|
8th Division (German Empire)
The 8th Division (''8. Division'') was a unit of the Prussian/German Army. It was formed in Erfurt in November 1816 as a brigade and became a division on September 5, 1818. The division was subordinated in peacetime to the IV Army Corps (''IV. Armeekorps''). The division was disbanded in 1919 during the demobilization of the German Army after World War I. The division was recruited primarily in the Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony and the smaller states of the German Empire around Prussian Saxony. Combat chronicle The division fought in the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, including the Battle of Königgrätz. In the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71, the division saw action in the battles of Beaumont and Sedan, and in the Siege of Paris. The division was mobilized as the 8th Infantry Division in August 1914 and sent to the west for the opening campaigns of the war. It fought in the Battle of the Marne and then participated in the Race to the Sea. The division then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian Von Prittwitz
Maximilian “Max” Wilhelm Gustav Moritz von Prittwitz und Gaffron (27 November 1848 – 29 March 1917) was an Imperial German general. He fought in the Austro-Prussian War, the Franco-Prussian War, and briefly in the First World War. Family Prittwitz came from an old aristocratic Silesian family in Bernstadt (now Bierutów, Poland). His father was Gustav von Prittwitz, a Prussian general, and his mother was Elizabeth von Klass. On 19 May 1874 Prittwitz married Olga von Dewitz (30 August 1848 – 9 January 1938), the daughter of Kurt von Dewitz, a landowner and his wife Euphemia, née von der Groeben. Their only son died on 23 May 1918. Early military career After attending a school in Oels, Prittwitz joined the 3rd Guard Grenadier Regiment and fought in the Austro-Prussian War. He was then commissioned as a junior officer in the 38th Fusileers with which regiment he served in the Franco-Prussian War. After attending the Prussian Military Academy Prittwitz was appoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christmas Truce
ckb: ئاگربەستی کریسماس The Christmas truce (german: Weihnachtsfrieden; french: Trêve de Noël; nl, Kerstbestand) was a series of widespread unofficial ceasefires along the Western Front of the First World War around Christmas 1914. The truce occurred five months after hostilities had begun. Lulls occurred in the fighting as armies ran out of men and munitions and commanders reconsidered their strategies following the stalemate of the Race to the Sea and the indecisive result of the First Battle of Ypres. In the week leading up to 25 December, French, German and British soldiers crossed trenches to exchange seasonal greetings and talk. In some areas, men from both sides ventured into no man's land on Christmas Eve and Christmas Day to mingle and exchange food and souvenirs. There were joint burial ceremonies and prisoner swaps, while several meetings ended in carol-singing. Men played games of football with one another, creating one of the most memorable im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joyeux Noël
:''Joyeux Noel means Merry Christmas in French. For other uses, see Christmas (other) and Merry Christmas (other)'' ''Joyeux Noël'' ''('Merry Christmas')'' is a 2005 war drama film based on the Christmas truce of December 1914, depicted through the eyes of French, British, and German soldiers. It was written and directed by Christian Carion, and screened out of competition at the 2005 Cannes Film Festival. The film, which includes one of the last appearances of Ian Richardson before his death, was nominated for Best Foreign Language Film at the 78th Academy Awards. It is a fictionalised account of an actual event that took place in December 1914, when Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, sent the lead singer of the Berlin Imperial Opera company on a solo visit to the front line. Singing by the tenor, Walter Kirchhoff, to the 120th and 124th Württemberg regiments led French soldiers in their trenches to stand up and applaud. Plot The story centres mainly upon s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Division
A square division is a designation given to the way military divisions are organized. In a square organization, the division's main body is composed of four "maneuver," i.e., infantry regimental elements. Other types of regiments, such as artillery, are not "maneuver" units and thus are not considered in the "square," viz, "four" (infantry) regiments scheme. The usual internal organization within a square division would be two brigades, each compromising two infantry regiments (consisting of two or three battalions.) Hence, on an organizational chart, the two infantry brigade, each with two infantry regiments would resemble a square. However, such divisions typically also include additional, supporting units such as artillery regiments. By contrast, a triangular division generally has its infantry units organized in a "three by three" format. Historically, this has usually meant three regiments comprising three infantry battalions, with the three regiments either controlled by a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Division
A triangular division is a designation given to the way military divisions are organized. In a triangular organization, the division's main body is composed of three regimental maneuver elements. These regiments may be controlled by a brigade headquarters (more typical in World War I) or directly subordinated to the division commander. By contrast, in a square division, there were typically two brigades of two regiments. Other structures are possible, such as a pentomic division, where the division commander controls five maneuver elements, which was used in the United States Army in the late 1950s, with the regiments replaced by combined arms battlegroups.http://www.history.army.mil/html/books/060/60-14-1/cmhPub_60-14-1.pdf ''Wilson, John B. Maneuver and Firepower: The Evolution of Divisions and Separate Brigades'' (CMH Pub 60-14-1). Army Lineage Series. Washington: Center of Military History: 272-276. Asia Imperial Japanese Army and National Revolutionary Army Divisions wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
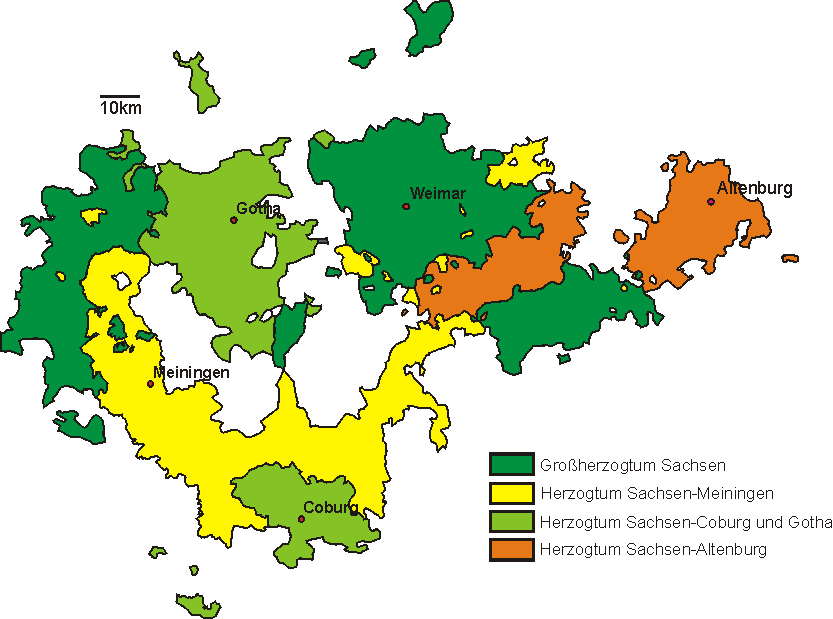
Duchy Of Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. History The duchy had its origins in the medieval Burgraviate of Altenburg in the Imperial Pleissnerland ''(Terra Plisensis)'', a possession of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen since 1243. Upon a partition treaty of 1485, Altenburg fell to Ernst, Elector of Saxony, the progenitor of the Ernestine We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Anhalt
The Duchy of Anhalt (german: Herzogtum Anhalt) was a historical German duchy. The duchy was located between the Harz Mountains in the west and the river Elbe and beyond to the Fläming Heath in the east. The territory was once ruled by the House of Ascania, and is now part of the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt. History Anhalt's origins lie in the Principality of Anhalt, a state of the Holy Roman Empire. Dukes of Anhalt During the 9th century, most of Anhalt was part of the duchy of Saxony. In the 12th century, it came under the rule of Albert the Bear, margrave of Brandenburg. Albert was descended from Albert, count of Ballenstedt, whose son Esico (died 1059 or 1060) appears to have been the first to bear the title of count of Anhalt. Esico's grandson, Otto the Rich, count of Ballenstedt, was the father of Albert the Bear, who united Anhalt with the Margraviate of Brandenburg (March of Brandenburg). When Albert died in 1170, his son Bernard, who received the title of duke of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12nd Thüringisches Hussar-Regiment
The 12th (Thuringian) Hussar Regiment (German: Thüringisches Husaren-Regiment Nr. 12) was a German Hussar regiment active during the Napoleonic Wars, the German revolutions of 1848–1849, the Austro-Prussian War, the Franco-Prussian War, and World War I. The unit was disbanded in 1920. Actions On 30 July 1791 the regiment was established as a new hussar unit in the Royal Saxon Army. The regiment was deployed in Mühlberg/Elbe by the end of the September 1791. As the Kingdom of Saxony was involved in the Napoleonic Wars, the regiment participated in Battle of Jena–Auerstedt on the French side. When Napoleon abdicated and Saxony lost territory to the victorious Kingdom of Prussia, the regiment was reestablished as a Prussian Army regiment. On 8 July 1815, the regiment participated in the invasion of Paris led by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher. During the German revolutions of 1848–1849, the regiment participated in suppressing the revolution as part of the 1st Division a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Paris (1870-1871)
Siege of Paris may refer to: *Siege of Paris (845), the Viking siege by Reginherus, possibly Ragnar Lodbrok *Siege of Paris (885–886), the Viking siege by Rollo *Siege of Paris (978), by Otto II of Germany *Siege of Paris (1429), by Charles VII of France and Joan of Arc *Siege of Paris (1465), by the League of the Public Weal *Siege of Paris (1590), the Protestant siege by Henry IV of France *Siege of Paris (1870–1871) The siege of Paris took place from 19 September 1870 to 28 January 1871 and ended in the capture of the city by forces of the various states of the North German Confederation, led by the Kingdom of Prussia. The siege was the culmination of the ..., the German siege in the Franco–Prussian War See also * Battle of Paris (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Saxony
The Province of Saxony (german: link=no, Provinz Sachsen), also known as Prussian Saxony () was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg. It was formed by the merger of various territories ceded or returned to Prussia in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna: most of the former northern territories of the Kingdom of Saxony (the remainder of which became part of Brandenburg or Silesia), the former French Principality of Erfurt, the Duchy of Magdeburg, the Altmark, the Principality of Halberstadt, and some other districts. The province was bounded by the Electorate of Hesse (the province of Hesse-Nassau after 1866), the Kingdom of Hanover (the province of Hanover after 1866) and the Duchy of Brunswick to the west, Hanover (again) to the north, Brandenburg to the north and east, Silesia to the south-east, and the rump kingdom of Saxony and the small Ernestine duchies to the south. Its shape was very irregular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |