Italy, Italy, Albanians in Croatia, Croatia, Albanians in Bulgaria, Bulgaria, and Albanians in Turkey, Turkey. Albanians also constitute a large diaspora with several communities established across Europe and the other continents. Albanian language, The language of the Albanians is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the only surviving representative of the Albanoid, Albanoid branch, which belongs to the Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan group. Albanians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Army
The Military of the Ottoman Empire () was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. It was founded in 1299 and dissolved in 1922. Army The Military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years between 1300 (Byzantine expedition) and 1453 ( Conquest of Constantinople), the classical period covers the years between 1451 (second enthronement of Sultan Mehmed II) and 1606 ( Peace of Zsitvatorok), the reformation period covers the years between 1606 and 1826 ( Vaka-i Hayriye), the modernisation period covers the years between 1826 and 1858 and decline period covers the years between 1861 (enthronement of Sultan Abdülaziz) and 1918 ( Armistice of Mudros). The Ottoman army is the forerunner of the Turkish Armed Forces. Foundation period (1300–1453) The earliest form of the Ottoman military was a steppe-nomadic cavalry force.Mesut Uyar, Edward J. Erickson, ''A Military History of the Ottomans: From Osman to Atatürk'', Pleager Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjakova
Gjakova or Đakovica, ) and Đakovica ( sr-Cyrl, Ђаковица, ) is the sixth largest city of Kosovo and seat of the Gjakova Municipality and the District of Gjakova, Gjakova District. According to the 2024 census, the municipality of Gjakova has 78,699 inhabitants. Geographically, it is located in the south-western part of Kosovo, about halfway between the cities of Peja and Prizren. It is approximately inland from the Adriatic Sea. The city is situated some north-east of Tirana, north-west of Skopje, west of the capital Pristina, south of Belgrade and east of Podgorica. The city of Gjakova has been populated since the prehistoric era. During the Ottoman Kosovo, Ottoman period, Gjakova served as a trading centre on the route between Shkodër, Shkodra and Istanbul, Constantinople. It was also one of the most developed trade centres at that time in the Balkans. Etymology The Albanian name for the city is ''Gjakova''. There are several theories on the origin of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
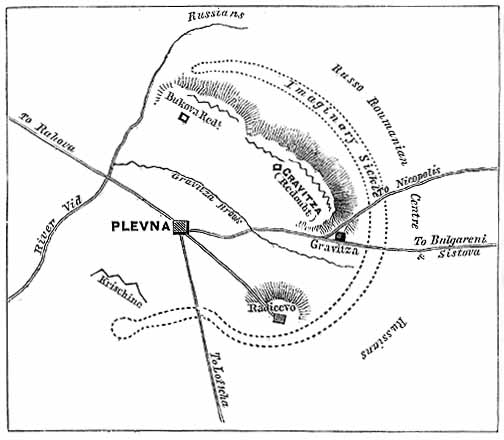
Siege Of Plevna
The siege of Plevna or Pleven, was a major battle of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, fought by the joint army of the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Romania against the Ottoman Empire. After the Russian army crossed the Danube at Svishtov, it began advancing towards the centre of modern Bulgaria, with the aim of crossing the Balkan Mountains to Constantinople, avoiding the fortified Turkish fortresses on the Black Sea coast. The Ottoman army led by Osman Pasha, returning from Serbia after a conflict with that country, was massed in the fortified city of Pleven, a city surrounded by numerous redoubts, located at an important road intersection. After two unsuccessful assaults, in which he lost valuable troops, the commander of the Russian troops on the Balkan front, Grand Duke Nicholas of Russia insisted by telegram on the help of his Romanian ally King Carol I. King Carol I crossed the Danube with the Romanian Army and was placed in command of the Russian-Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of these wars ended in losses for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a period of stagnation and decline. Conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of the Russian Empire as a significant European power after Peter the Great oversaw extensive modernization efforts in the early 18th century. Ultimately, however, the end of the Russo-Turkish wars came about with the dissolution of the two belligerents' respective states as a consequence of World War I: the Russian Empire collapsed in 1917 and was ultimately succeeded by the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922; while the Ottoman Empire was partitioned between 1918 and 1922 and succeeded by the Republic of Turkey in 1923. History Initial and intermediate phases (1568–1739) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of Egypt and it was also used in Morocco in the 20th century, where it denoted a regional official or governor of a district. Etymology The English word ''pasha'' comes from Turkish language, Turkish ('; also ()). The Oxford English Dictionary attributes the origin of the English borrowing to the mid-17th century. The etymology of the Turkish word itself has been a matter of debate. Contrary to titles like emir (''amīr'') and bey (sir), which were established in usage much earlier, the title ''pasha'' came into Ottoman Empire, Ottoman usage right after the reign of Osman I (d. 1324), though it had been used before the Ottomans by some Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian Turkish rulers of the same era. Old Turkish had no fixed distinction betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed Ali Pasha (marshal)
Mehmed Ali Pasha (November 18, 1827 – September 7, 1878Osman Selim Kocahanoğlu, "Bir Osmanlı Ailesi ve Ali Fuad Cebesoy", ''Ali Fuat Cebesoy'un Arşivinden Askeri ve Siyasi Belgeler'', Temel Yayınları, İstanbul, 2005, , p. 13. ) was a Prussia, Prussian-born Ottoman Empire, Ottoman career officer and marshal. He was the grandfather of the Turkish statesman Ali Fuat Cebesoy, and the great-grandfather of famous poets Nâzım Hikmet and Oktay Rıfat Horozcu and the socialist activist, lawyer, and athlete Mehmet Ali Aybar. Biography Mehmed Ali was born as Ludwig Karl Friedrich Detroit (also known as Carl Detroy) in Magdeburg, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. His parents were Carl Friedrich Detroit and Henriette Jeanette Severin. The French family name points to Huguenot ancestry, as a descendant of Protestant refugees from France in the 16th or 17th century. During his teenage years in 1843 he ran away to sea, and traveled to the Ottoman Empire, where he converted to Islam and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack Against Mehmed Ali Pasha
The Attack against Mehmed Ali Pasha (), known in Albanian historiography as the Action of Gjakova (Albanian language, Albanian: Aksioni i Gjakovës; ), was undertaken from 3–6 September 1878 by the Gjakova Committee of the League of Prizren in the estate of Abdullah Pasha Dreni near Gjakova. During the battle Mehmed Ali Pasha (marshal), Mehmed Ali Pasha, the Ottoman marshal who was to overview the cession of the predominantly Albanian Plav, Montenegro, Plav and Gusinje region to the Principality of Montenegro, Abdullah Pasha Dreni, a notable official of the region and former member of the league, many Ottoman soldiers, and volunteers of the Gjakova Committee were killed. The attack was the first military operation of the League of Prizren and marked the beginning of hostilities between the organization and the Ottoman Empire. On an international level, it was the first in a series of battles that changed the terms of the Congress of Berlin as regards the cessions to Montenegro an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gjergj Fishta
Gjergj Fishta (; 23 October 187130 December 1940) was an Albanian Franciscan friar, poet, educator, rilindas, politician, translator and writer. He is regarded as one of the most influential Albanian writers of the 20th century, particularly for his epic masterpiece '' Lahuta e Malcís'', and as the editor of two of the most authoritative magazines after Albania's independence, ''Posta e Shqypniës'' and '' Hylli i Dritës''. Fishta was the chairman of the Congress of Manastir, which sanctioned the official Albanian alphabet, and he was part of the Albanian delegation to the Versailles Conference in 1919. In 1921, he was a member of the Albanian parliament and eventually became the deputy chairman. Later on, during the 1920s and the 1930s, he was among the most influential cultural and literary figures in Albania. After the Communist regime came to power, his literary oeuvre had been taken out of circulation until the fall of communism in the early 1990s. In recognition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahuta E Malcís
''The Highland Lute'' (, original and standard language of the time based on Gheg Albanian) is the Albanian national epic poem, completed and published by the Albanian friar and poet Gjergj Fishta in 1937. It consists of 30 songs and over 17,000 verses. The was heavily inspired by northern Albanian oral verse composed by the traditional cycle of epic songs and by the cycles of historical verse of the 18th century. It contains elements of Albanian mythology and south Slavic literary influences: Fishta was influenced by Croatian Franciscan friars as a student in monasteries in Austria-Hungary. In the poem the struggle against the Ottoman Empire became secondary and as a central theme substituted with fighting Slavs (Serbs and Montenegrins), whom he saw as more harmful after the recent massacres and expulsions of Albanians by them. The work was banned in Yugoslavia and Communist Albania due to anti-Slavic rhetoric. The work was described as "chauvinist" and "anti-Slavic" in the ''Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poetry
In poetry, an epic is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. With regard to oral tradition, epic poems consist of formal speech and are usually learnt word for word, and are contrasted with narratives that consist of everyday speech where the performer has the license to recontextualize the story to a particular audience, often to a younger generation. Influential epics that have shaped Western literature and culture include Homer's ''Iliad'' and '' Odyssey''; Virgil's '' Aeneid''; and the anonymous '' Beowulf'' and '' Epic of Gilgamesh''. The genre has inspired the adjective '' epic'' as well as derivative works in other mediums (such as epic films) that evoke or emulate the characteristics of epics. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin , which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |