|
A Correct Transcript Of Pilate's Court
The ''Archko Volume'' or ''Archko Library'' is a 19th-century volume containing what purports to be a series of reports from Jewish and pagan sources contemporary with Jesus that relate to the biblical texts describing his life. The work went through a number of versions and has remained in print ever since. The texts are otherwise unknown, and the author was convicted by an ecclesiastical court of falsehood and plagiarism. The ''Archko Volume'' is regarded as fraudulent by the scholar M.R. James, as he described the work as a "ridiculous and disgusting American book." In 1879, the Rev. William Dennes Mahan, a Cumberland Presbyterian minister of Boonville, Missouri, published a pamphlet of thirty-two pages entitled ''A Correct Transcript of Pilate's Court''. It purported to be an official report of the trial and death of Jesus made directly to the Roman Emperor Tiberius by Pilate as governor of Judaea. Mahan claimed the text was supplied to him in 1856 by a German scholar, Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar J
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of ''wikt:en:ead, ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''Gar (spear), gar'' "spear"). Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Middle Ages; it was, however, revived in the 18th century, and was popularised by its use for a character in Sir Walter Scott's ''The Bride of Lammermoor'' (1819). The name was more common in the United States than elsewhere in the Anglosphere during the 19th century. It has been a particularly fashionable name in Latin American countries since the 20th century. People with the given name * Edgar the Peaceful (942–975), king of England * Edgar the Ætheling (c. 1051 – c. 1126), last member of the Anglo-Saxon royal house of England * Edgar of Scotland (1074–1107), king of Scotland * Edgar Alaffita (born 1996), Mexican footballer * Edgar Allan (other), multiple people * Edgar Allen (other), multiple people * Edgar Angara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamaliel
Gamaliel the Elder (; also spelled Gamliel; ''Rabban Gamlīʾēl hazZāqēn''; ''Gamaliēl ho Presbýteros''), or Rabban Gamaliel I, was a leading authority in the Sanhedrin in the early first century CE. He was the son of Simeon ben Hillel and grandson of the great Jewish teacher Hillel the Elder. He fathered Simeon ben Gamliel, who was named for Gamaliel's father, and a daughter, who married a priest named Simon ben Nathanael. In the Christian tradition, Gamaliel is recognized as a Pharisaic doctor of Jewish Law. Gamaliel was named as a member of the Sanhedrin in the fifth chapter of Acts and the teacher of Paul the Apostle in . Gamaliel encouraged his fellow Pharisees to show leniency to the apostles of Jesus in . In Jewish tradition In the Talmud, Gamaliel is described as bearing the titles Nasi (Hebrew: נָשִׂיא ''Nāśīʾ'' "prince") and ''Rabban'' ("our master") as the president of the Great Sanhedrin in Jerusalem; it is not doubted that he held a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia (; ; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque (; ), is a mosque and former Church (building), church serving as a major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The last of three church buildings to be successively erected on the site by the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, it was completed in AD 537, becoming the world's largest interior space and among History of Roman and Byzantine domes, the first to employ a fully pendentive dome. It is considered the epitome of Byzantine architecture and is said to have "changed the history of architecture". From its dedication in 360 until 1453 Hagia Sophia served as the cathedral of Constantinople in the Divine Liturgy#Byzantine Rite, Byzantine liturgical tradition, except for the period 1204‑1261 when the Latin Empire, Latin Crusaders installed their own Hierarchy of the Catholic Church, hierarchy. After the fall of Constantinople in 1453, it served as a mosque, having its Minaret, minarets added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbis
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as '' semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of the rabbi developed in the Pharisaic (167 BCE–73 CE) and Talmudic (70–640 CE) eras, when learned teachers assembled to codify Judaism's written and oral laws. The title "rabbi" was first used in the first century CE. In more recent centuries, the duties of a rabbi became increasingly influenced by the duties of the Protestant Christian minister, hence the title "pulpit rabbis." Further, in 19th-century Germany and the United States, rabbinic activities such as sermons, pastoral counseling, and representing the community to the outside all increased in importance. Within the various Jewish denominations, there are different requirements for rabbinic ordination and differences in opinion regarding who is recognized as a rabbi. Non-Ort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; ; ; ), also called , was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt. The only event in Philo's life that can be decisively dated is his representation of the Alexandrian Jews in a delegation to the Roman emperor Caligula in 40 CE following civil strife between the Jewish and Greek communities of Alexandria. Philo was a leading writer of the Hellenistic Jewish community in Alexandria, Egypt. He wrote expansively in Koine Greek on philosophy, politics, and religion in his time; specifically, he explored the connections between Greek Platonic philosophy and late Second Temple Judaism. For example, he maintained that the Greek-language Septuagint and the Jewish law still being developed by the rabbis of the period together serve as a blueprint for the pursuit of individual enlightenment. Philo's deployment of allegory to harmonize Jewish scripture, mainly the Torah, with Greek philosophy was the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed Hasmonean royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Roman Empire during the First Jewish–Roman War as general of the Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in AD 67 to the Roman army led by military commander Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Roman emperor. In response, Vespasian decided to keep him as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became emperor in AD 69, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the Emperor's family name of '' Flavius''. Flavius Josephus fully defected to the Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod Antipas
Herod Antipas (, ''Hērṓidēs Antípas''; ) was a 1st-century ruler of Galilee and Perea. He bore the title of tetrarch ("ruler of a quarter") and is referred to as both "Herod the Tetrarch" and "King Herod" in the New Testament. He was a son of Herod the Great and a grandson of Antipater the Idumaean. He is widely known today for accounts in the New Testament of his role in events that led to the executions of John the Baptist and Jesus of Nazareth (, ). Following the death of his father (4 BC in Schürer's 1890 publication, 1 BC in much of the more recent scholarship, such as Jack Finegan, W. E. Filmer, and Andrew Steinmann), Herod Antipas was recognized as tetrarch by Caesar Augustus and subsequently by his brother, the ethnarch Herod Archelaus. Antipas officially ruled Galilee and Perea as a client state of the Roman Empire.Marshall, Taylor, 2012. ''The Eternal City'', Dallas: St. John, pp. 35–65. He was responsible for building projects at Sepphoris and Betharam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massacre Of The Innocents
The Massacre (or Slaughter) of the Innocents is a story recounted in the Nativity narrative of the Gospel of Matthew ( 2:16– 18) in which Herod the Great, king of Judea, orders the execution of all male children who are two years old and under in the vicinity of Bethlehem. Modern scholarship finds no evidence that it happened outside the passages in Matthew, though it is congruous with Herod's character. The Feast of the Holy Innocents, also known as Childermas, is celebrated in the Western Christian Churches on 28 December, the fourth day of Christmastide. In Eastern Christianity, the feast is celebrated on various dates, depending on the denomination. Biblical narrative The Gospel of Matthew tells how the Magi visit Jerusalem to seek guidance as to where the king of the Jews has been born; King Herod directs them to Bethlehem and asks them to return to him and report, but they are warned in a dream that Herod wishes to find the child and kill him, and do not do so. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod The Great
Herod I or Herod the Great () was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman Jewish client king of the Herodian kingdom of Judea. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea. Among these works are the rebuilding of the Second Temple#Herod's Temple, Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of its base—the Western Wall being part of it. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Despite Herod's successes, including forging a new aristocracy, he has been criticized by various historians. His reign polarizes opinion among historians, some viewing his legacy as evidence of success, and some viewing it as a reminder of his tyrannical rule. Herod the Great is described in the Christian Bible as the coordinator of the Massacre of the Innocents. However, most of the New Testament references are to his son Herod Antipas (such as the events leading to the executions of John the Baptist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Magi
In Christianity, the Biblical Magi ( or ; singular: ), also known as the Three Wise Men, Three Kings, and Three Magi, are distinguished foreigners who visit Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh in homage to him. In Western Christianity, they are commemorated on the feast day of Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany—sometimes called "Three Kings Day"—and commonly appear in the Nativity of Jesus, nativity celebrations of Christmas. In Eastern Christianity, they are commemorated on Christmas day. The Magi appear solely in the Gospel of Matthew, which states that they came "from the east" () to worship the "one who has been born king of the Jews". Their names, origins, appearances, and exact number are unmentioned and derive from the inferences or traditions of later Christians. In Western Christianity and Eastern Orthodox Christianity, they are usually assumed to have been three in number, corresponding with each gift; in Syriac Christianity, they ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
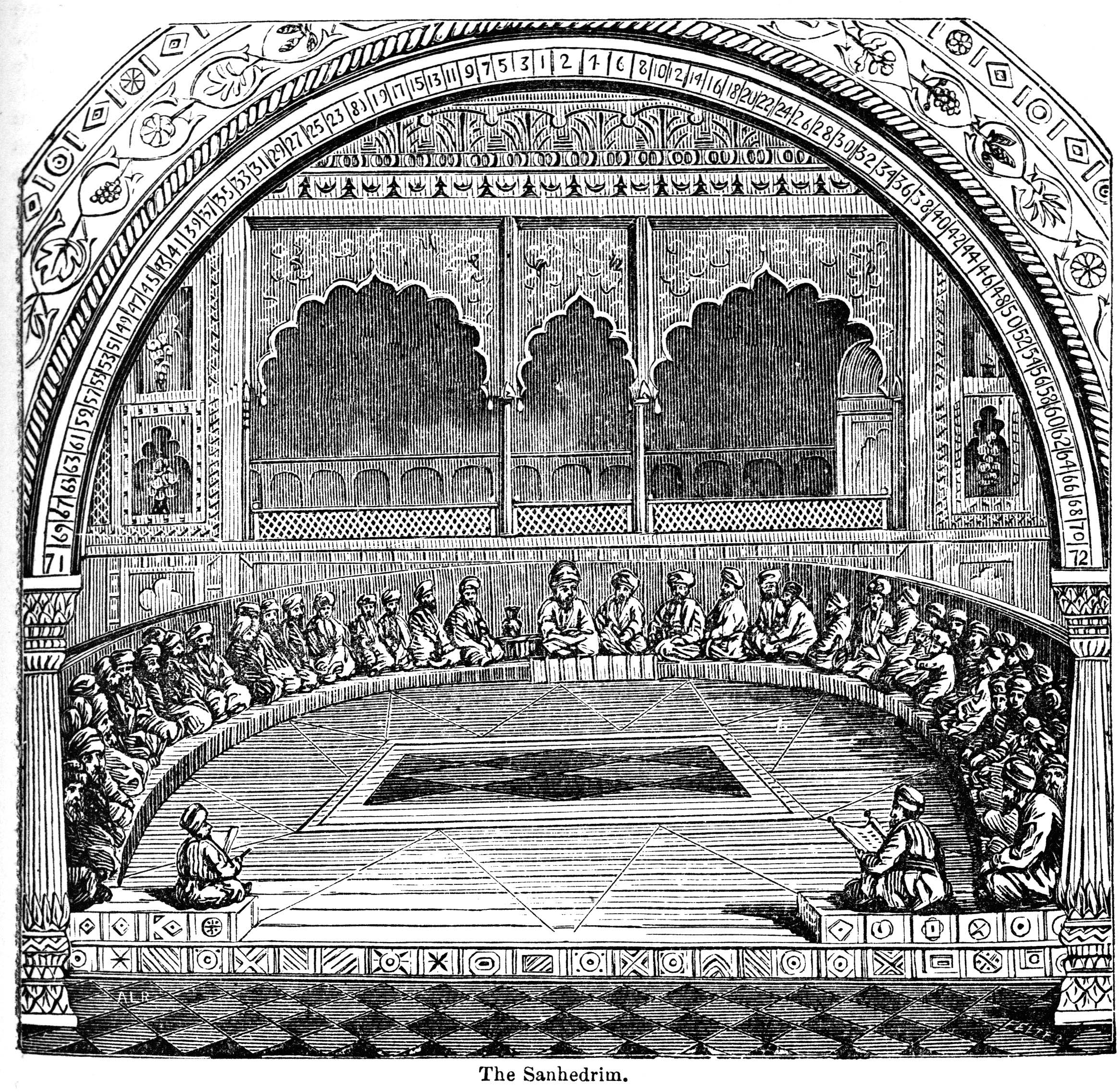
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |