|
541132 Leleākūhonua
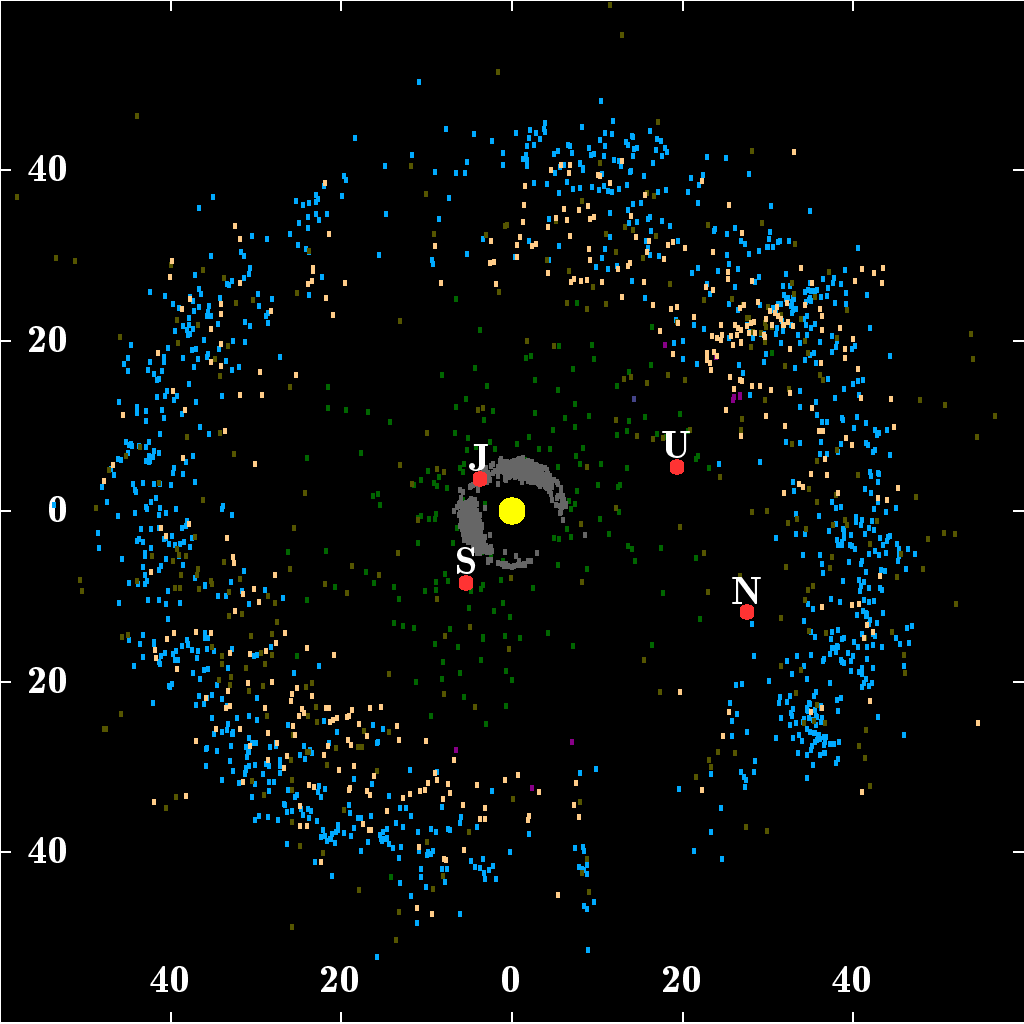
541132 Leleākūhonua () ( provisional designation ) is an extreme trans-Neptunian object and sednoid in the outermost part of the Solar System. It was first observed on 13 October 2015, by astronomers at the Mauna Kea Observatories, Hawaii. Based on its discovery date near Halloween and the letters in its provisional designation , the object was informally nicknamed "The Goblin" by its discoverers and later named Leleākūhonua, comparing its orbit to the flight of the Pacific golden plover. It was the third sednoid discovered, after and , and measures around in diameter. Discovery Leleākūhonua was first observed on 13 October 2015 at the Mauna Kea Observatory , by American astronomers David Tholen, Chad Trujillo and Scott Sheppard during their astronomical survey for objects located beyond the Kuiper Cliff. The unofficial discovery was publicly announced on 1 October 2018. The survey uses two principal telescopes: For the Northern hemisphere, the 8.2-meter Subaru T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sednoid
A sednoid is a trans-Neptunian object with a large semi-major axis and a high perihelion, similar to the orbit of the dwarf planet Sedna. The consensus among astronomers is that there are only four objects that are known from this population: Sedna, , 541132 Leleākūhonua (), and . All four have perihelia greater than . These objects lie outside an apparently nearly empty gap in the Solar System and have no significant interaction with the planets. They are usually grouped with the detached objects. Some astronomers consider the sednoids to be Inner Oort Cloud (IOC) objects, though the inner Oort cloud, or Hills cloud, was originally predicted to lie beyond 2,000 AU, beyond the aphelia of the known sednoids. One attempt at a precise definition of sednoids is any body with a perihelion greater than and a semi-major axis greater than . However, this definition applies to the objects , , and which have perihelia beyond 50 AU and semi-major axes over 700 AU. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper Cliff
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region. The Kuiper belt is named in honor of the Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper, who conjectured the existence of the belt in 1951. There were researchers befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills Cloud
In astronomy, the Hills cloud (also called the inner Oort cloud and inner cloud) is a theoretical vast circumstellar disc, interior to the Oort cloud, whose outer border would be located at around 20,000 to 30,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, and whose inner border, less well defined, is hypothetically located at , well beyond planetary and Kuiper Belt object orbits—but distances might be much greater. If it exists, the Hills cloud likely contains roughly 5 times as many comets as the Oort cloud. Overview The need for the Hills cloud hypothesis is intimately connected with the dynamics of the Oort cloud: Oort cloud comets are continually perturbed in their environment. A non-negligible fraction leave the Solar System, or tumble into the inner system where they evaporate, fall into the Sun, or collide with or are ejected by the giant planets. Hence, the Oort cloud should have been depleted long ago, but it is still well supplied with comets. The Hills cloud h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet Nine
Planet Nine is a List of hypothetical Solar System objects, hypothetical ninth planet in the outer region of the Solar System. Its gravitational effects could explain the peculiar clustering of orbits for a group of extreme trans-Neptunian objects (ETNOs)—bodies beyond Neptune that orbit the Sun at distances averaging more than 250 times that of the Earth, over 250 astronomical units (AU). These ETNOs tend to make their closest approaches to the Sun in one sector, and their orbits are similarly tilted. These alignments suggest that an undiscovered planet may be shepherding the orbits of the most distant known Solar System objects. Nonetheless, some astronomers question this conclusion and instead assert that the clustering of the ETNOs' orbits is due to observational biases stemming from the difficulty of discovering and tracking these objects during much of the year. Based on earlier considerations, this hypothetical super-Earth-sized planet would have had a predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Neptunian Object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has an orbital semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (AU). Typically, TNOs are further divided into the classical and resonant objects of the Kuiper belt, the scattered disc and detached objects with the sednoids being the most distant ones. As of February 2025, the catalog of minor planets contains 1006 numbered and more than 4000 unnumbered TNOs. However, nearly 5900 objects with semimajor axis over 30 AU are present in the MPC catalog, with 1009 being numbered. The first trans-Neptunian object to be discovered was Pluto in 1930. It took until 1992 to discover a second trans-Neptunian object orbiting the Sun directly, 15760 Albion. The most massive TNO known is Eris, followed by Pluto, , , and . More than 80 satellites have been discovered in orbit of trans-Neptunian objects. TNOs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * Circular orbit: * Elliptic orbit: * Parabolic trajectory: * Hyperbolic trajectory: The eccentricity is given by e = \sqrt where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-major Axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longest semidiameter or one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (minor semiaxis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle. The length of the semi-major axis of an ellipse is related to the semi-minor axis's length through the eccentricity and the semi-latus rectum \ell, as follows: The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches. Thus it is the distance from the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowell Discovery Telescope
The Lowell Discovery Telescope (LDT), formerly the Discovery Channel Telescope (DCT), is a aperture telescope owned and operated by Lowell Observatory. The LDT was built at a dark sky site in the Coconino National Forest near Happy Jack, Arizona. Happy Jack is located at an elevation of and is approximately south-south-east of Flagstaff. The project was initially a partnership between Discovery Communications and Lowell Observatory. The research partnerships have been extended to include Boston University, The University of Maryland, The University of Toledo, Northern Arizona University, and Yale University. The telescope cost $53 million. It significantly augments Lowell Observatory's observational capability and enables pioneering studies in a number of important research areas. With its 4-meter class primary mirror, the Lowell Discovery Telescope is the fifth largest telescope in the continental United States (). Final construction of the telescope was completed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellan Telescopes
The Magellan Telescopes are a pair of optical telescopes located at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. The two telescopes are named after the astronomer Walter Baade and the philanthropist Landon T. Clay. First light for the telescopes was on September 15, 2000 for the Baade, and September 7, 2002 for the Clay. A consortium consisting of the Carnegie Institution for Science, University of Arizona, Harvard University, the University of Michigan and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology built and operate the twin telescopes. The telescopes were named after the sixteenth-century Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. The Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT) is an extremely large telescope under construction, as part of the US Extremely Large Telescope Program. Current instruments on the Magellan Telescopes Baade telescope: * Inamori Magellan Areal Camera and Spectrograph (IMACS) * FourStar * Folded port InfraRed Echellette (FIRE) * Magellan Echellete (MagE) Clay telescope: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an Astronomy, astronomical observatory located on the summit of Mt. Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Mt. Cerro Pachón about to the southeast. It is approximately east of La Serena, Chile, La Serena, where support facilities are located. The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel Blanco, and the 4.1 m Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, which is situated on Cerro Pachón. Other telescopes on Cerro Tololo include the 1.5 m, 1.3 m, 1.0 m, and 0.9 m telescopes operated by the SMARTS consortium. CTIO also hosts other research projects, such as PROMPT (telescope), PROMPT, WHAM, and Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network, LCOGTN, providing a platform for access to the southern hemisphere for U.S. and worldwide scientific research. History In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |