|
ABCB11
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B member 11 (ABCB11), also known as the bile salt export pump (BSEP), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene. Function The product of the ''ABCB11'' gene is an ABC transporter named BSEP (bile salt export pump), or sPgp (sister of P-glycoprotein). This membrane-associated protein is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MDR/TAP subfamily. Some members of the MDR/TAP subfamily are involved in multidrug resistance. This particular protein is responsible for the transport of taurocholate and other cholate conjugates from hepatocytes (liver cells) to the bile. In humans, the activity of this transporter is the major determinant of bile formation and bile flow. Clinical significanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP-binding Cassette Transporter
The ABC transporters, ATP synthase (ATP)-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene family, gene families. It is represented in all extant taxon, extant Phylum, phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases. ABC transporters often consist of multiple subunits, one or two of which are transmembrane proteins and one or two of which are membrane-associated AAA proteins, AAA ATPases. The ATPase subunits utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis to provide the energy needed for the translocation of substrates across membranes, either for uptake or for export of the substrate. Most of the uptake systems also have an extracytoplasmic receptor, a solute binding protein. Some homologous ATPases function in non-transport-related processes such as RNA translation, translation of RNA and DNA repair. ABC transporters are considered to be an ABC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
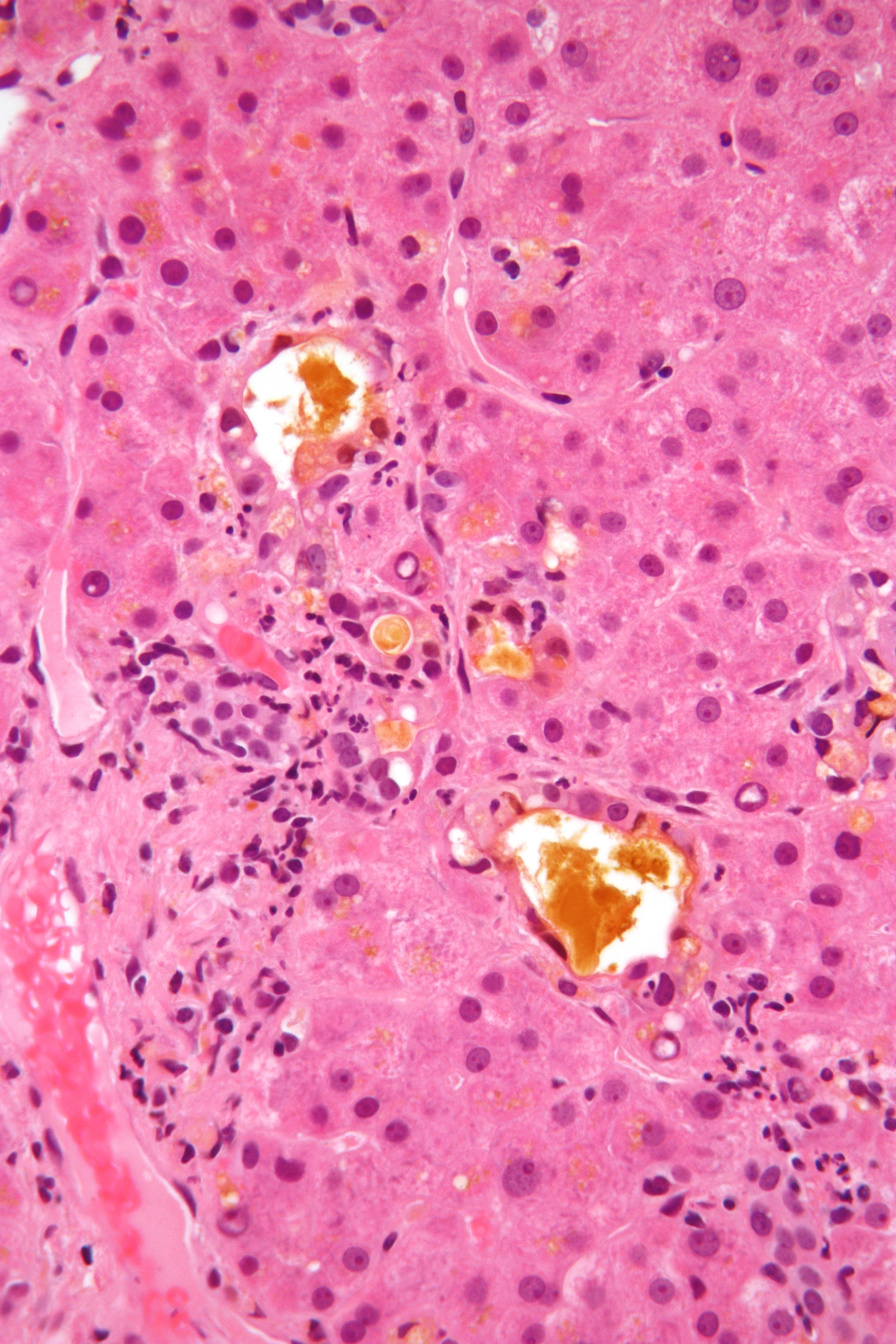
Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of Genetic disorder, familial cholestasis, cholestatic conditions caused by defects in bile, biliary Epithelium, epithelial transporters. The clinical presentation usually occurs first in childhood with progressive cholestasis. This usually leads to failure to thrive, cirrhosis, and the need for liver transplantation. Types Types of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis are as follows: * Type 1 (OMIM #211600), also called Byler disease * Type 2 (OMIM #601847), also called ABCB11 deficiency or BSEP deficiency * Type 3 (OMIM #602347), also called ABCB4 deficiency or MDR3 deficiency * Type 4 (OMIM #615878), from mutation in ''tight junction protein 2, TJP2'' Signs and symptoms The onset of the disease is usually before age 2, but patients have been diagnosed with PFIC even into adolescence. Of the three entities, PFIC-1 usually presents earliest. Patients usually present in early childhood with cholestasis, jau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. HCC most commonly occurs in those with chronic liver disease especially those with cirrhosis or fibrosis, which occur in the setting of chronic liver injury and inflammation. HCC is rare in those without chronic liver disease. Chronic liver diseases which greatly increase the risk of HCC include hepatitis infection such as (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, C or hepatitis D, D), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcoholic liver disease, or exposure to toxins such as aflatoxin, or pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Certain diseases, such as HFE hereditary haemochromatosis, hemochromatosis and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, markedly increase the risk of developing HCC. The five-year survival in those with HCC is 18%. As with any cancer, the treatment and prognosis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidrug Resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasitism, parasites (resistant to multiple antifungal, antiviral drug, antiviral, and antiparasitic drugs of a wide chemical variety). Recognizing different degrees of MDR in bacteria, the terms ''extensively drug-resistant'' (''XDR'') and ''pandrug-resistant'' (''PDR'') have been introduced. ''Extensively drug-resistant (XDR)'' is the non-susceptibility of one bacteria species to all antimicrobial agents except in two or less antimicrobial categories. Within XDR, ''pandrug-resistant (PDR)'' is the non-sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurocholic Acid
Taurocholic acid, known also as cholaic acid, cholyltaurine, or acidum cholatauricum, is a deliquescent yellowish crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate of cholic acid with taurine. In medical use, it is administered as a cholagogue and choleretic. Hydrolysis of taurocholic acid yields taurine. For commercial use, taurocholic acid is manufactured from cattle bile, a byproduct of the meat-processing industry. This acid is also one of the many molecules in the body that has cholesterol as its precursor. In a large prospective study (involving 569 incident colon cancer cases and 569 matched controls) it was found that prediagnostic concentrations of circulating taurocholic acid, as well as six other bile acids, were statistically significantly associated with increased colon cancer risk. Toxicity The median lethal dose In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for " l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also observed (wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is produced continuously by the liver, and is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After a human eats, this stored bile is discharged into the first section of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Composition In the human liver, bile is composed of 97–98% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats ( cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is orange-yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties, but may still be harmful to health. The term benign in more general medical use characterizes a condition or growth that is not cancerous, i.e. does not spread to other parts of the body or invade nearby tissue. Sometimes the term is used to suggest that a condition is not dangerous or serious. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP8B1
Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ATP8B1'' gene. This protein is associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 as well as benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Function This gene encodes a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family and specifically belongs to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. This protein is highly expressed in the small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and prostate and is also found in cholangiocytes and the canalicular membranes of hepatocytes A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile ... in the liver. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to another. Mutat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile Acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver in peroxisomes. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts. Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts. The salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids. Description Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |