|
ASIL D
Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) is a risk classification scheme defined by the ISO 26262 - Functional Safety for Road Vehicles standard. This is an adaptation of the Safety Integrity Level (SIL) used in IEC 61508 for the automotive industry. This classification helps defining the safety requirements necessary to be in line with the ISO 26262 standard. The ASIL is established by performing a risk analysis of a potential hazard by looking at the Severity, Exposure and Controllability of the vehicle operating scenario. The safety goal for that hazard in turn carries the ASIL requirements. There are four ASILs identified by the standard: ASIL A, ASIL B, ASIL C, ASIL D. ASIL D dictates the highest integrity requirements on the product and ASIL A the lowest. Hazards that are identified as QM do not dictate any safety requirements. Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment Because of the reference to SIL and because the ASIL incorporate 4 levels of hazard with a 5th non-hazardous lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 26262
ISO 26262, titled "Road vehicles – Functional safety", is an international standard for functional safety of electrical and/or electronic systems that are installed in serial production road vehicles (excluding mopeds), defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2011, and revised in 2018. Overview of the Standard Functional safety features form an integral part of each automotive product development phase, ranging from the specification, to design, implementation, integration, verification, validation, and production release. The standard ISO 26262 is an adaptation of the Functional Safety standard IEC 61508 for Automotive Electric/Electronic Systems. ISO 26262 defines functional safety for automotive equipment applicable throughout the lifecycle of all automotive electronic and electrical safety-related systems. The first edition (ISO 26262:2011), published on 11 November 2011, was limited to electrical and/or electronic systems installed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-254
RTCA DO-254 / EUROCAE ED-80, Design Assurance Guidance for Airborne Electronic Hardware is a document providing guidance for the development of airborne electronic hardware, published by RTCA, Incorporated and EUROCAE. Initially released in 2000, the DO-254/ED-80 standard was not necessarily considered policy until recognized by the FAA in 2005 through AC 20-152 as a means of compliance for the design assurance of electronic hardware in airborne systems. The guidance in this document is applicable, but not limited, to such electronic hardware items as * Line Replaceable Units (quickly replaceable components) * Circuit board assemblies (CBA) * Custom micro-coded components such as field programmable gate arrays (FPGA), programmable logic devices (PLD), and application-specific integrated circuits (ASIC), including any associated macro functions * Integrated technology components such as hybrid integrated circuits and multi-chip modules * Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of Mechanical engineering, mechanical, Electrical engineering, electrical, Electronic engineering, electronic, Software engineering, software, and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles, and trucks and their respective engineering subsystems. It also includes modification of vehicles. Manufacturing domain deals with the creation and assembling the whole parts of automobiles is also included in it. The automotive engineering field is research intensive and involves direct application of mathematical models and formulas. The study of automotive engineering is to design, develop, fabricate, and test vehicles or vehicle components from the concept stage to production stage. Production, development, and manufacturing are the three major functions in this field. Disciplines Automobile engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
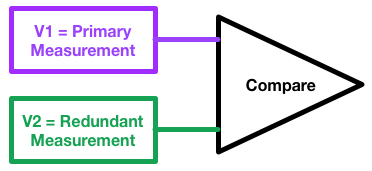
ASIL Accuracy
ASIL accuracy describes the maximum possible deviation of a measurement in a system in which a single point fault occurred before some diagnostic detects this fault. This concept applies to automotive systems designed under the ISO 26262, ISO-26262 methodology for automotive functional safety, which defines Automotive Safety Integrity Level, Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASILs) to classify risks. While Accuracy and precision, accuracy refers to a single measurement, ASIL accuracy considers variation in the primary measurement being assessed as well as variation in the diagnostic measurement or measurements used to detect single point faults. How to calculate A conceptually simple implementation incorporates a fully redundant measurement. A fault in the primary measurement can be detected by comparing the primary and diagnostic measurements, and signaling a fault if the difference is outside the expected operating range. If the two measurements are truly independent and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP4754
ARP4754(), Aerospace Recommended Practice (ARP) Guidelines for Development of Civil Aircraft and Systems, is a published standard from SAE International, dealing with the development processes which support certification of Aircraft systems, addressing "the complete aircraft development cycle, from systems requirements through systems verification." Since their joint release in 2002, compliance with the guidelines and methods described within ARP4754() and its companion ARP4761() have become mandatory for effectively all civil aviation world-wide. Revision A was released in December 2010. It was recognized by the FAA through Advisory Circular AC 20-174 published November 2011. EUROCAE jointly issued the document as ED–79. Revision B was released in December 2023 and inherits the "mandates" conferred through FAA advisory circulars AC 25.1309-1 and AC 20-174 as acceptable means of demonstrating compliance with 14 CFR 25.1309 in the U.S. Federal Aviation Adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP4761
ARP4761, Guidelines for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Aircraft, Systems, and Equipment is an Aerospace Recommended Practice from SAE International. In conjunction with ARP4754, ARP4761 is used to demonstrate compliance with 14 CFR 25.1309 in the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) airworthiness regulations for transport category aircraft, and also harmonized international airworthiness regulations such as European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) CS–25.1309. This Recommended Practice defines a process for using common modeling techniques to assess the safety of a system being put together. The first 30 pages of the document covers that process. The next 140 pages give an overview of the modeling techniques and how they should be applied. The last 160 pages give an example of the process in action. Some of the methods covered: * Functional Hazard Assessment (FHA) *Preliminary System Safety Assessment (PSSA) *System Safety Assessment (SSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Data Research Associates
LDRA, previously known as the Liverpool Data Research Associates, is a privately held company producing software analysis, testing, and requirements traceability tools for the public and private sectors. It is involved static and dynamic software analysis. History ''Liverpool Data Research Associates'' was founded in 1975 by Professor Michael Hennell to commercialize a software test-bed created to perform quality assessments on the mathematical libraries on which his nuclear physics research at the University of Liverpool depended.M. A. Hennell, ''An experimental test bed for numerical software. . '', The Computer Journal 21(4):333--336, @nov, 1978M. A. Hennell and D. Hedley, ''An experimental testbed for numerical software. . '', The Computer Journal 22(1):53--56, @feb, 1979 This research included the invention of the Linear Code Sequence and Jump (LCSAJ) software analysis method.M.A. Hennell, M.R.Woodward and D.Hedley, "On program analysis", Information Processing Letters, 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 25119
ISO 25119, titled "Tractors and machinery for agriculture and forestry – Safety-related parts of control systems", is an international standard for functional safety of electrical and/or electronic systems that are installed in tractors and machines used in agriculture and forestry, defined by the International Organization for Standardization The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. M ... (ISO). Parts of ISO 25119 ISO 25119 consists of following parts: # General principles for design and development # Concept phase # Series development, hardware and software # Production, operation, modification and supporting processes See also * IEC 61508 References {{Reflist #25119 Safety engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 13849
ISO 13849 is a safety standard which applies to parts of machinery control systems that are assigned to providing safety functions (called safety-related parts of a control system). The standard is one of a group of sector-specific functional safety standards that were created to tailor the generic system reliability approaches, e.g., IEC 61508, MIL-HDBK-217, MIL-HDBK-338, to the needs of a particular sector. ISO 13849 is simplified for use in the machinery sector. The standard has two parts: * ISO 13849-1, Part 1: General principles for design, provides safety requirements and guidance on the principles of design and integration of safety-related parts of control systems (hardware or software). * ISO 13849-2, Part 2: Validation, specifies the procedures to be followed for validating by analysis or tests, the safety functions of the system, the category achieved and the performance level achieved. ISO 13849 is designed for use in machinery with high to continuous demand rates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 60730
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology, and marine energy, as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards. All electrotechnologies are covered by IEC Standards, including energy production and distribution, electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunications and medical technology, as well as associated general disciplines such as terminology and symbols, electromagnetic compatibility, measurement and performance, dependability, desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 62304
IEC 62304 – medical device software – software life cycle processes is an international standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The standard specifies life cycle requirements for the development of medical software and software within medical devices. It has been adopted as national standards and therefore can be used as a benchmark to comply with regulatory requirements. Implications of IEC 62304 for software The IEC 62304 standard calls out certain cautions on using software, particularly SOUP ( software of unknown pedigree or provenance). The standard spells out a risk-based decision model on when the use of SOUP is acceptable, and defines testing requirements for SOUP to support a rationale on why such software should be used. Contents Source: General requirements * Quality management system * Risk management * Software safety classification Software development process * Software development planning * Software require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |