|
586
__NOTOC__ Year 586 ( DLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 586 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Emperor Maurice rejects a peace proposal of the Persians, in exchange for renewed payments in gold. * Battle of Solachon: A Byzantine army under command of Philippicus defeats the Sassanid Persians, near Dara. * The Avars besiege Thessalonica (Central Macedonia), the second city of the Byzantine Empire.History of the Byzantine Empire from DCCXVI to MLVII, George Finlay, p. 316 * The Vlachs are first mentioned in a Byzantine chronicle (approximate date). Europe * April 21 – King Liuvigild dies at Toledo after an 18-year reign, and is succeeded by his second son Reccared I. * Slavs advance to the gates of Thessaloniki and the Peloponnese. * Avar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liuvigild
Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or ''Leovigildo'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese), ( 519 – 586) was a Visigoths, Visigothic Visigothic Kingdom, king of Hispania and Septimania from 569 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between the Visigothic and Hispania, Hispano-Roman population, his kingdom covered modern Spain down to Toledo, Spain, Toledo and Portugal. Liuvigild ranks among the greatest Visigothic kings of the Arianism, Arian period. Life, campaigns and reign When the Visigothic king Athanagild died in 567, Liuva I was elevated to the kingship at a ceremony held in Narbonne, the last bastion of Visigothic rule. Recognizing the leadership qualities of his younger sibling, in the second year of his reign, King Liuva I declared his brother Liuvigild co-king and heir, assigning him Hispania Citerior, or the eastern part of Hispania (Spain), to directly rule over. Both co-regents were Arian Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Solachon
The Battle of Solachon was fought in 586 CE in northern Mesopotamia between the East Roman (Byzantine) forces, led by Philippicus, and the Sasanian Persians under Kardarigan. The engagement was part of the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 572–591. The Battle of Solachon ended in a major Byzantine victory which improved the Byzantine position in Mesopotamia, but it was not in the end decisive. The war dragged on until 591, when it ended with a negotiated settlement between Maurice and the Persian shah Khosrau II (r. 590–628). In the days before the battle, Philippicus, newly assigned to the Persian front, moved to intercept an anticipated Persian invasion. He chose to deploy his army at Solachon, controlling the various routes of the Mesopotamian plain, and especially access to the main local watering source, the Arzamon River. Kardarigan, confident of victory, advanced against the Byzantines, but they had been warned and were deployed in battle order when Kardarigan reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbula Gospels
The Rabbula Gospels, or Rabula Gospels (Florence, Biblioteca Medicea Laurenziana, cod. Plut. I, 56), is a 6th-century illuminated Syriac Gospel Book. One of the finest Byzantine works produced in West Asia, and one of the earliest Christian manuscripts with large miniatures, it is distinguished by the miniaturist's predilection for bright colours, movement, drama, and expressionism. Created during a period from which little art survived, it nevertheless saw great development in Christian iconography. The manuscript has a significant place in art history, and is very often referred to. Recent scholarship has suggested that the manuscript, completed in 586 AD, was later partly overpainted by restorers and bound together with miniatures from other sources in the 15th or 16th century. Description The Gospel was completed in 586 at Monastery of St. John of Zagba (Syriac: , ), which, although traditionally thought to have been in Northern Mesopotamia, is now thought to have been i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reccared I
Reccared I (or Recared; ; ; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was the king of the Visigoths, ruling in Hispania, Gallaecia and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianism in favour of Nicene Christianity in 587. Reign Reccared was the younger son of King Leovigild by his first wife. Like his father, Reccared had his capital at Toledo. The Visigothic kings and nobles were traditionally Arian Christians, while the Hispano-Roman population were Chalcedonian Christians. The bishop Leander of Seville was instrumental in converting the elder son and heir of Leovigild, Hermenegild, to Chalcedonianism. Leander supported his rebellion and was exiled for his role. When King Leovigild died, within a few weeks of April 21, 586, bishop Leander was swift to return to Toledo. The new king had been associated with his father in ruling the kingdom and was acclaimed king by the Visigothic nobles without opposition. In January 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avars (Carpathians)
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in the Avar–Byzantine wars from 568 to 626 and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars (Caucasus), Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice (emperor)
Maurice (; ; 539 – 27 November 602) was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tiberius II. Maurice's reign was troubled by almost constant warfare. After he became emperor, he brought the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 572–591, war with Sasanian Persia to a Battle of the Blarathon, victorious conclusion. The empire's eastern border in the South Caucasus was vastly expanded and, for the first time in nearly two centuries, the Romans were no longer obliged to pay the Persians thousands of pounds of gold annually for peace. Afterward, Maurice Maurice's Balkan campaigns, campaigned extensively in the Balkans against the Pannonian Avars, Avars—pushing them back across the Danube by 599. He also conducted campaigns across the Danube, the first Roman emperor to do so in over two centuries. In the west, he established two large semi-autonomous provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
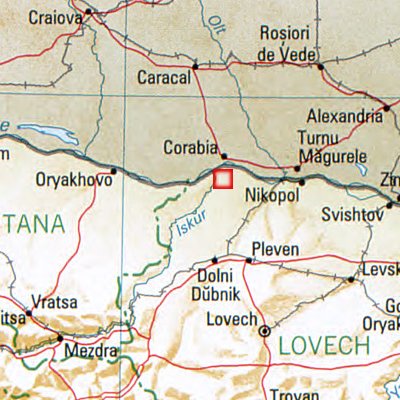
Colonia Ulpia Oescus
Oescus, Palatiolon or Palatiolum (, ) was an important ancient city on the Danube river in Roman Moesia. It later became known as ''Ulpia Oescus''. It lay northwest of the modern Bulgarian city of Pleven, near the village of Gigen. For a short time it was linked by the longest and most famous stone bridge across the Danube, Constantine's Bridge, with the ancient city of Sucidava (modern-day Corabia, Romania). The city seems to have at one point reached a area of 280,000 m2 and a population of 100,000. Archaeological excavations have brought to light parts of the ancient city and are continuing. Etymology The name of the Roman town comes from the river Oescus (today Iskar). It probably meant "water" in the local Thracian dialect. History The Greek geographer Claudius Ptolemy (ca. 90–168 AD) described Ulpia Oescus as a city of the Triballi, an independent ancient tribe which inhabited today’s northwestern Bulgaria. Under Roman rule, Oescus began as an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, the administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek as , literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the "co-reigning" city () of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the Axios Delta National Park, delta of the Axios. The Thessaloniki (municipality), municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical centre, had a population of 319,045 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metropolitan are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratiaria
Ratiaria (or: Ratsaria, Raetiaria, Retiaria, Reciaria, Razaria; ; ;) was a city founded by the Moesians, a Daco- Thracian tribe, in the 4th century BC, along the river Danube. In Roman times it was named '' Colonia Ulpia Traiana Ratiaria''. It is located 2 km west of the present village of Archar in Vidin Province, northwestern Bulgaria and 3 km east of the present Balta Neagră Natural Reserve in southern Romania. The closest modern cities are Vidin (27 km to the north west), Lom (28 km to the east) in Bulgaria and Calafat (41 km to the north) in Romania. An archaeological museum for the site has recently been established in Dimovo. History Ratiaria was conquered by the Dacians of Burebista and later by the Romans. There was a gold mine in the city, which was exploited by the Thracians. The city may have owed its success to the goldsmiths. The earliest involvement of the Romans occurred in 75 BC when Gaius Scribonius Curio, prefect of Macedonia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippicus (comes Excubitorum)
Philippicus (; fl. 580s–610s) was an Eastern Roman general, ''comes excubitorum'', and brother-in-law of Emperor Maurice (r. 582–602). His successful career as a general spanned three decades, chiefly against the Sassanid Persians. Career under Maurice Little is known about Philippicus's early years. He was married to Gordia, sister of Emperor Maurice (reigned 582–602), probably in 583,. and was at some point raised to the high rank of '' patricius''.. At about the same time, he was appointed ''comes excubitorum'' (Commander of the Excubitors, the imperial bodyguard), and in 584, he replaced John Mystacon as ''magister militum'' for the East, thus becoming responsible for the conduct of the ongoing war against the Sassanid Persians. He commanded numerous raids into Persian territory in 584–585, ravaging the plains near Nisibis, and making inroads in the regions of Arzanene and eastern Mesopotamia.. During the same period, he actively tried to improve the disciplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |