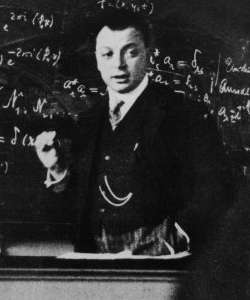|
Aage Bohr
Aage Niels Bohr (; 19 June 1922 – 8 September 2009) was a Danish nuclear physicist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1975 with Ben Roy Mottelson and James Rainwater "for the discovery of the connection between collective motion and particle motion in atomic nuclei and the development of the theory of the structure of the atomic nucleus based on this connection". His father was Niels Bohr. Starting from Rainwater's concept of an irregular-shaped liquid drop model of the nucleus, Bohr and Mottelson developed a detailed theory that was in close agreement with experiments. Since his father, Niels Bohr, had won the prize in 1922, he and his father are one of the six pairs of fathers and sons who have both won the Nobel Prize and one of the four pairs who have both won the Nobel Prize in Physics. Early life and education Bohr was born in Copenhagen on 19 June 1922, the fourth of six sons of the physicist Niels Bohr and his wife Margrethe Bohr (née Nørlund). His oldes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Vikings, Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. During the 16th century, the city served as the ''de facto'' capital of the Kalmar Union and the seat of the Union's monarchy, which governed most of the modern-day Nordic countries, Nordic region as part of a Danish confederation with Sweden and Norway. The city flourished as the cultural and economic centre of Scandinavia during the Renaissance. By the 17th century, it had become a regional centre of power, serving as the heart of the Danish government and Military history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nuclei
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlsberg Group
Carlsberg A/S (; ) is a Danish multinational brewer. Founded in 1847 by J. C. Jacobsen, the company's headquarters is in Copenhagen, Denmark. Since Jacobsen's death in 1887, the majority owner of the company has been the Carlsberg Foundation. The company's flagship brand is #Carlsberg, Carlsberg (named after Jacobsen's son Carl Jacobsen, Carl). The company employs around 41,000 people, primarily in Europe and Asia. Carlsberg is currently the sixth largest brewery in the world based on revenue. History Carlsberg was founded by J. C. Jacobsen, a philanthropist and admirer of science. The first brew was finished on 10 November 1847, and the export of Carlsberg beer began in 1868 with the export of one barrel to Edinburgh, Scotland. Some of the company's original logos include an elephant, after which Carlsberg Group#Elephant beer, some of its lagers are named, and the swastika, the use of which was discontinued in the 1930s because of its association with the Nazi party in ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jacobsen
Carl Christian Hillman Jacobsen (2 March 1842 – 11 January 1914) was a Danish brewer, art collector and philanthropist. Though often preoccupied with his cultural interests, Jacobsen was a shrewd and visionary businessman and initiated the transition of the brewery Carlsberg from a local Copenhagen brewery to the multinational conglomerate that it is today. Background Carl Jacobsen was born in Copenhagen, Denmark. He was the son of J. C. Jacobsen (1811-1887), who founded the brewery Carlsberg. After 1861, he became a student from the Borgerdyd School in Christianshavn. From 1866, he conducted a four year study trip to the leading breweries abroad. Career Jacobsen worked for his father but partly because of his conflicts between them, he founded his own brewery in 1882. It was first named Valby Brewery but upon his father's approval changed its name to Ny Carlsberg ( English: New Carlsberg), while his father's enterprise at the same occasion changed its name to Gammel Carlsbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Heisenberg
Werner Karl Heisenberg (; ; 5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist, one of the main pioneers of the theory of quantum mechanics and a principal scientist in the German nuclear program during World War II. He published his Umdeutung paper, ''Umdeutung'' paper in 1925, a major reinterpretation of old quantum theory. In the subsequent series of papers with Max Born and Pascual Jordan, during the same year, his matrix mechanics, matrix formulation of quantum mechanics was substantially elaborated. He is known for the uncertainty principle, which he published in 1927. Heisenberg was awarded the 1932 Nobel Prize in Physics "for the creation of quantum mechanics". Heisenberg also made contributions to the theories of the Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamics of turbulent flows, the atomic nucleus, ferromagnetism, cosmic rays, and subatomic particles. He introduced the concept of a wave function collapse. He was also instrumental in planning the first West Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshio Nishina
was a Japanese physicist who was called "the founding father of modern physics research in Japan". He led the efforts of Japan to develop an atomic bomb during World War II. Early life and career Nishina was born in Satoshō, Okayama. He received a silver watch from the emperor as he graduated at the top of his class at Tokyo Imperial University as an electrical engineer in 1918. He became a staff member at the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (now RIKEN) where he began studying physics under Hantaro Nagaoka. In 1921, he was sent to Europe for research. He visited some European universities and institutions, including Cavendish Laboratory, Georg August University of Göttingen, and University of Copenhagen. In Copenhagen, he did research with Niels Bohr, and they became good friends. In 1928, he wrote a paper on incoherent or Compton scattering with Oskar Klein in Copenhagen, from which the Klein–Nishina formula derives. In 1929, he returned to Japan, where he e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Klein
Oskar Benjamin Klein (; 15 September 1894 – 5 February 1977) was a Swedish theoretical physics, theoretical physicist. Oskar Klein is known for his work on Kaluza–Klein theory, which is partially named after him. Biography Klein was born in Danderyd Municipality, Danderyd outside Stockholm, son of the chief rabbi of Stockholm, Gottlieb Klein from Humenné in Kingdom of Hungary, now Slovakia and Antonie (Toni) Levy. He became a student of Svante Arrhenius at the Nobel Institute at a young age and was on the way to Jean-Baptiste Perrin in France when World War I broke out and he was drafted into the military. From 1917, he worked a few years with Niels Bohr in the University of Copenhagen and received his doctoral degree at the University College of Stockholm (now Stockholm University) in 1921. In 1923, he received a professorship at University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, Michigan, Ann Arbor and moved there with his recently wedded wife, Gerda Koch from Denmark. Klein returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Kramers
Hendrik Anthony "Hans" Kramers (17 December 1894 – 24 April 1952) was a Dutch physicist who worked with Niels Bohr to understand how electromagnetic waves interact with matter and made important contributions to quantum mechanics and statistical physics. Background and education Hans Kramers was born on 17 December 1894 in Rotterdam. the son of Hendrik Kramers, a physician, and Jeanne Susanne Breukelman. In 1912 Hans finished secondary education ( HBS) in Rotterdam, and studied mathematics and physics at the University of Leiden, where he obtained a master's degree in 1916. Kramers wanted to obtain foreign experience during his doctoral research, but his first choice of supervisor, Max Born in Göttingen, was not reachable because of the First World War. Because Denmark was neutral in this war, as was the Netherlands, he travelled (by ship, overland was impossible) to Copenhagen, where he visited unannounced the then still relatively unknown Niels Bohr. Bohr took him on as a P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr Institute
The Niels Bohr Institute () is a research institute of the University of Copenhagen. The research of the institute spans astronomy, geophysics, nanotechnology, particle physics, quantum mechanics, and biophysics. Overview The institute was founded in 1921, as the Institute for Theoretical Physics of the University of Copenhagen, by the Danish theoretical physicist Niels Bohr, who had been on the staff of the University of Copenhagen since 1914, and who had been lobbying for its creation since his appointment as professor in 1916. On the 80th anniversary of Niels Bohr's birth – October 7, 1965 – the Institute officially became the Niels Bohr Institute. Much of its original funding came from the charitable foundation of the Carlsberg Group, Carlsberg brewery, and later from the Rockefeller Foundation. During the 1920s, and 1930s, the institute was the center of the developing disciplines of atomic physics and quantum physics. Physicists from across Europe (and sometimes furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobelprize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death. The original Nobel Prizes covered five fields: physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature, and peace, specified in Nobel's will. A sixth prize, the Prize in Economic Sciences, was established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) in memory of Alfred Nobel. The Nobel Prizes are widely regarded as the most prestigious awards available in their respective fields. Shalev, p. 8. Except in extraordinary circumstances, such as war, all six prizes are given annually. Each recipient, known as a laureate, receives a green gold medal plated with 24 karat gold, a diploma, and a monetary award. As of 2023, the Nobel Prize monetary award is , equivalent to approximately . The medal shows Nobel in profile with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Summer Olympics
The 1948 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and officially branded as London 1948, were an international multi-sport event held from 29 July to 14 August 1948 in London, United Kingdom. Following a twelve-year hiatus caused by the outbreak of World War II, these were the first Summer Olympics held since the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 Games in Berlin. The 1940 Summer Olympics, 1940 Olympic Games had been scheduled for Tokyo and then for Helsinki, while the 1944 Summer Olympics, 1944 Olympic Games had been provisionally planned for London. This was the second time London hosted the Olympic Games, having previously hosted them in 1908 Summer Olympics, 1908, making it the second city to host summer olympics twice (after Paris). The Olympics would return again to London 64 years later in 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012, making London the first city to host the games thrice, and the only such city until Paris, who hosted their third games in 2024 Summer Olympics, 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |