|
792
__NOTOC__ Year 792 ( DCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 792 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Constantine VI suppresses a rebellion, and restores his mother Irene to her former position as co-empress of the Byzantine Empire. The rival factions in Constantinople continue their intrigues against Constantine. * Battle of Marcellae: Constantine VI leads a Byzantine expeditionary force into northern Thrace. At the border castle of Marcellae, near the modern town of Karnobat (Bulgaria), the Bulgarians under Kardam defeat the Byzantines. Europe * The Westphalians rise up against the Saxons, in response to a forcible recruitment for wars against the Avars. However, Pepin, sub-king of Northern Italy and son of King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepin The Hunchback
Pepin, or Pippin the Hunchback (French: Pépin le Bossu, German: Pippin der Buckelige; c. 768 / 769 – 811) was a Frankish prince. He was the eldest son of Charlemagne and noblewoman Himiltrude. He developed a humped back after birth, leading early medieval historians to give him the epithet "hunchback". He lived with his father's court after Charlemagne dismissed his mother and took another wife, Hildegard. Around 781, Pepin's half brother Carloman was rechristened as "Pepin of Italy"—a step that may have signaled Charlemagne's decision to disinherit the elder Pepin, for a variety of possible reasons. In 792, Pepin the Hunchback revolted against his father with a group of leading Frankish nobles, but the plot was discovered and put down before the conspiracy could put it into action. Charlemagne commuted Pepin's death sentence, having him tonsured and exiled to the monastery of Prüm instead. Since his death in 811, Pepin has been the subject of numerous works of historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offa Of Mercia
Offa (died 29 July 796 AD) was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald. Offa defeated the other claimant, Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign, it is likely that he consolidated his control of Midland peoples such as the Hwicce and the Magonsæte. Taking advantage of instability in the kingdom of Kent to establish himself as overlord, Offa also controlled Sussex by 771, though his authority did not remain unchallenged in either territory. In the 780s he extended Mercian Supremacy over most of southern England, allying with Beorhtric of Wessex, who married Offa's daughter Eadburh, and regained complete control of the southeast. He also became the overlord of East Anglia and had King Æthelberht II of East Anglia beheaded in 794, perhaps for rebelling against him. Offa was a Christian king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene (empress)
Irene of Athens ( el, Εἰρήνη, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaina (), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally empress regnant and sole ruler of the Eastern Roman Empire from 797 to 802. A member of the politically prominent Sarantapechos family, she was selected as Leo IV's bride for unknown reasons in 768. Even though her husband was an iconoclast, she harbored iconophile sympathies. During her rule as regent, she called the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, which condemned iconoclasm as heretical and brought an end to the first iconoclast period (730–787). Her public figure was very polarizing during her 5 year reign, as most saw a woman not right to solely rule. Her sole reign made her the first ever empress regnant, ruling in her own right, in Roman and Byzantine imperial history. She was influential in gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine VI
Constantine VI ( gr, Κωνσταντῖνος, ''Kōnstantinos''; 14 January 771 – before 805Cutler & Hollingsworth (1991), pp. 501–502) was Byzantine emperor from 780 to 797. The only child of Emperor Leo IV, Constantine was named co-emperor with him at the age of five in 776 and succeeded him as sole Emperor in 780, aged nine. His mother Irene exercised control over him as regent until 790, assisted by her chief minister Staurakios. The regency ended when Constantine reached maturity, but Irene sought to remain an active participant in the government. After a brief interval of sole rule Constantine named his mother empress in 792, making her his official colleague. Constantine suffered military defeats and made controversial decisions, such as blinding his loyal general Alexios Mosele and illicitly marrying his mistress, Theodote. Taking advantage of her son's unpopularity, Irene had Constantine deposed, blinded and imprisoned in 797 and seized power for herself alone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
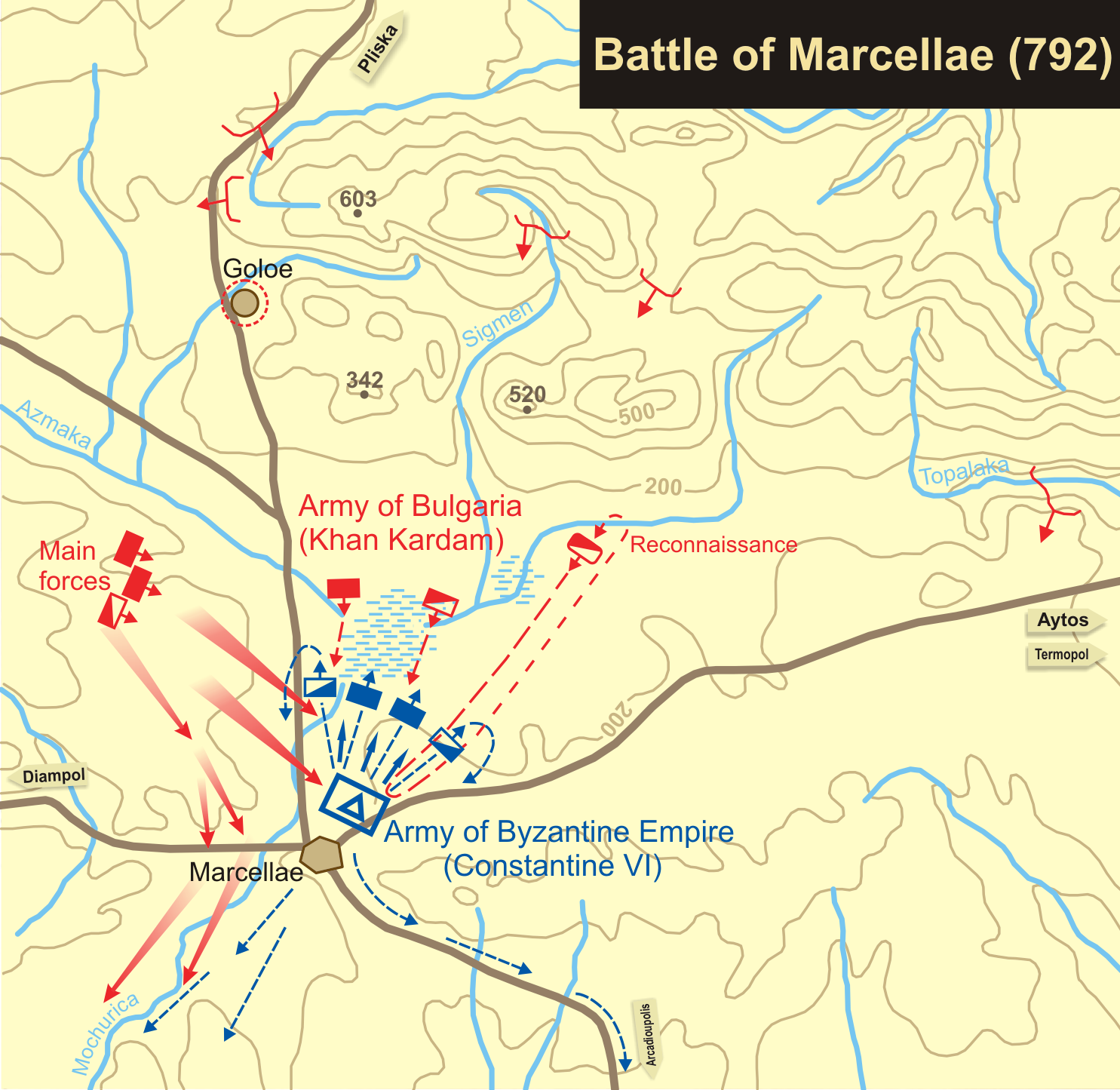
Battle Of Marcellae
The Battle of Marcellae ( bg, Битката при Маркели; el, Μάχη των Μαρκελλών) was fought in 792 between the forces of the Byzantine Empire, led by Constantine VI, and those of the First Bulgarian Empire under Kardam. The Byzantines were routed and forced to retreat to Constantinople. Fighting took place at Marcellae ( Markeli), near the modern town of Karnobat in southeastern Bulgaria, the same site as an earlier battle in 756. Prelude In the last quarter of the 8th century Bulgaria overcame the internal political crisis after the end of the rule of the Dulo. The khans Telerig and Kardam managed to consolidate the central authority and put an end of the quarrels among the nobility. The Bulgarians finally had the opportunity to intensify their campaigns in Slavic-populated Macedonia. In 789 they penetrated deep into the valley of the Struma river and heavily defeated the Byzantines, killing the ''strategos'' of Thrace Filites. In order to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Emperor of the Romans from 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of western and central Europe and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire around three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the Carolingian Empire. He was canonized by Antipope Paschal III—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as beatified (which is a step on the path to sainthood) in the Catholic Church. Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. He was born before their canonical marriage. He became king of the Franks in 768 following his father's death, and was initially co-ruler with his brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ælfflæd Of Mercia
Ælfflæd was a daughter of Offa of Mercia and Cynethryth. She may have witnessed a charter with her father, mother, and brother Ecgfrith in the 770s. She certainly witnessed a charter in 787 with her mother, father, brother, and two sisters; here she is described as ''virgo''—unmarried. It is possible that she was the daughter of Offa whose proposed marriage to Charles the Younger caused a dispute between Charlemagne Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ... and Offa in around 789–790. In 792 she married Æthelred I of Northumbria at Catterick. Here she is described as "queen", which has suggested to some historians that she had been previously married, and to a king, perhaps to one of Æthelred's predecessors. References Further reading * * * Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markeli
Markeli ( bg, Маркели; el, Μαρκέλλαι, ''Markellai''; la, Marcellae) was a medieval Byzantine and Bulgarian frontier stronghold, the ruins of which are located in Karnobat Municipality, Burgas Province, southeastern Bulgaria. Dating to Late Antiquity, the castle lay some from the modern town of Karnobat. It was the site of two notable medieval battles between Byzantines and Bulgarians, the Battle of Marcellae of 756 and the Battle of Marcellae of 792. History Markeli acquired its strategic importance in the late 7th century, when the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire and its expansion turned it into a vital frontier stronghold just south of the Balkan Mountains. It would often change hands between Bulgarians and Byzantines, who would use it as a favourable starting point for military campaigns southwards and northwards respectively. Markeli first came under Bulgarian rule in 705, when it, together with the whole region of Zagore, was ceded to Bulga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardam Of Bulgaria
Kardam ( bg, Кардам) was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire (777 – after 796/before 803). The name of Kardam is first encountered in the Byzantine sources in 791, when Emperor Constantine VI embarked on an expedition against Bulgaria, in retaliation for Bulgarian incursions in the Struma valley since 789. Kardam pre-empted the Byzantine invasion and met the enemy near Adrianople in Thrace. The Byzantine army was defeated and turned to flight. In 792 Constantine VI led another army against the Bulgarians and encamped at Marcellae (near Karnobat), which he proceeded to fortify. Kardam arrived with his army on July 20 and occupied the neighboring heights. After some time passed with the two forces sizing up, Constantine VI gave in to the reassuring advice of a "false prophet" and ordered the attack. But the Byzantine forces lost formation and once again were defeated and turned to flight, while Kardam captured the imperial tent and the emperor's servants. After hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelred I Of Northumbria
Æthelred (; c. 762 – 18 April 796), was the king of Northumbria from 774 to 779 and again from 790 until he was murdered in 796. He was the son of Æthelwald Moll and Æthelthryth and possibly became king while still a child after Alhred was deposed. Family and early life The origin of Æthelred's family isn't recorded, but his father Æthelwald, who was also called Moll, seems to have come from a noble background. Æthelwald first appears in the historical records in a letter written by Pope Paul I to king Eadberht, ordering him to return lands taken from an Abbot Fothred, which were given to his brother Moll. After the abdication of king Eadberht in 758, his son Oswulf took his place but despite his father's long reign and his powerful uncle Ecgbert, he was murdered just a year later in 759 at Market Weighton by his own bodyguards. The murder was possibly ordered by Æthelwald as he became king soon after. In 761 Oswulf's brother Oswine met Æthelwald in battle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar Era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era (the Coptic Orthodox and Ethiopian Orthodox churches have their own Christian eras). In antiquity, regnal years were counted from the accession of a monarch. This makes the chronology of the ancient Near East very difficult to reconstruct, based on disparate and scattered king lists, such as the Sumerian King List and the Babylonian Canon of Kings. In East Asia, reckoning by era names chosen by ruling monarchs ceased in the 20th century except for Japan, where they are still used. Ancient dating systems Assyrian eponyms For over a thousand years, ancient Assyria used a system of eponyms to identify each year. Each year at the Akitu festival (celebrating the Mesopotamian new year), one of a small group of high officials (including the king in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions: Aosta Valley, Piedmont, Liguria, Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, Veneto, Friuli-Venezia Giulia and Trentino-Alto Adige. As of 2014, its population was 27,801,460. Rhaeto-Romance and Gallo-Italic languages are spoken in the region, as opposed to the Italo-Dalmatian languages spoken in the rest of Italy. The Venetian language is sometimes considered to be part of the Italo-Dalmatian languages, but some major publications such as '' Ethnologue'' (to which UNESCO refers on its page about endangered languages) and '' Glottolog'' define it as Gallo-Italic. For statistic purposes, the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (ISTAT) uses the terms Northwest Italy and Northeast Italy for two of Italy's five statistical regions in its reporting. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.png)
