|
88 Modern Constellations
In contemporary astronomy, 88 constellations are recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Each constellation is a region of the sky bordered by arcs of right ascension and declination, together covering the entire celestial sphere. Their boundaries were officially adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1928 and published in 1930. The ancient Mesopotamians and later the Greek astronomy, Greeks established most of the northern constellations in international use today, listed by the Roman-Egyptian astronomer Ptolemy. The constellations along the ecliptic are called the zodiac. When explorers mapped the stars of the southern skies, European astronomers proposed new constellations for that region, as well as ones to fill gaps between the traditional constellations. Because of their Roman and European origins, every constellation has a Latin name. In 1922, the International Astronomical Union adopted three-letter abbreviations for 89 constellations, the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
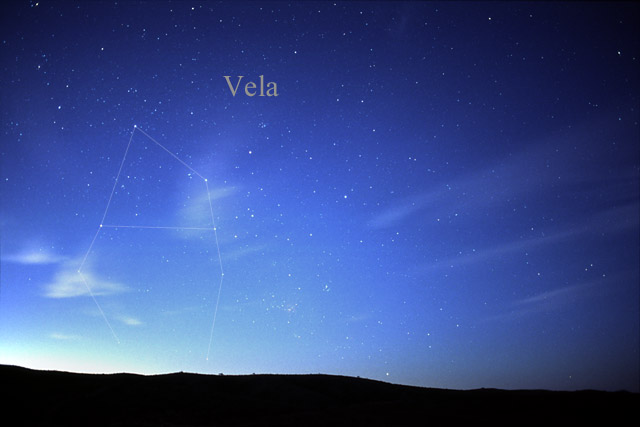
Vela Constellation
Vela is a constellation in the southern sky, which contains the Vela Supercluster. Its name is Latin for the sails of a ship, and it was originally part of a larger constellation, the ship ''Argo Navis'', which was later divided into three parts, the others being Carina and Puppis. With an apparent magnitude of 1.8, its brightest star is the hot blue multiple star Gamma Velorum, one component of which is the closest and brightest Wolf-Rayet star in the sky. Delta and Kappa Velorum, together with Epsilon and Iota Carinae, form the asterism known as the False Cross. 1.95-magnitude Delta is actually a triple or quintuple star system. History Argo Navis was one of the 48 classical constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and represented the ship ''Argo'', used by Jason and the Argonauts on their quest for the Golden Fleece in Greek mythology. German cartographer Johann Bayer depicted the constellation on his '' Uranometria'' of 1603, and gave the stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apus
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. First depicted on a celestial globe by Petrus Plancius in 1598, it was charted on a star atlas by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. The five brightest stars are all reddish in hue. Shading the others at apparent magnitude 3.8 is Alpha Apodis, an orange giant that has around 48 times the diameter and 928 times the luminosity of the Sun. Marginally fainter is Gamma Apodis, another aging giant star. Delta Apodis is a double star, the two components of which are 103 Minute and second of arc, arcseconds apart and visible with the naked eye. Two star systems have been found to have exoplanet, planets. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Antliae
Alpha Antliae is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Antlia but it has not been given a proper name. Its Bayer designation is Latinized from α Antliae, which is abbreviated Alpha Ant or α Ant, respectively. It is approximately 366 light-years from the Solar System. α Antliae has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.25, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. It has been reported to vary in brightness between magnitude 4.22 and 4.29, first in 1879 by Benjamin Gould, but this has not been confirmed in modern times. It is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 12 km/s. It is a K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K4 III. The evolutionary state of α Antliae is not clear but it is suspected of being on the asymptotic giant branch, with an inert carbon core. It has 2.2 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 41 times the solar radius. Compared to the Sun, it has o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pump
An air pump is a pump for pushing air. Examples include a bicycle pump, pumps that are used to aerate an aquarium or a pond via an airstone; a gas compressor used to power a pneumatic tool, air horn or pipe organ; a bellows used to encourage a fire; a vacuum cleaner and a vacuum pump. All air pumps contain a part that moves (vane, piston, impeller, diaphragm etc.) which drives the flow of air. When the air gets moved, an area of low pressure gets created which fills up with more air. Pumps and compressors use very similar mechanisms, and basically perform the same action, but in different fluid regimes. At some point there is a crossover point in terminology, but here are some stereotypes: *Compressors operate on compressible fluids, typically gases. Pumps operate on fluids, typically liquids, approximated as in-compressible. *Compressors are intended to develop a very high pressure rise against a closed system; pumps are designed to develop relatively little pressure agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antlia
Antlia (; from Ancient Greek ''ἀντλία'') is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "pump" in Latin and Greek language, Greek; it represents an air pump. Originally Antlia Pneumatica, the constellation was established by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. Its non-specific (single-word) name, already in limited use, was preferred by John Herschel then welcomed by the astronomic community which officially accepted this. North of stars forming some of the sails of the ship Argo Navis (the constellation Vela (constellation), Vela), Antlia is completely visible from latitudes south of 49th parallel north, 49 degrees north. Antlia is a faint constellation; its brightest star is Alpha Antliae, an orange giant star, giant that is a suspected variable star, ranging between apparent magnitudes 4.22 and 4.29. S Antliae is an Binary star#Eclipsing binaries, eclipsing binary star system, changing in brightness as one star passes in front of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
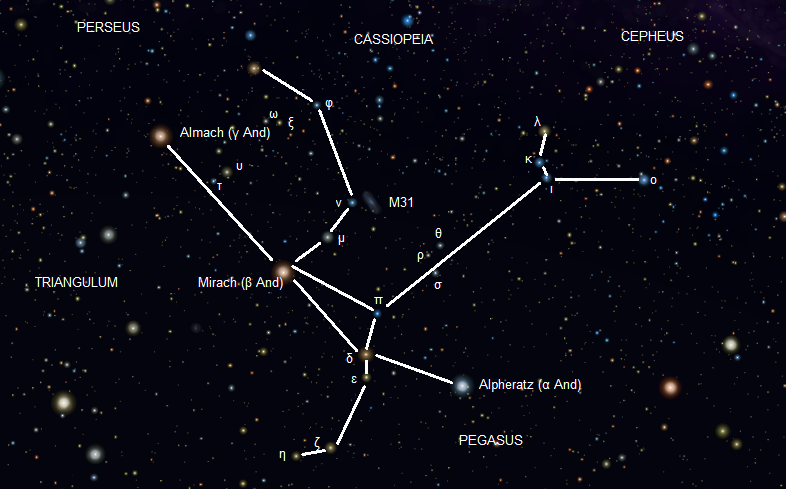
Alpheratz
Alpheratz is a prominent star system in the constellation of Andromeda. Pronounced , it has the Bayer designation Alpha Andromedae, Latinised from α Andromedae, and abbreviated Alpha And or α And, respectively. Alpheratz is the brightest star in the constellation when Mirach (βAndromedae) undergoes its periodical dimming. Immediately northeast of the constellation of Pegasus, it is the upper left star of the Great Square of Pegasus. It is located at a distance of 97 light-years from Earth. Although it appears to the naked eye as a single star with overall apparent visual magnitude +2.06, it is actually a binary system composed of two stars in close orbit. The chemical composition of the brighter of the two stars is unusual as it is a mercury-manganese star whose atmosphere contains abnormally high abundances of mercury, manganese, and other elements, including gallium and xenon.Alpheratz, Kaler Star2/14/2013 It is the brightest mercury-manganese star known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Andromeda (; or ) is the daughter of Cepheus (father of Andromeda), Cepheus, the king of Aethiopia, and his wife, Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia. When Cassiopeia boasts that she (or Andromeda) is more beautiful than the Nereids, Poseidon sends the sea monster Cetus (mythology), Cetus to ravage the coast of Aethiopia as divine punishment. Queen Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), Cassiopeia understands that chaining Andromeda to a rock as a human sacrifice is what will appease Poseidon. Perseus finds her as he is coming back from his quest to decapitate Medusa, and brings her back to Greece to marry her and let her reign as his queen. With the head of Medusa, Perseus Petrifaction in mythology and fiction, petrifies Cetus to stop it from terrorizing the coast any longer. As a subject, Andromeda has been popular in art since classical antiquity; rescued by a Greek hero cult, Greek hero, Andromeda's narration is considered the forerunner to the "pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpheratz (Alpha Andromedae), is a binary star that has also been counted as a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Spelling And Pronunciation
Latin phonology is the system of sounds used in various kinds of Latin. This article largely deals with what features can be deduced for Classical Latin as it was spoken by the educated from the late Roman Republic to the early Roman Empire, Empire. Evidence comes in the form of comments from Roman grammarians, common spelling mistakes, transcriptions into other languages, and the outcomes of various sounds in the Romance languages. Latin orthography refers to the writing system used to spell Latin from its Old Latin, archaic stages down to the present. Latin was nearly always spelt in the Latin alphabet, but further details varied from period to period. The alphabet developed from Old Italic script, which had developed from a variant of the Greek alphabet, which in turn had developed from a variant of the Phoenician alphabet. The Latin alphabet most resembles the Greek alphabet that can be seen on black-figure pottery dating to c. 540 BC, especially the Archaic Greek alphabets#Eub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |