|
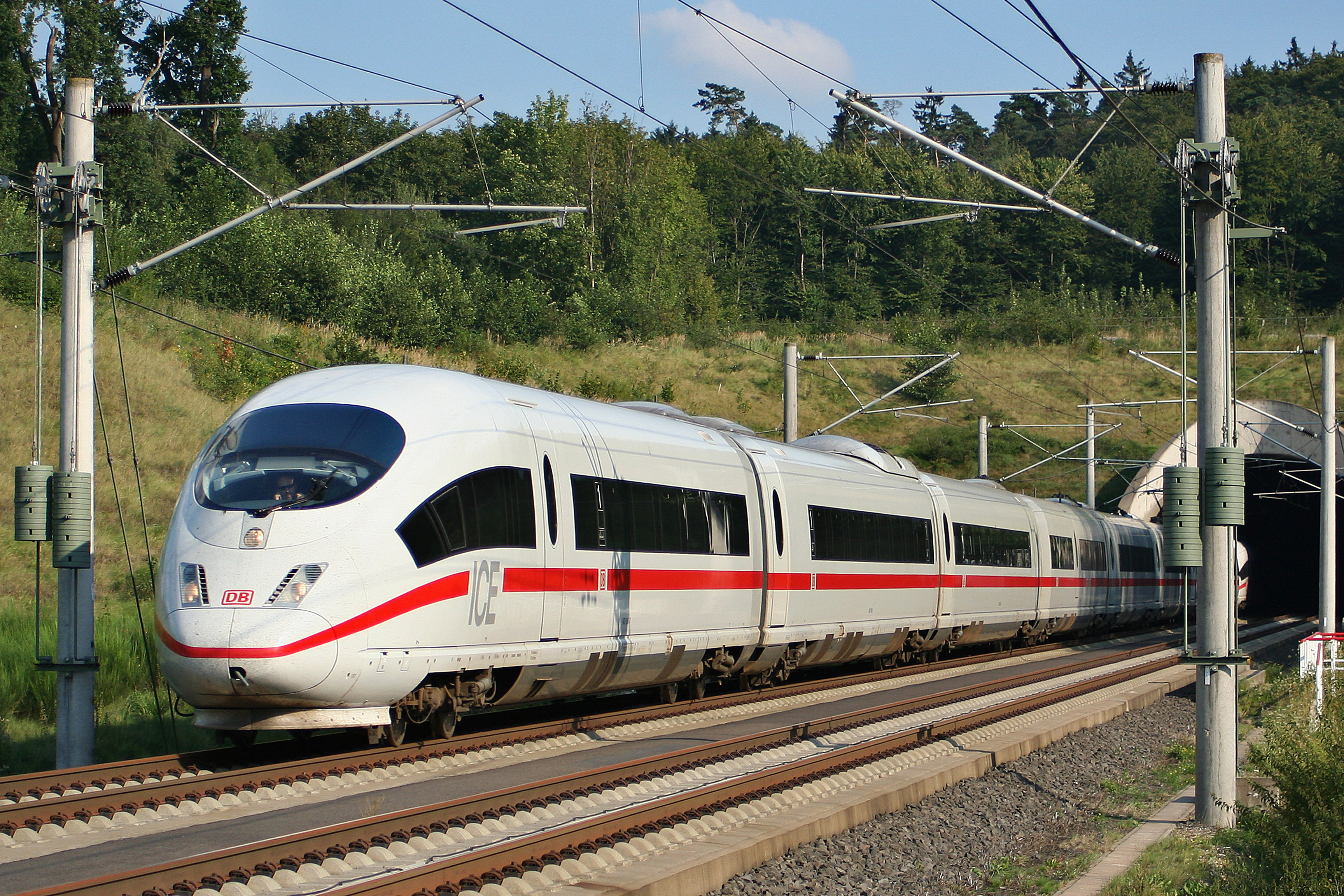
AVE Class 103
The Renfe Class 103 is a high-speed train used for the AVE service and operated in Spain by the state-run railway company Renfe. The trainset is also known as S103 or S/103. The trains were constructed by Siemens, as the second member of the company's Velaro family. History On 24 March 2001, Siemens won one half of Renfe's tender to supply 32 high-speed trains for the Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line, offering a modified version of the ICE 3 high-speed train used by German Railways (Deutsche Bahn) for its InterCityExpress service. Changes involved an up-rate to higher power () for higher acceleration and top speed to cover the between Barcelona and Madrid in 2h30m, the ability to operate in a high range of temperatures, and a different interior. The ICE 3 trains were a joint production with other Germany-based train manufacturers, who refused to supply parts or sell licenses to Siemens for the AVE Class 103. This caused a delay (for which Siemens eventually paid €21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens Mobility
Siemens Mobility GmbH is a division of Siemens. With its global headquarters in Munich, Siemens Mobility has four core business units: Mobility Management, dedicated to rail technology and intelligent traffic systems, Railway Electrification, Rolling Stock, and Customer Services. History Innovations from the late 19th century, such as the world's first electric train, when Siemens & Halske unveiled a train in which power was supplied through the rails, and the world's first electric tram, with the implementation of 2.5-kilometer-long electric tramway located in Berlin, built at the company's own expense, cemented the use of electric power in transportation systems. In the following years, inventions such as the first electric trolleybus, mine locomotives, and the first underground railway in continental Europe (in Budapest), set the path from trams and subways to today's high-speed trains. Siemens, alongside ThyssenKrupp and Transrapid International, was part of the Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Bahn
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). DB was founded after the merger between Deutsche Bundesbahn and the East German Deutsche Reichsbahn in 1994 after the unification of Germany and has been operating ever since. is the second-largest transport company in Germany, after the German postal and logistics company / DHL. DB provides both long-distance and regional transport, serving around 132 million long distance passengers and 1.6 billion regional passengers in 2022. In 2022, DB transported 222 million tons of cargo. Company profile The group is divided into several companies, including '' DB Fernverkehr'' (long-distance passenger), '' DB Regio'' (local passenger services) and '' DB Cargo'' (rail freight). The Group subsidiary '' DB InfraGO'' also operates large parts of the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calatayud Railway Station
Calatayud station is a railway station located in the Spanish city of Calatayud in Aragon. It brings together the classic Iberian gauge route between Madrid and Barcelona and the new high speed line. For the arrival of the latter, it was decided to remodel the old station known as Calatayud-Jalon. It is served by the AVE high speed trains between Madrid and Barcelona and onwards to Figueres Figueres (; ) is the capital city of Alt Empordà county, in the Girona region, Catalonia, Spain. The town is the birthplace of artist Salvador Dalí, and houses the Dalí Theatre and Museum, a large museum designed by Dalí himself which att .... Services References Railway stations in Spain opened in 1863 Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line {{Spain-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalajara, Spain
Guadalajara ( , ) is a city and municipality in Spain, located in the autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. It is the capital of the Province of Guadalajara. Guadalajara lies on the central part of the Iberian Peninsula at roughly metres above sea level. Most of the city housing is located on the left (southern bank) of the Henares, in between the river and the moors of La Alcarria. In addition to the city, the municipality also includes the villages of Iriépal, Taracena, , and . , Guadalajara has a registered population of 93,470, which makes it the region's second most populated municipality. Founded in the 9th century as Madīnat al-Faraŷ under the Emirate of Córdoba, it became a stronghold of the Masmuda Berber clan of the Banū Sālim. After Christian conquest in 1085 from the Taifa of Toledo, it grew into becoming a sizeable town of the Crown of Castile under control of the Mendoza family. It was a hub for mystical iluminismo in the 16th century in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Public Works And Transport (Spain)
The Ministry of Transport and Sustainable Mobility (MITMA) (), traditionally known as the Ministry of Development (MIFOM), is the department of the Government of Spain responsible for preparing and implementing the government policy on land, air and maritime transport infrastructure and the control, planning and regulation of the transport services on this areas. It is also responsible for guaranteeing access to housing; urban, soil and architecture policies; planning and controlling the postal and telegraph services, directing the services related to astronomy, geodesy, geophysics and mapping, and planning and programing the government investments on infrastructure and services related to this scope. The Ministry's headquarters are in the New Ministries government complex. MITMA is headed by the Minister of Transport, Mobility and Urban Agenda, who is appointed by the King of Spain at request of the Prime Minister. The Minister is assisted by two main officials, the Secretar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Train Control System
The European Train Control System (ETCS) is a train protection system designed to replace the many incompatible systems used by European railways, and railways outside of Europe. ETCS is the signalling and control component of the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS). ETCS consists of 2 major parts: #trackside equipment #on-board (on train) equipment ETCS can allow all trackside information to be passed to the driver cab, removing the need for trackside signals. This is the foundation for future automatic train operation (ATO). Trackside equipment aims to exchange information with the vehicle for safely supervising train circulation. The information exchanged between track and trains can be either continuous or intermittent according to the ERTMS/ETCS level of application and to the nature of the information itself. The need for a system like ETCS stems from more and longer running trains resulting from economic integration of the European Union (EU) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software. The origins of the conglomerate can be traced back to 1847 to the ''Telegraphen Bau-Anstalt von Siemens & Halske'' established in Berlin by Werner von Siemens and Johann Georg Halske. In 1966, the present-day corporation emerged from the merger of three companies: Siemens & Halske, Siemens-Schuckert, and Siemens-Reiniger-Werke. Today headquartered in Munich and Berlin, Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 320,000 people worldwide and reported a global revenue of around €78 billion in 2023. The company is a component of the DAX and Euro Stoxx 50 stock market indices. As of December 2023, Siemens is the second largest German company by market ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a medium, such as a plasma, dielectric, shielding material, glass, etc. An opaque object is neither transparent (allowing all light to pass through) nor translucent (allowing some light to pass through). When light strikes an interface between two substances, in general, some may be reflected, some absorbed, some scattered, and the rest transmitted (also see refraction). Reflection can be diffuse, for example light reflecting off a white wall, or specular, for example light reflecting off a mirror. An opaque substance transmits no light, and therefore reflects, scatters, or absorbs all of it. Other categories of visual appearance, related to the perception of regular or diffuse reflection and transmission of light, have been organized under the concept of cesia in an order sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogies
A bogie ( ) (or truck in North American English) comprises two or more wheelsets (two wheels on an axle), in a frame, attached under a vehicle by a pivot. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transport. A bogie may remain normally attached (as on many railroad cars and semi-trailers) or be quickly detachable (as for a dolly in a road train or in railway bogie exchange). It may include suspension components within it (as most rail and trucking bogies do), or be solid and in turn be suspended (as are most bogies of tracked vehicles). It may be mounted on a swivel, as traditionally on a railway carriage or locomotive, additionally jointed and sprung (as in the landing gear of an airliner), or held in place by other means (centreless bogies). Although ''bogie'' is the preferred spelling and first-listed variant in various dictionaries, bogey and bogy are also used. Railway A ''bogie'' in the UK, or a ''railroad truck'', ''wheel truck'', or simply ''truck'' in No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Traction
In rail transport, distributed power (DP) is a generic term referring to the physical distribution—at intermediate points throughout the length of a train—of separate motive power groups. Such "groups" may be single units or multiple consists, and are remotely controlled from the leading locomotive. The practice allows locomotives to be placed anywhere within the length of a train when standard multiple-unit (MU) operation is impossible or impractical. DP can be achieved by wireless (RF connectivity) or wired (trainlined) means. Wired systems now provided by various suppliers use the cabling already extant throughout a train equipped with electronically controlled pneumatic brakes (ECP). History Since the 1960s, railroad distributed power technology has been dominated by one company, Harris Controls (originally Harris Corporation — Controls & Composition Division, later purchased by General Electric—the division now known as GE Transportation) who have manufactured and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
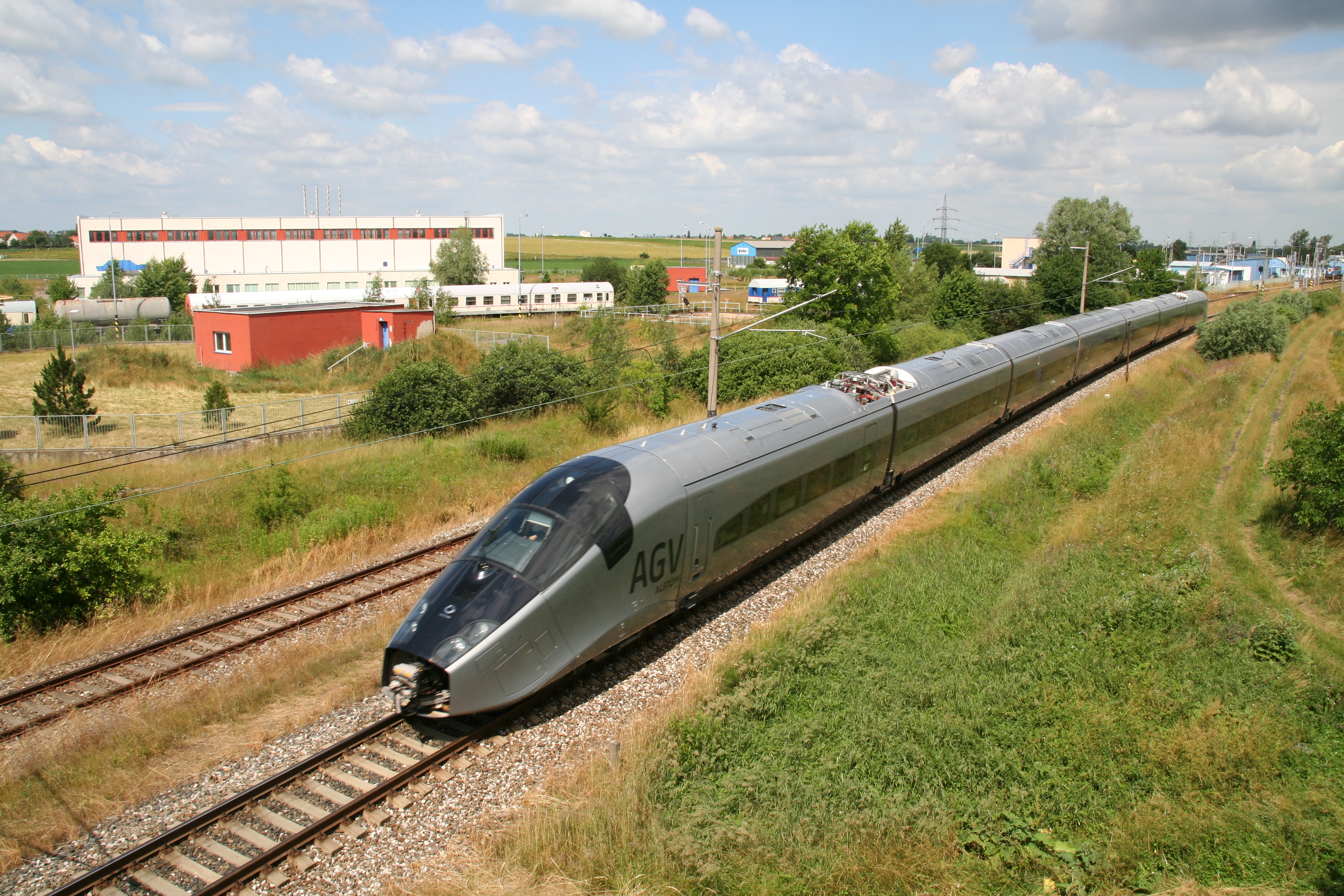
Automotrice à Grande Vitesse
The AGV (acronym for French: ''Automotrice à grande vitesse''; lit. "high-speed railcar") is a standard gauge, high-speed, electric multiple-unit train designed and built by Alstom. Alstom offers the AGV in configurations from seven to fourteen carriages, with seating that can carry as much as 245 to 446 people. The trains are constructed from units comprising three cars (each with one transformer and two traction electronics packages located underneath the cars) and single-car driver-trailers. The maximum commercial speed is . Design of the train took place through the early 2000s, with a prototype, ''"Pégase"'', produced in 2008. Italian transport company NTV ordered 25 trains in 2008 (classified as AGV 575) with services beginning in 2012. According to Alstom, the advantages of the AGV are: increased seating area per train length (compared to a single-deck TGV); safety and maintenance advantages of the Jacobs bogie articulation design as well as higher energy efficienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alstom
Alstom SA () is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional and urban trains along with trams. The company and its name (originally spelled Alsthom) was formed by a merger between the electric engineering division of Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (Als) and Compagnie Française Thomson-Houston (thom) in 1928. Significant acquisitions later included the Constructions Électriques de France (1932), shipbuilder Chantiers de l'Atlantique (1976), and parts of ACEC (late 1980s). A merger with parts of the British General Electric Company formed GEC Alsthom in 1989. Throughout the 1990s, the company expanded its holdings in the rail sector, acquiring German rolling stock manufacturer Linke-Hofmann-Busch and Italian rail signaling specialist Sasib Railways. In 1998, GEC Alsthom was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |