|
AND-OR-Invert
AND-OR-invert (AOI) logic and AOI gates are two-level compound (or complex) logic functions constructed from the combination of one or more AND gates followed by a NOR gate (equivalent to an OR gate through an Inverter gate, which is the "OI" part of "AOI"). Construction of AOI cells is particularly efficient using CMOS technology, where the total number of transistor gates can be compared to the same construction using NAND logic or NOR logic. The complement of AOI logic is OR-AND-invert (OAI) logic, where the OR gates precede a NAND gate. Overview Most logic optimization result in a Canonical normal form, sum-of-products or product-of-sums logic expression. AOI is used for sum-of-products, the variables are ANDed to form minterms which are ORed together then inverted: * is known as a AOI 2-1 gate. * is known as a AOI 2-2 gate. * is known as a AOI 3-3 gate. * is known as a AOI 4-4 gate. * is known as a AOI 4-3-2 gate. * and other variations. Examples AOI gates perform one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of 7400-series Integrated Circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name SN74xx. Due to the popularity of these parts, other manufacturers released pin-to-pin compatible logic devices and kept the 7400 sequence number as an aid to identification of compatible parts. However, other manufacturers use different prefixes and suffixes on their part numbers. Overview Some TTL logic parts were made with an extended military-specification temperature range. These parts are prefixed with 54 instead of 74 in the part number. A short-lived 64 prefix on Texas Instruments parts indicated an industrial temperature range; this prefix had been dropped from the TI literature by 1973. Most recent 7400-series parts are fabricated in CMOS or BiCMOS technology rather than TTL. Surface-mount parts with a single gate (often in a 5-pin or 6-pin package) are prefixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of 4000-series Integrated Circuits
The following is a list of CMOS 4000-series digital logic integrated circuits. In 1968, the original 4000-series was introduced by RCA. Although more recent parts are considerably faster, the 4000 devices operate over a wide power supply range (3V to 18V recommended range for "B" series) and are well suited to unregulated battery powered applications and interfacing with sensitive analogue electronics, where the slower operation may be an EMC advantage. The earlier datasheets included the internal schematics of the gate architectures and a number of novel designs are able to 'mis-use' this additional information to provide semi-analog functions for timing skew and linear signal amplification. Due to the popularity of these parts, other manufacturers released pin-to-pin compatible logic devices and kept the 4000 sequence number as an aid to identification of compatible parts. However, other manufacturers use different prefixes and suffixes on their part numbers, and not all device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
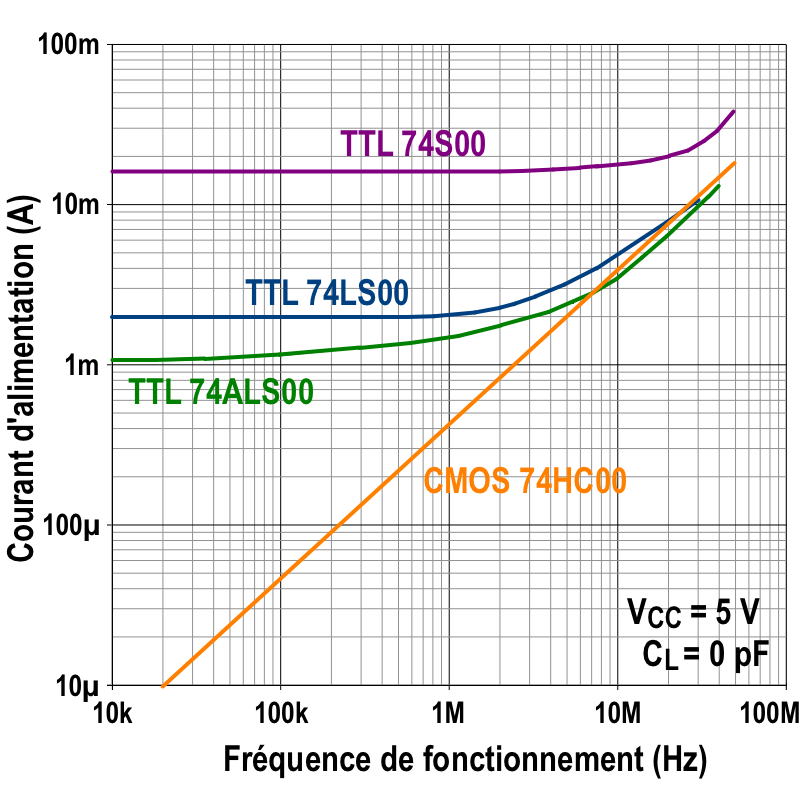
7400-series Integrated Circuits
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs). In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming ''de facto'' standardized electronic components. Since the introduction of the original bipolar-transistor TTL parts, pin-compatible parts were introduced with such features as low power CMOS technology and lower supply voltages. Surface mount packages exist for several popular logic family functions. Overview The 7400 series contains hundreds of devices that provide everything from basic logic gates, flip-flops, and counters, to special purpose bus transceivers and arithmetic logic units (ALU). Specific functions are described in a list of 7400 series integrated circuits. Some TTL parts were made with an ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-state Logic
In digital electronics, a tri-state or three-state buffer is a type of digital buffer that has three stable states: a high voltage output state (logical 1), a low output state (logical 0), and a high-impedance (Hi-Z) state. In the Hi-Z state, the output of the buffer is effectively disconnected from the subsequent circuit. Tri-state buffers are commonly used in bus-based systems where multiple devices are connected to the same shared bus, because the Hi-Z state allows other devices to drive the bus without interference from the tri-state buffer. For example, in a computer system, multiple devices such as the CPU, memory, and peripherals may be connected to the same data bus. To ensure that only one device can transmit data on the bus at a time, each device is equipped with a tri-state buffer. When a device wants to transmit data, it activates its tri-state buffer, which connects its output to the bus and allows it to transmit data. When the transmission is complete, the devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces digital light processing (DLP) technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufactured the first transistor radio. Jack Kilby invented the integrated circuit in 1958 while working at TI's Central Research Labs. TI also invented the hand-held calculator in 1967, and intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4000-series Integrated Circuits
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It was slowly migrated into the 4000B buffered series after about 1975. It had a much wider supply voltage range than any contemporary logic family (3V to 18V recommended range for "B" series). Almost all IC manufacturers active during this initial era fabricated models for this series. Its naming convention is still in use today. History The 4000 series was introduced as the ''CD4000 COS/MOS'' series in 1968 by RCA as a lower power and more versatile alternative to the 7400 series of transistor-transistor logic (TTL) chips. The logic functions were implemented with the newly introduced CMOS, Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor (CMOS) technology. While initially marketed with "COS/MOS" labeling by RCA (which stood for Complementary Symmetry Metal-Oxide Semiconductor), the shorter ''CMOS'' terminology emerged as the industry preference to refer to the technology. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor–transistor Logic
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor"), as opposed to earlier resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and diode–transistor logic (DTL). TTL integrated circuits (ICs) were widely used in applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, and synthesizers. After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania Electric Products, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies. The 7400 series by Texas Instruments became particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gates, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Variations of the original TTL circuit design offered higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow design optimization. TTL devices w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Logic (digital Electronics)
In integrated circuit design, dynamic logic (or sometimes clocked logic) is a design methodology in combinational logic circuits, particularly those implemented in metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology. It is distinguished from the so-called static logic by exploiting temporary storage of information in stray and gate capacitances. It was popular in the 1970s and has seen a recent resurgence in the design of high-speed digital electronics, particularly central processing units (CPUs). Dynamic logic circuits are usually faster than static counterparts and require less surface area, but are more difficult to design. Dynamic logic has a higher average rate of voltage transitions than static logic, but the capacitive loads being transitioned are smaller so the overall power consumption of dynamic logic may be higher or lower depending on various tradeoffs. When referring to a particular logic family, the dynamic adjective usually suffices to distinguish the design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depletion-load NMOS Logic
In integrated circuits, depletion-load NMOS is a form of digital logic family that uses only a single power supply voltage, unlike earlier NMOS logic, NMOS (n-type metal-oxide semiconductor) logic families that needed multiple power supply voltages. Although manufacturing these integrated circuits required additional processing steps, improved switching speed and the elimination of the extra power supply made this logic family the preferred choice for many microprocessors and other logic elements. Depletion and enhancement modes, Depletion-mode n-type MOSFETs as load transistors allow single voltage operation and achieve greater speed than possible with enhancement-load devices alone. This is partly because the depletion-mode MOSFETs can be a better current source approximation than the simpler enhancement-mode transistor can, especially when no extra voltage is available (one of the reasons early PMOS and NMOS chips demanded several voltages). The inclusion of depletion-mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMOS Logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. NMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the n-channel, can conduct electrons between n-type ''source'' and ''drain'' terminals. The n-channel is created by applying voltage to the third terminal, called the ''gate''. Like other MOSFETs, nMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off (or subthreshold), triode, saturation (sometimes called active), and velocity saturation. NMOS AND-by-default logic can produce unusual glitches or buggy behavior in NMOS components, such as the 6502 "illegal opcodes" which are absent in CMOS 6502s. In some cases such as Commodore's VIC-II chip, the bugs present in the chip's logic were extensively exploited by programmers for graphics effects. For many years, NMOS ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |